Joint optimization method for heterogeneous network user access and time domain interference coordination based on graph theory
A technology of time-domain interference coordination and joint optimization, which is applied in access restriction, wireless communication, electrical components, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
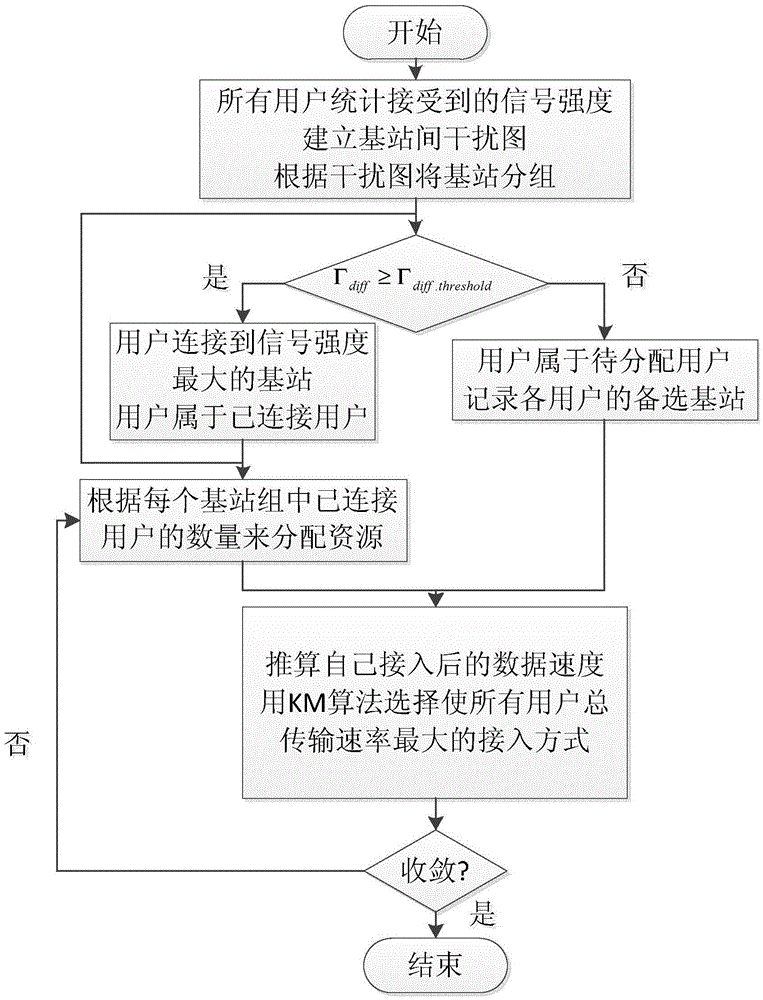
[0037] Specific implementation mode one: as figure 1 As shown, the implementation process of the joint optimization method for heterogeneous network user access and time-domain interference coordination based on graph theory described in the implementation mode is as follows:
[0038] Step 1. Link the macro base station and the micro base station to the general control center, and the user access and time-domain interference coordination are all performed through the general control center;
[0039] Step 2. In the stage of user communication initiation, each base station obtains the channel information of the user through signaling, and each base station reports the channel information of the user connected to the base station to the general control center;
[0040] Step 3. Determine the optional range of ABSF ratio is 1 / 10 to 5 / 10, choose from small to large;
[0041] Step 4. Every time an ABSF ratio is selected, the general control center maximizes the objective function th...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0043] Embodiment 2: This implementation method mainly explains in detail the user access algorithm in Step 4 of Embodiment 1. refer to figure 1 This embodiment will be described. The joint user access algorithm method described in this embodiment is implemented through the following steps:
[0044] Step 1. The UE counts and receives the RSSI values from each base station. If the user's first and second strongest received signal strength difference Γ diff ≥Γ diff.threshold , the users are connected to the first strongest base station, and these users belong to the assigned user group. If Γ diff diff.threshold , such users belong to the user group to be assigned.
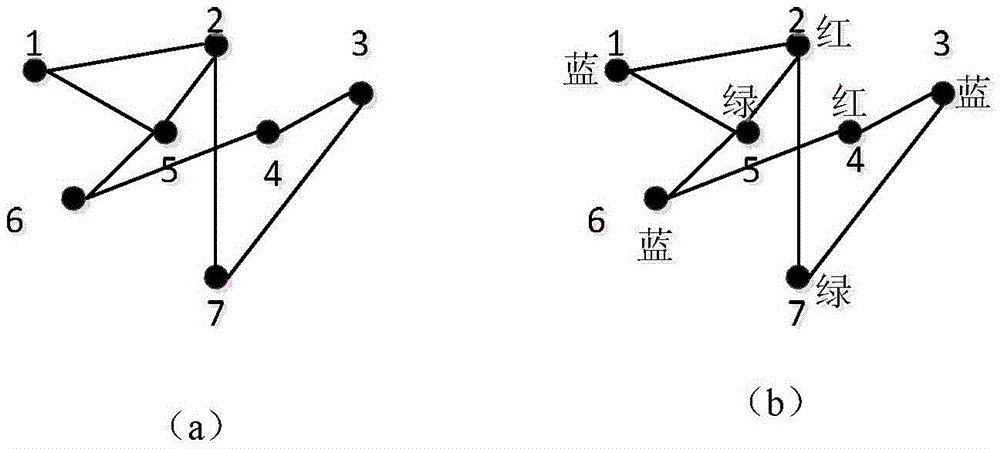
[0045] Step 2. Define another threshold Γ th , for each user, the received signal strength Γ BSi Greater than Γ th All micro base stations of , defined as mutual interference micro base stations. Through the vertex coloring method, the micro base stations are divided into several groups according to the m...
specific Embodiment approach 3
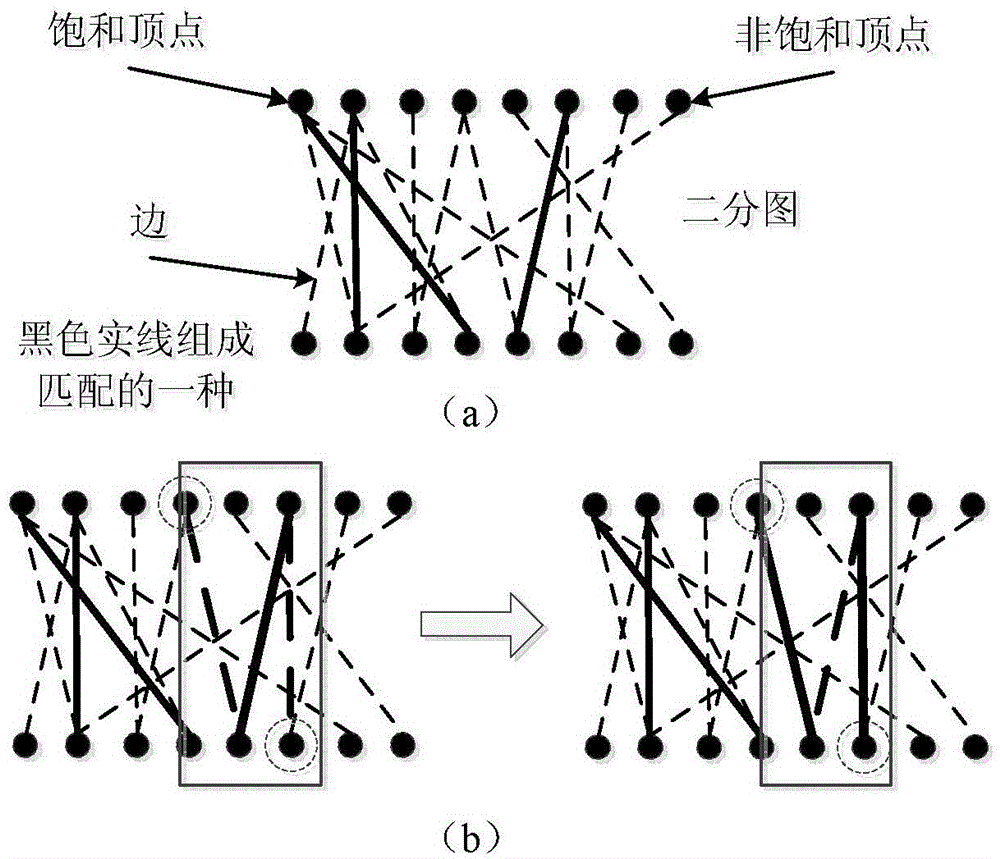
[0053] Specific implementation mode three: this implementation mode is to further illustrate the improved KM algorithm in the above-mentioned implementation mode:
[0054] Since each vertex in the KM algorithm can only be connected by one edge, and in our scenario there may be many users connected to the same vertex, so here we make an improvement. For a base station, if this base station exists in multiple candidate base stations of users to be allocated, then as many vertices as there are such users are established for this base station. For example, there are base station 1 among the candidate base stations of 5 users to be allocated, then 5 vertices are established for base station 1.
[0055] first according to figure 2 Introduce the definitions in several graph theory algorithms:
[0056] Adjacent: In graph theory, there is a connectable relationship between two points, which is called adjacent. The user and the candidate base station are in an adjacent relationship....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com