System for codon optimization and pichia pastoris expression of genes of cellobiohydrolase II
An exo-glucanase and codon optimization technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of insufficient yield, different peak secretion periods, and inability to exert enzymatic hydrolysis effect, and achieve the effects of increasing protein expression and improving expression efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Example 1: Trichoderma reesei exoglucanase II (CBHII) gene codon optimization and expression vector construction.
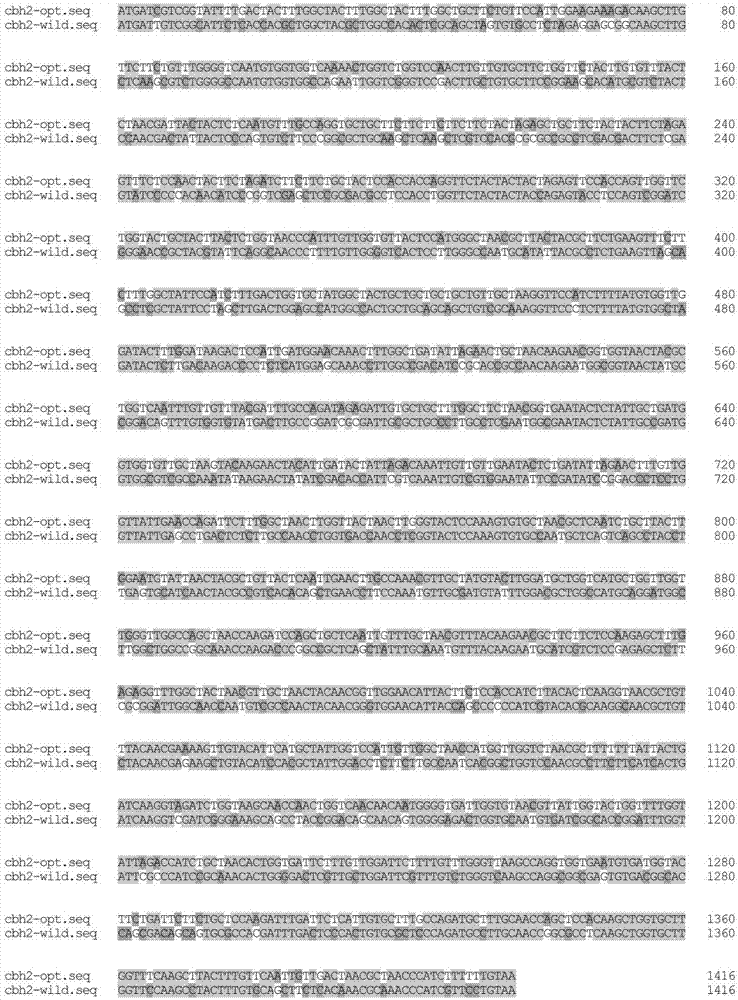
[0043] 1. The present invention utilizes GeneDesigner (DNA2.0, MenloPark, CA, USA) to realize CBHII (NCBIReferenceSequence: XM_006962518.1) nucleotide sequence codon bias optimization as shown in SEQIDNO.1, and the optimized nucleotide sequence is as follows: Shown in SEQ ID NO.3. The codon-optimized amino acid sequence is consistent with the original amino acid sequence, as shown in SEQ ID NO.2. Using Pichiapastoris GS115 as the host, the nucleotide sequence after codon bias optimization and the original nucleotide sequence are compared, see figure 1 , compare the amino acid sequence after codon bias optimization with the original amino acid sequence, see figure 2 .
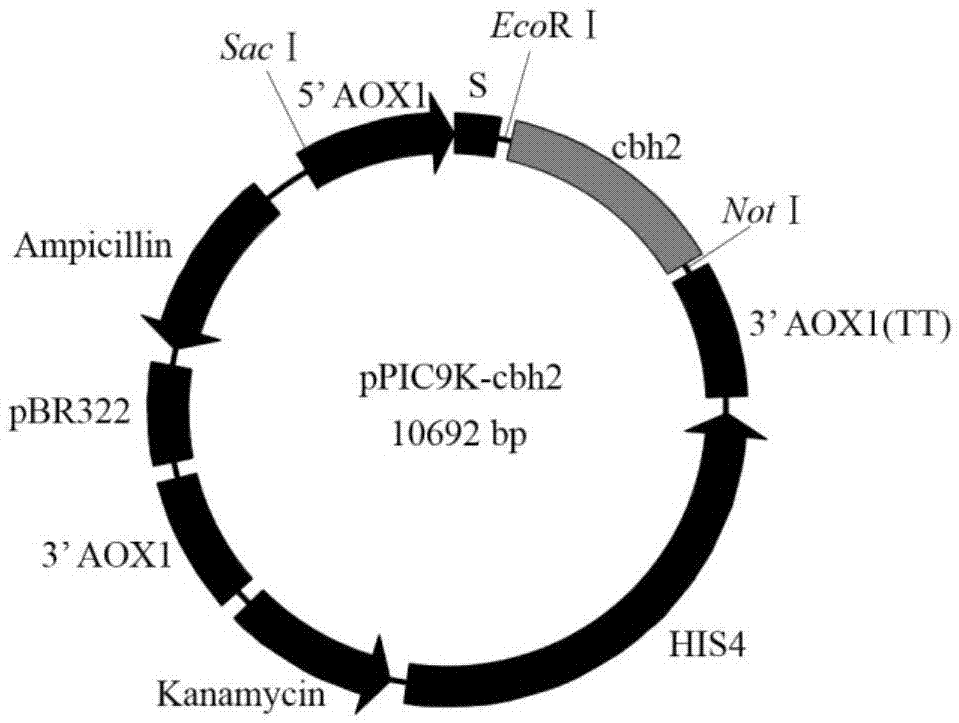
[0044] 2. The restriction site at the 5' end is EcoRI, and the restriction site at the 3' end is NotI as the double restriction site, and inserted into the downstream of the AOX1 promote...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Example 2: Linearizing expression vectors and performing electrotransformation and screening high-yielding strains.
[0046] 1. Use SacI as the linearization site of the pPIC9K-cbh2 expression vector to realize the linearization of the expression vector, and verify the linearized plasmid by nucleic acid electrophoresis, see Figure 4. Transferred into Pichiapastoris GS115 by electroporation to obtain recombinant strains. Using colony PCR, colonies with clear amplified bands were fermented in shake flasks to obtain high-yield strains. Samples were taken at 120 hours and the CMC enzyme activity of the fermentation supernatant was determined by DNS method. See Figure 5 , wherein, 1 unit of enzyme activity is defined as the amount of enzyme that can convert 1 μmol of substrate in 1 minute under the condition of 50°C water bath.
Embodiment 3
[0047] Example 3: Optimizing the conditions for inducing enzyme production.
[0048] 1. Use BMMY as the enzyme-producing medium, methanol as the inducer, and add 0.5%, 1.0%, 1.5%, 2.0%, and 2.5% of methanol to produce enzymes, and use the DNS method to measure the fermentation supernatant at 192 hours CMC enzyme activity, and its bacterial concentration was measured, the optimization results are shown in Image 6 .
[0049] 2. Optimize the enzyme production by adjusting the pH of the potassium phosphate buffer in the BMMY medium to 5.0, 5.5, 6.0, 6.5, 7.0, and 7.5. At 192 hours, use the DNS method to measure the CMC enzyme activity of the fermentation supernatant, and measure its bacteria Concentration, optimization results see Figure 7 . For the comparison of CMC enzyme activity after optimization and before optimization, see Figure 8 .
[0050]
[0051]
[0052]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com