High-speed non-salient-pole electrically excited synchronous motor rotor in air gap magnetic field sine distribution and structural parameter determination method of rotor
A technology of sinusoidal distribution and air-gap magnetic field, which is used in synchronous motors for single-phase current, manufacturing stator/rotor bodies, etc., which can solve the problems of difficulty in realizing sinusoidal distribution of air-gap magnetic field and limited selection range.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
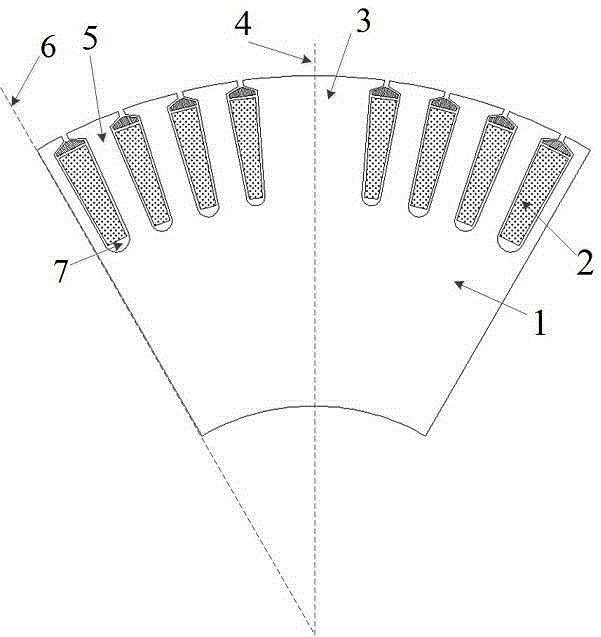
[0075] see Figure 1 ~ Figure 3 , the high-speed secluded pole electric excitation synchronous motor rotor with sinusoidal air gap magnetic field distribution, including the rotor core (1) and the field winding (2) embedded therein, is characterized in that:
[0076] (a) Each pole has 2n teeth, the middle one is a large tooth (3), and its center line is the pole center line (4); each small tooth (5) has equal tooth spacing, and the magnetic pole neutral line (6) is the centerline of the small tooth;
[0077] (b) There are n slots (7) on both sides of the large tooth of each pole, which are used to place the excitation winding (2) of the pole. The number of wires embedded in each slot is determined according to the principle of the sinusoidal distribution of the air gap magnetic field. The maximum slot depth is restricted by the mechanical strength, stiffness and magnetic density of the yoke, and the size of each slot is determined by the number and diameter of the wires in th...
Embodiment 2
[0080] The method for determining the structural parameters of the high-speed hidden pole electric excitation synchronous motor rotor with sinusoidal distribution of the air gap magnetic field is characterized in that the specific operation steps are as follows:
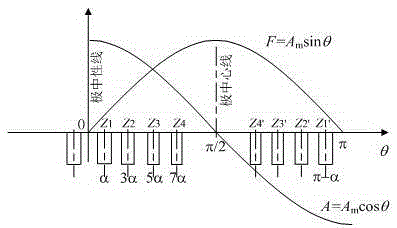
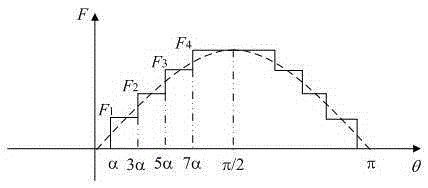
[0081] Note the half-pitch angle—the space angle between the centerline of the small tooth and the centerline of the adjacent slot is α, and the unit is arc degrees. Take the neutral line of the magnetic pole as the origin of the angle coordinates, that is, θ=0, then the center of the magnetic pole θ=π / 2, θ at the center of the ith slot i =(2i-1)α, i=1,2,...,n.
[0082] (a) Determine the value of n according to the technical requirements and actual size. The value of n needs to be large if the magnetic force sine degree is high; the value of n can be large if the rotor size is large;
[0083] (b) In order to make the magnetic potential distribution close to sine, the winding turns must be close to cosine distributio...
Embodiment 3
[0100] This implementation example is a high-speed hidden pole electric excitation synchronous motor rotor with 6 poles and a sinusoidal distribution of the air gap magnetic field where n is 4, such as figure 1 shown.
[0101] (a) Each pole has 8 teeth, the middle one is a large tooth, the center line of which is the center line of the pole, each small tooth is equally spaced, and the neutral line of the magnetic pole is the center line of the small tooth.
[0102] (b) There are 4 slots on both sides of the large teeth of each pole, which are used to place the field winding of the pole. The number of wires embedded in each slot is determined according to the principle of the sinusoidal distribution of the air gap magnetic field. The maximum slot depth of each slot is restricted by the mechanical strength, stiffness and magnetic flux of the yoke. In this case, the slot depth of each slot is the same, and the slot width is determined by the The number of wires in the groove and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com