Method for deep removing nickel and cobalt impurities in zinc hydrometallurgy solution
A technology for hydrometallurgy of zinc and zinc sulfate solution, which is applied in the field of nickel and cobalt, can solve problems such as difficult to meet the development trend of zinc smelting technology, obvious cobalt remelting phenomenon, limited purification depth, etc., and achieves easy industrial implementation and strong activity , the effect of low cost of use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
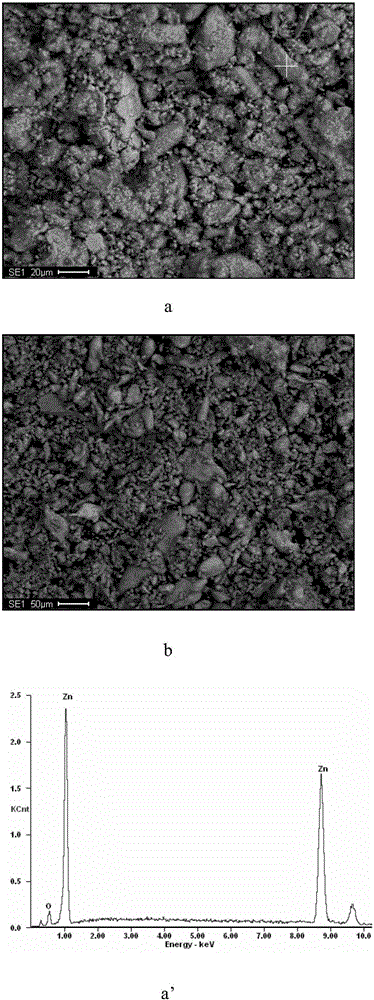
[0028] Pump 8m into the reactor 3 neutral leaching solution (Zn: 142g / L, Ni: 7.4mg / L, Co: 11.5mg / L), add dilute sulfuric acid to adjust the pH of the solution to about 4.5, stir and heat up to 75°C, and then add 4.4kg of manganese-zinc Binary alloy powder (particle size: -100 mesh, manganese and zinc contents are 94.2% and 3.7% respectively), stirred for 60 minutes, and the filtrate and filter residue were collected by filtration. The contents of nickel and cobalt in the obtained filtrate were respectively 0.15mg / L and 0.52 mg / L, the removal rates of nickel and cobalt were 98.18% and 95.69%, respectively, and the contents of nickel and cobalt in the filter residue were 2.62% and 3.89%, respectively.
[0029] The microscopic morphology and EDS analysis results of manganese-zinc alloy powder before and after cobalt replacement are as follows: figure 1 Shown: by figure 1 a and figure 1 b, it can be seen that the morphology of manganese-zinc alloy powder does not change much be...
Embodiment 2
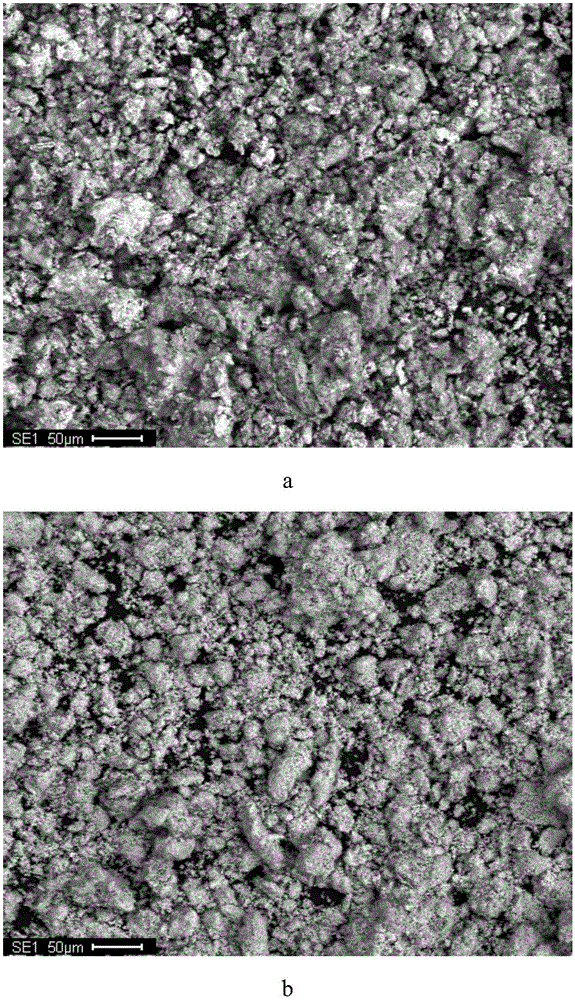
[0031] Pump 8m into the reactor 3 neutral leaching solution (Zn: 142g / L, Ni: 7.4mg / L, Co: 11.5mg / L), add dilute sulfuric acid to adjust the pH of the solution to about 5, stir and heat up to 85°C, and then add 3.68kg of manganese powder ( The particle size is: -140 mesh, the manganese content is 98.5%), stirred for 80 minutes, and the filtrate and filter residue were collected by filtration. The contents of nickel and cobalt in the obtained filtrate were 0.22mg / L and 0.75mg / L respectively, and the removal rates of nickel and cobalt were respectively The contents of nickel and cobalt in the filter residue are 3.11% and 4.61%, respectively.
[0032] The microscopic morphology and EDS analysis results before and after cobalt extraction by metal manganese powder are as follows: figure 2 Shown: by figure 2 a and figure 2 b It can be seen that the morphology of manganese powder changes greatly before and after replacement, from irregular particles with smooth and dense surface...
Embodiment 3
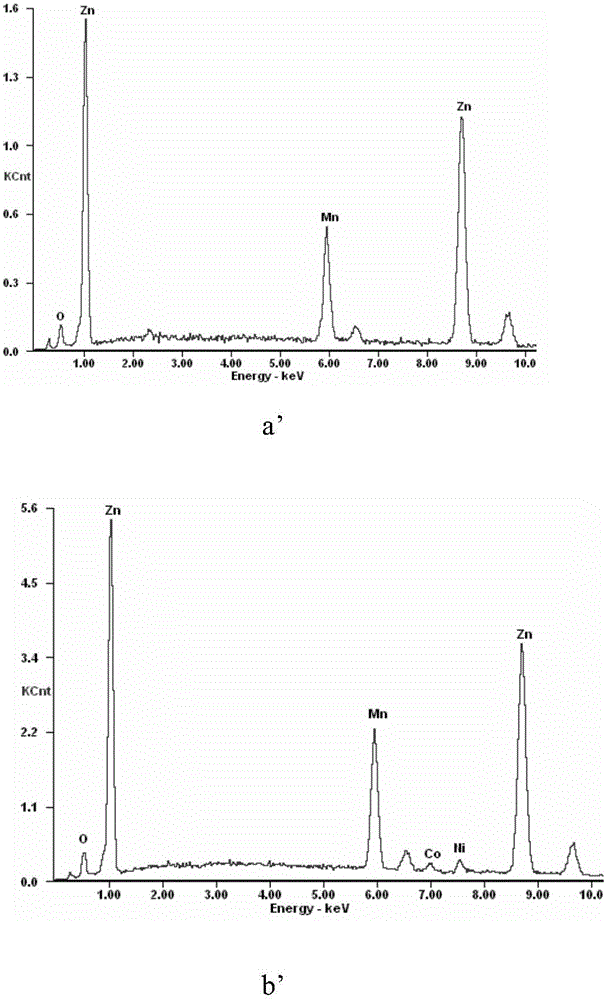
[0034] Pump 8m into the reactor 3 The neutral leaching solution (Zn: 142g / L, Ni: 7.4mg / L, Co: 11.5mg / L), adjust the pH of the solution to about 3 by adding dilute sulfuric acid, and stir the temperature to 80°C, then add 4.64kg manganese- Copper binary alloy powder (particle size is: -100 mesh, manganese and copper content are respectively 92.5% and 5.1%), stir reaction 50min, filter and collect filtrate and filter residue, in the gained filtrate, nickel, cobalt content are respectively 0.07mg / L, 0.28mg / L, the removal rates of nickel and cobalt were 99.07% and 97.15% respectively, and the contents of nickel and cobalt in the filter residue were 2.41% and 3.69% respectively.
[0035] The microscopic morphology and EDS analysis results of manganese-copper alloy powder before and after cobalt replacement are as follows: image 3 Shown: by image 3 a and image 3 b, it can be seen that the morphology of the manganese-copper alloy powder does not change much before and after the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com