Selective synthesis method of diltiazem chiral intermediate
A chiral intermediate, diltiazem technology, applied in the field of selective synthesis of diltiazem chiral intermediates, can solve the problem of high cost, achieve the effect of increasing yield, improving utilization rate, and reducing cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
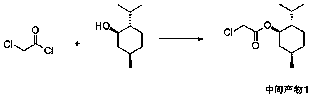
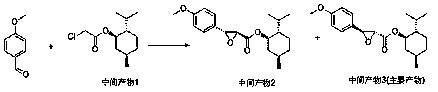
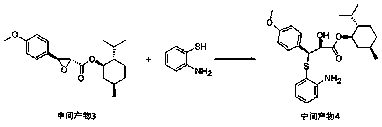
[0036] The selective synthesis method of diltiazem chiral intermediate of the present invention, such as Figure 1 to Figure 5 As shown, using anisaldehyde as the main raw material, it is first condensed with the intermediate product 1 formed by the reaction of chloroacetyl chloride and L-menthol, after purification, it reacts with o-aminothiophenol and undergoes hydrolysis and ring-forming steps to obtain the diltiazem chiral intermediate body, including the following steps:
[0037]Step 1. Add L-menthol, 0.01-0.1 equivalent (moles / L-menthol moles) of DMAP (N,N-dimethyl-4-aminopyridine) and the first solvent into the reactor, and stir After dissolving, add 1.0-2.0 equivalents (moles / L-menthol moles) of acid-binding agent, then dropwise add 1.0-2.0 equivalents (moles / L-menthol moles) of chloroacetyl chloride, and stir after the addition reaction, after the reaction is completed, add water to separate the layers, remove the water layer and then dry the remaining organic layer ...
Embodiment 1
[0049] Add 62.5g of L-menthol, 0.5g of N,N-dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP), and 200mL of dichloromethane into a 1L reaction flask, and stir to dissolve. Add 63.0 g of sodium carbonate, add 56.5 g of chloroacetyl chloride dropwise at a controlled temperature of 25°C to 30°C, and keep stirring at 25°C to 30°C for 2 hours after dropping. After the reaction was completed, 400 mL of water was added, and after stirring and separating, the organic layer was dried by adding 10 g of anhydrous sodium sulfate. After filtration, the filtrate was concentrated to dryness under reduced pressure to obtain intermediate product 1, which was directly used in the next reaction without purification.
Embodiment 2
[0051] Add 62.5g of L-menthol, 0.5g of N,N-dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP), and 200mL of chloroform into a 1L reaction bottle, and stir to dissolve. Add 63.0 g of sodium bicarbonate, add 56.5 g of chloroacetyl chloride dropwise at a controlled temperature of 25°C to 30°C, and keep stirring at 25°C to 30°C for 2 hours after dropping. After the reaction was completed, 400 mL of water was added, and after stirring and separating, the organic layer was dried by adding 10 g of anhydrous sodium sulfate. After filtration, the filtrate was concentrated to dryness under reduced pressure to obtain intermediate product 1, which was directly used in the next reaction without purification.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| optical purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com