Method and device for detecting microorganisms in blood
A microbial and blood technology, applied in the field of microbial detection, can solve the problems of cumbersome and time-consuming culture techniques, and achieve the effect of relieving pain, alleviating pain, and benefiting healthy blood transfusion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1 Determination of the free nucleic acid sequence of the plasma sample
[0036] The blood / plasma samples of patients with fever of unknown origin came from the Inner Mongolia Maternal and Child Health Hospital. After the nucleic acid was extracted, the library construction and sequencing were carried out according to the library construction and sequencing instructions of BGI’s microchip semiconductor sequencing platform BGISEQ100.
[0037] This detection technology uses a new generation of high-throughput sequencing technology to detect pathogens in the plasma of patients with fever of unknown origin. The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0038] Extraction of nucleic acid from plasma samples
[0039] Use Tiangen's Micro Sample Genome Extraction Kit to extract nucleic acid from plasma samples according to the instructions in the kit.
[0040] 2. DNA library construction
[0041] 2.1 End Repair
[0042] 2.1.1 Take out 10×PolynucleotideKinase (PNK...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Example 2 Microorganism / Pathogen Detection
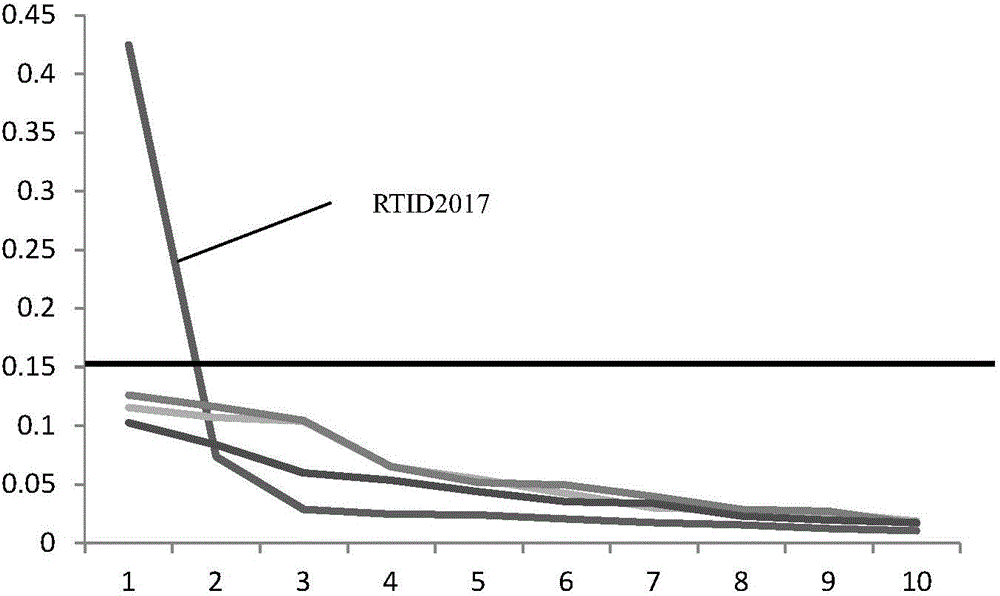
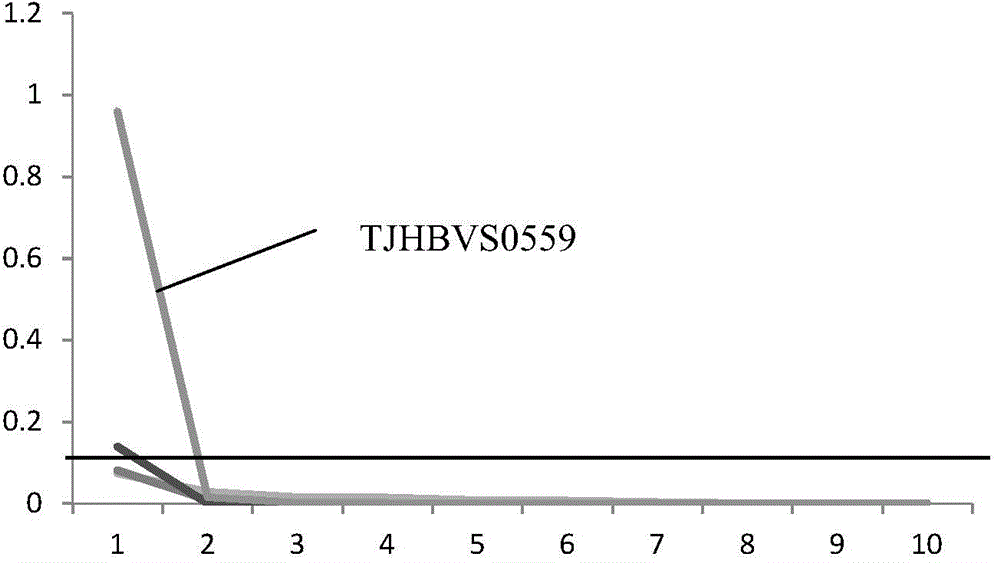
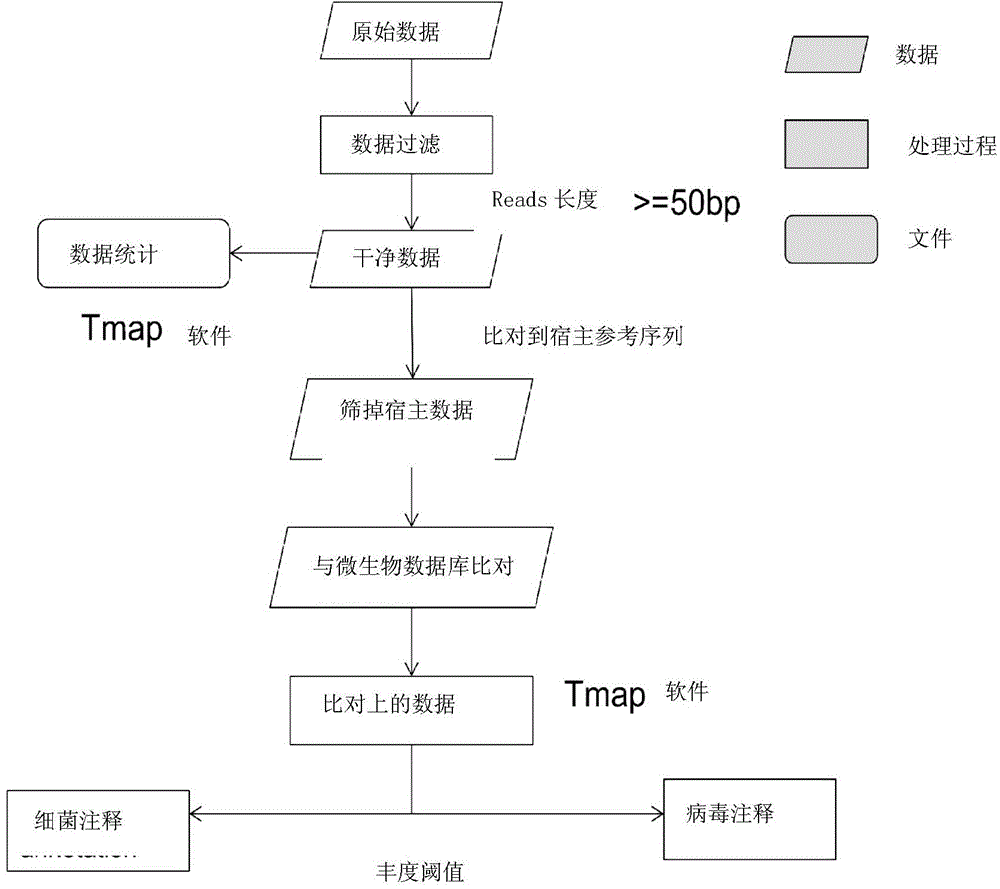
[0065] The overall detection and analysis process is as follows: image 3 shown.
[0066] According to steps 1-4 of the method in Embodiment 1, the sequence determination data of the plasma sample nucleic acid is obtained, and the sequence data consists of multiple reads of different lengths.
[0067] 5. Data preprocessing
[0068] 5.1 Filter raw data, for BGISEQ100 sequencing data, remove reads less than 50bp.
[0069] 5.2 Filter host human genetic material. Most of the plasma samples are cell-free DNA of the host, the data shows that it is as high as more than 95%, and the content of the remaining microorganisms is less than 1%. In order to avoid the influence of the host’s genetic material when detecting pathogenic microorganisms, TMAP software and human reference genome reference sequences are used Perform comparison, mask out the sequence on the comparison, and obtain non-human sequence data.
[0070] 6. Pathogen da...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com