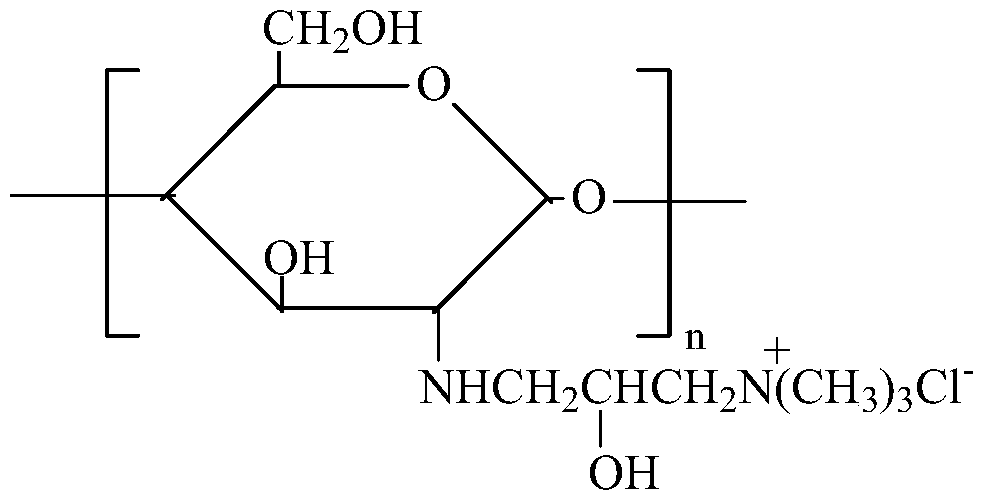
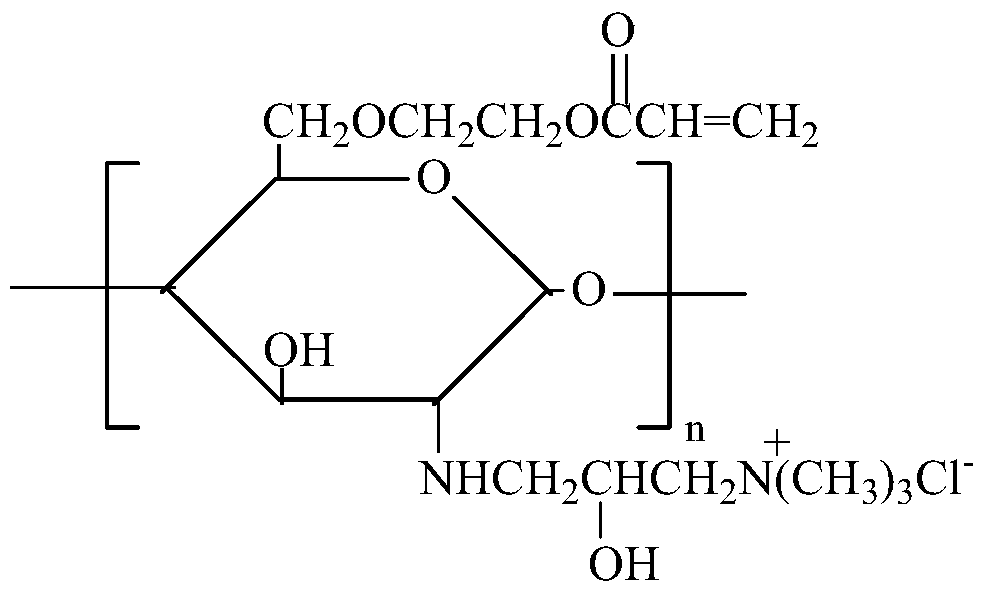
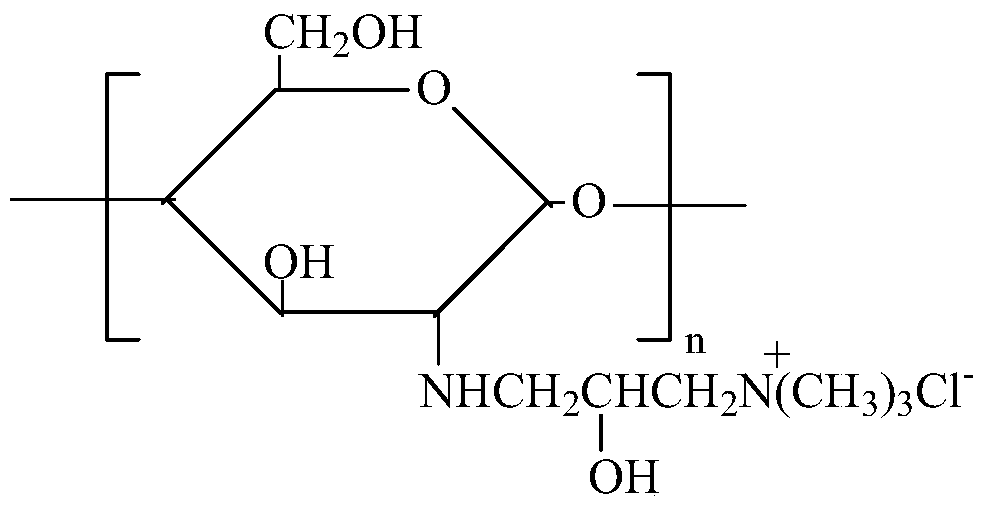
Modification method and dyeing process of a salt-free and low-alkali deep-dyed cellulose fiber fabric
A technology of cellulose fibers and fabrics, which is applied in the modification method and dyeing process of non-salt and low-alkali deep-dyed cellulose fiber fabrics, which can solve the problems of poor dyeing depth, stiffness, and colored flowers, and achieve enhanced adsorption , The surface is white and soft, and the effect of reducing the amount of use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Embodiment 1: the preparation of chitosan oligosaccharide:
[0039] After the chitosan was completely dissolved with acetic acid solution, the catalyst MnO was added 2 / CuO, shake for 5min to 15min, then slowly add 30% (mass fraction) hydrogen peroxide, control the constant temperature at 60°C to carry out the degradation reaction in a shaking table water bath for 3h, adjust the pH of the degradation solution to neutral, and remove the hydrogen peroxide in the degradation product The metal ions are concentrated by vacuum rotary evaporation, precipitated with three times the volume of absolute ethanol, centrifuged to separate the chitosan oligosaccharide precipitate, and then dried in vacuum and ground into powder for use. Wherein the mass concentration fraction of chitosan in the degradation reaction is 3.5%, catalyst MnO 2 The mass concentration fraction of / CuO is 1.2%, the mass concentration fraction of 30% hydrogen peroxide is 4%, the consumption of acetic acid is ...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Embodiment 2: the preparation of chitosan oligosaccharide:
[0042] After the chitosan was completely dissolved with acetic acid solution, the catalyst MnO was added 2 / CuO, shake for 5min to 15min, then slowly add 30% (mass fraction) hydrogen peroxide, control the constant temperature at 50°C to carry out the degradation reaction in a shaking table water bath for 2h, adjust the pH of the degradation solution to neutral, and remove the hydrogen peroxide in the degradation product The metal ions are concentrated by vacuum rotary evaporation, precipitated with three times the volume of absolute ethanol, centrifuged to separate the chitosan oligosaccharide precipitate, and then dried in vacuum and ground into powder for use. Wherein the mass concentration fraction of chitosan in the degradation reaction is 3.5%, catalyst MnO 2 The mass concentration fraction of / CuO is 1.1%, the mass concentration fraction of 30% hydrogen peroxide is 3%, the consumption of acetic acid is ...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Embodiment 3: the preparation of chitosan oligosaccharide:
[0045] After the chitosan was completely dissolved with acetic acid solution, the catalyst MnO was added 2 / CuO, shake for 5min to 15min, then slowly add 30% (mass fraction) hydrogen peroxide, control the constant temperature at 50°C to carry out the degradation reaction in a shaking table water bath for 4h, adjust the pH of the degradation solution to neutral, and remove the hydrogen peroxide in the degradation product The metal ions are concentrated by vacuum rotary evaporation, precipitated with three times the volume of absolute ethanol, centrifuged to separate the chitosan oligosaccharide precipitate, and then dried in vacuum and ground into powder for use. Wherein the mass concentration fraction of chitosan in the degradation reaction is 3.5%, catalyst MnO 2 The mass concentration fraction of / CuO is 1%, the mass concentration fraction of 30% hydrogen peroxide is 5%, the consumption of acetic acid is 3%...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| degree of polymerization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of substitution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com