Method of manufacturing a semiconductor device
A technology for semiconductors and devices, applied in the field of manufacturing semiconductor devices, can solve problems such as increasing the size of memory cells, and achieve the effect of improving performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
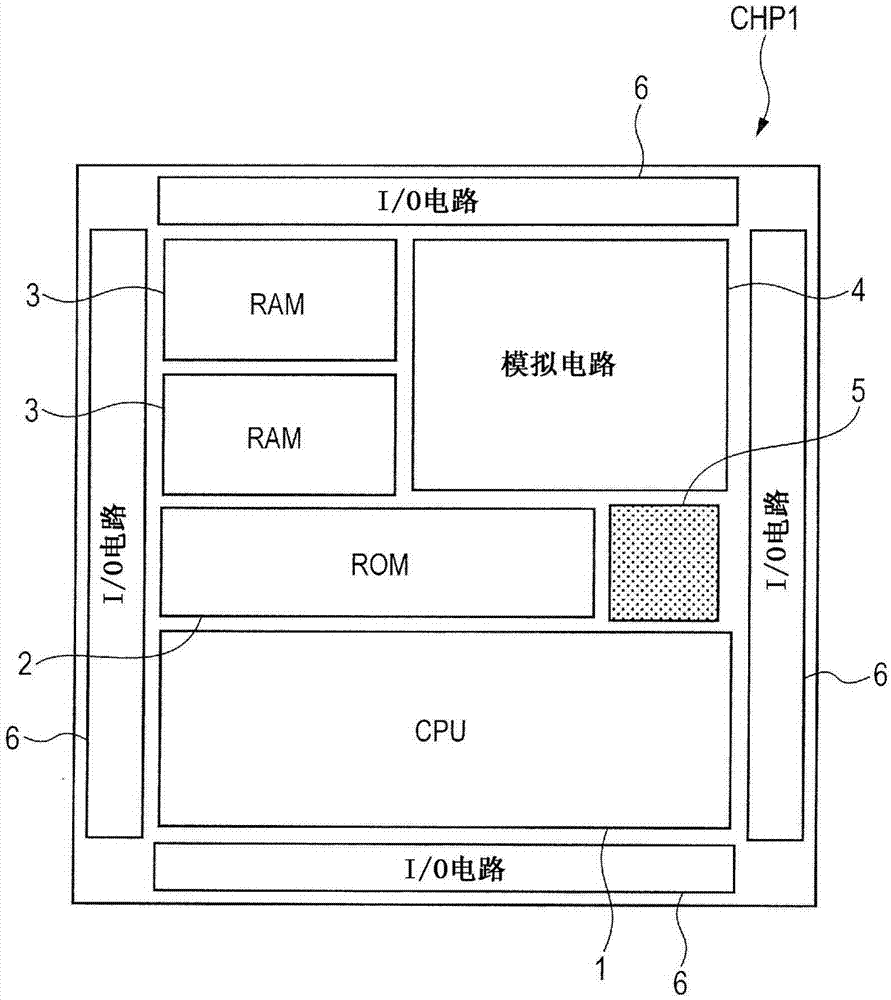
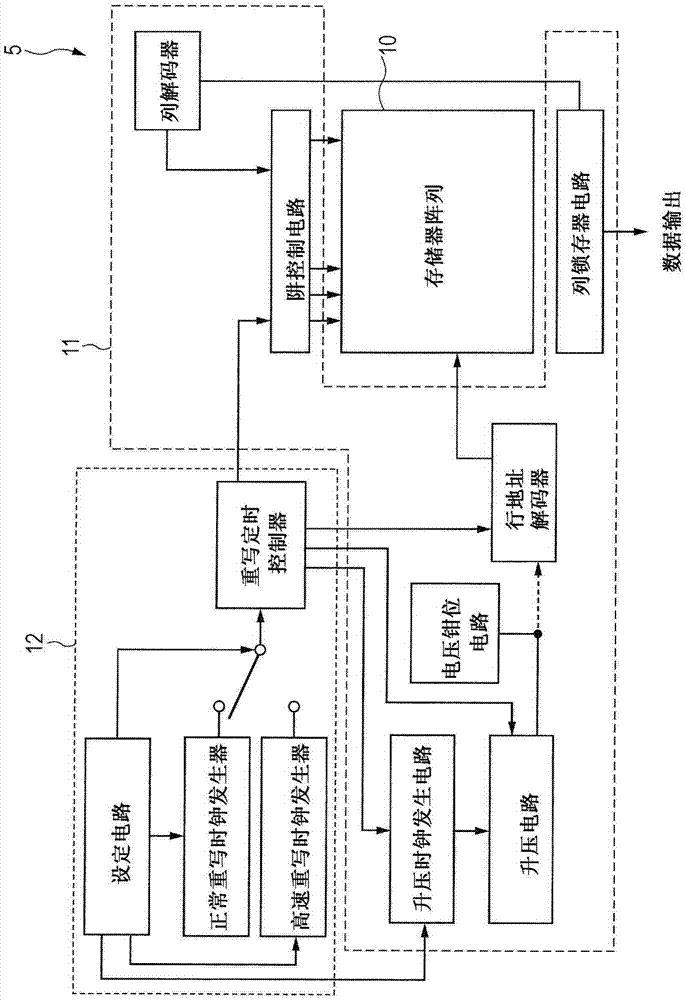
[0093] The technical idea in Embodiment 1 relates to a semiconductor device including, in the same semiconductor chip, a main circuit that provides the main functions of the semiconductor chip and a circuit that is added to the main circuit and is called an add-on circuit (add-on circuit). The additional circuit (additionalcircuit). In this semiconductor device, an attached circuit is formed of a MONOS rewritable nonvolatile memory.
[0094] For example, an SOC (System on Chip) includes a main circuit as shown below. That is, examples of the main circuit include: memory circuits such as DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory) or SRAM (Static Random Access Memory); logic circuits such as CPU (Central Processing Unit) or MPU (Micro Processing Unit); and mixed signal circuits including memory circuits and logic circuits.
[0095] On the other hand, examples of the auxiliary circuit include a storage circuit that stores relatively low-capacity information associated with the main ci...
Embodiment 2
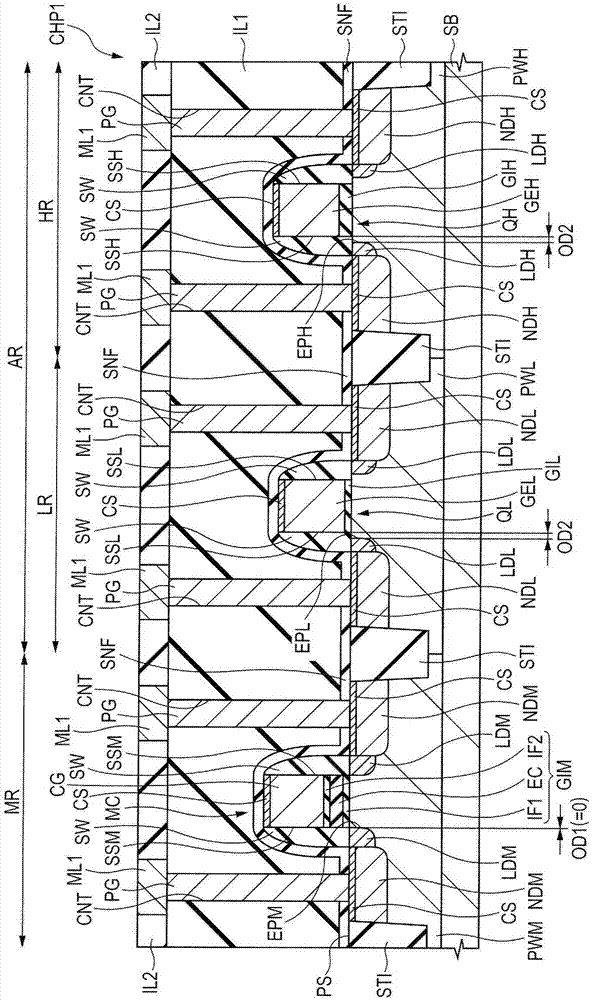
[0316] In the method of manufacturing the semiconductor device in Embodiment 1, in a state where the offset spacer OF2 is not formed on both side surfaces of the gate electrode CG, impurities are introduced into the semiconductor substrate SB to form n - type semiconductor region LDM. In contrast, in the method of manufacturing the semiconductor device in Embodiment 2, in which each has a thickness greater than that of each of the offset spacers OF2 is formed on both side surfaces of the gate electrode CG. In the state of offset spacer OF1, impurities are introduced into the semiconductor substrate SB to form n - type semiconductor region LDM.
[0317] It should be noted that also in Embodiment 2, the layout of semiconductor chips and circuit blocks in the nonvolatile memory may be the same as in Embodiment 1.
[0318]
[0319] Next, the structure of the semiconductor chip CHP1 as the semiconductor device in Embodiment 2 will be described with reference to the drawings. ...
Embodiment 3
[0370]In the method of manufacturing the semiconductor device in Embodiment 1, in the memory formation region MR, the insulating film IFG having the internal charge storage portion is patterned by dry etching. In contrast, in Example 3, the insulating film IFG having the internal charge storage portion was patterned by wet etching.
[0371] Note that the structure of the semiconductor device in Embodiment 3 is the same as that of the semiconductor device in Embodiment 1.
[0372]
[0373] Figure 57 is a process flowchart showing a part of the manufacturing process of the semiconductor device in Embodiment 3. Figure 58 to Figure 61 is a sectional view of the main part during the demanufacturing process of the semiconductor device in Embodiment 3. Figure 58 to Figure 61 A main part cross-sectional view of the memory formation region MR and the main circuit formation region AR is shown.
[0374] In the method of manufacturing the semiconductor device in Embodiment 3, in t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com