Switching tube control circuit
A technology for controlling circuits and switching tubes, applied in control/regulating systems, electrical components, regulating electrical variables, etc., can solve the problems affecting system efficiency, detection errors, and the inability to detect the lowest point of voltage difference, so as to improve system efficiency, The effect of reducing switching losses
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
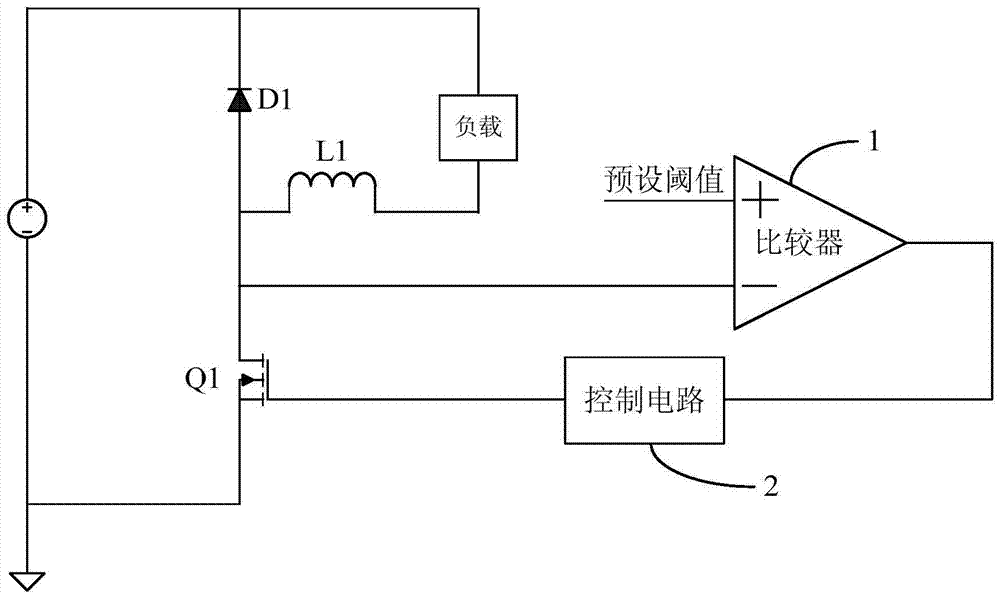
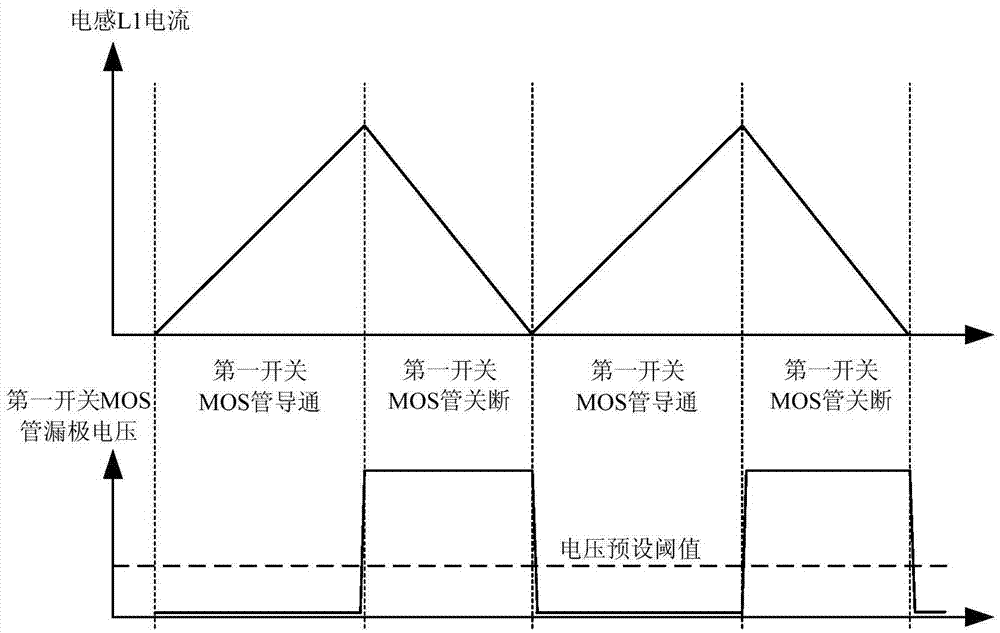
[0028] Please refer to Figure 4 , the embodiment of the present invention discloses a switching tube control circuit, including a second inductor L2, a second freewheeling diode D2, a second switching tube Q2, a load, a differential circuit 3, a comparator 4 and a control circuit 5.
[0029] In this embodiment, the second switching transistor Q2 is a second switching MOS transistor Q2.
[0030] In this embodiment, the differential circuit 3 includes a first resistor R1 and a first capacitor C1, the two ends of the first resistor R1 are respectively connected to the output terminal of the differential circuit 3 and the zero potential, and the two ends of the first capacitor C1 are respectively connected to the second The drain of the switch MOS transistor Q2 and the output terminal of the differential circuit 3 .
[0031] In this embodiment, the first input terminal of the comparator 4 is connected to the output terminal of the differential circuit 3 , and the second input te...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Please refer to Figure 6 , the embodiment of the present invention discloses a second control circuit, including a second inductor L2, a second freewheeling diode D2, a second switching tube Q2, a differential circuit 3, a comparator 4 and a control circuit 5.
[0040] In this embodiment, the second switching transistor Q2 is a second switching MOS transistor Q2.
[0041] In this embodiment, the differential circuit 3 includes a second resistor R2 and the drain and gate parasitic capacitance Cgd of the second switch MOS transistor Q2, and the two ends of the second resistor R2 are respectively connected to the gate of the second switch MOS transistor Q2 and the zero potential . The gate of the second switch MOS transistor Q2 serves as the input terminal and the output terminal of the differential current detection circuit 3 at the same time.
[0042] In this embodiment, the first input terminal of the comparator 4 is connected to the gate of the second switching MOS ...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Please refer to Figure 7 , the embodiment of the present invention discloses a third control circuit, including a second inductor L2, a second freewheeling diode D2, a load, a second switching tube Q2, a differential circuit 3, a comparator 4 and a control circuit 5.
[0051] In this embodiment, the second switching transistor Q2 is a second switching MOS transistor Q2.
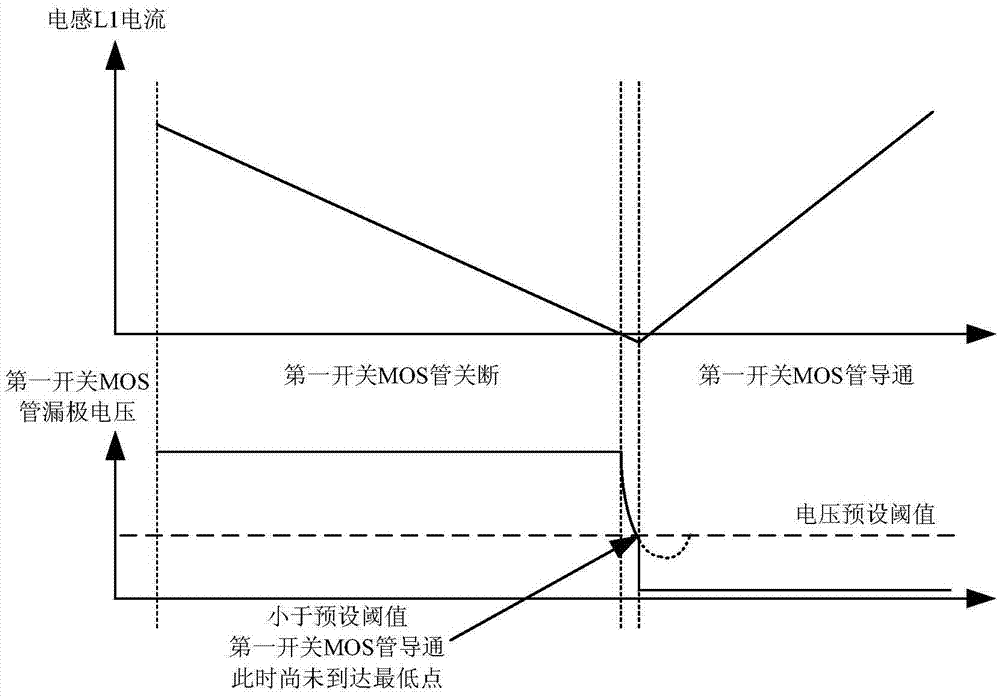
[0052] In this embodiment, the control circuit 5 includes an edge detection circuit 6 , a control drive circuit 7 , a switching transistor turn-on switch S1 and a gate pull-down MOS transistor Q3 . The input end of the edge detection circuit 6 is the input end of the control circuit 5, and the edge detection circuit 6 and the control drive circuit 7 are electrically connected in sequence; The second output terminal of the circuit 7 is connected to the gate of the gate pull-down MOS transistor Q3. The switch tube is turned on, and the two ends of the switch S1 are respectively connected to the gate o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com