Method for three-dimensional registration and brain tissue extraction of individual human brain multimodality medical images
A medical imaging and three-dimensional registration technology, which is used in medical science, instruments for radiological diagnosis, diagnosis, etc. It can solve the difference of electrode position, cannot adjust the color setting of PET imaging, and can only perform single image registration in stages, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0038] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
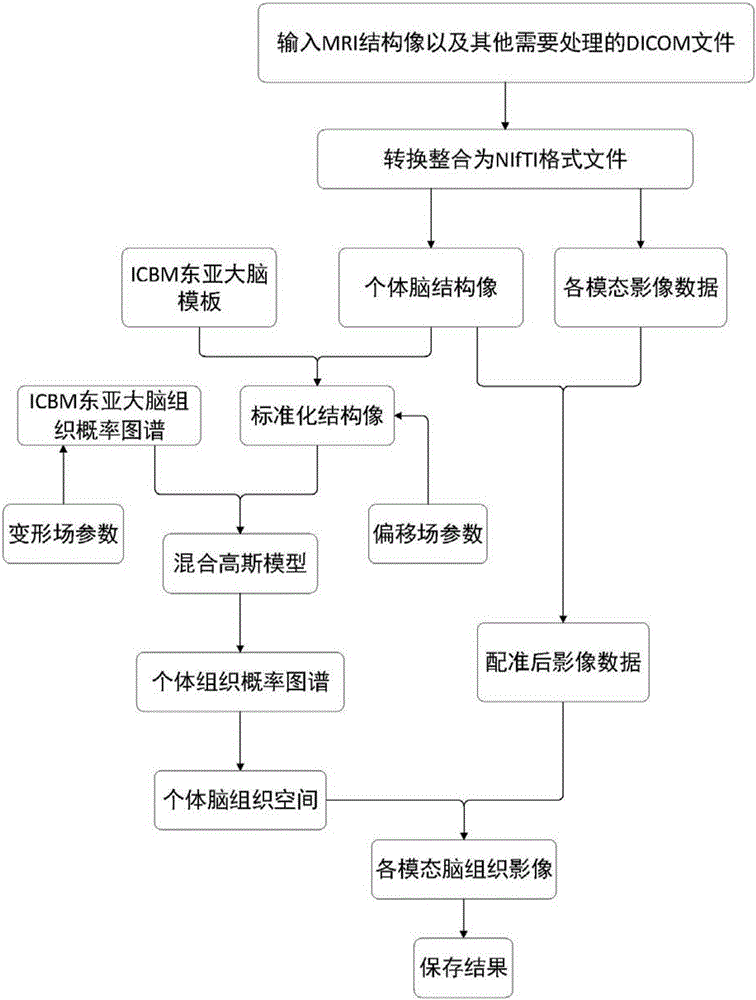
[0039] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention provides a method for three-dimensional registration and brain tissue extraction of individualized multimodal medical images of the human brain, which includes the following steps:
[0040] (1) Read DICOM medical image data, and convert DICOM format data into NIfTI format;
[0041] (1.1) Convert the nuclear magnetic resonance structure image (3TT1-MPR) DICOM format data into NIfTI format and save it;
[0042] (1.2) Each modality (such as CT, MRA, MRV, T2-flair, MEG, 18 FDG-PET metabolic imaging, etc.) DICOM format image data is converted to NIfTI format file and saved;
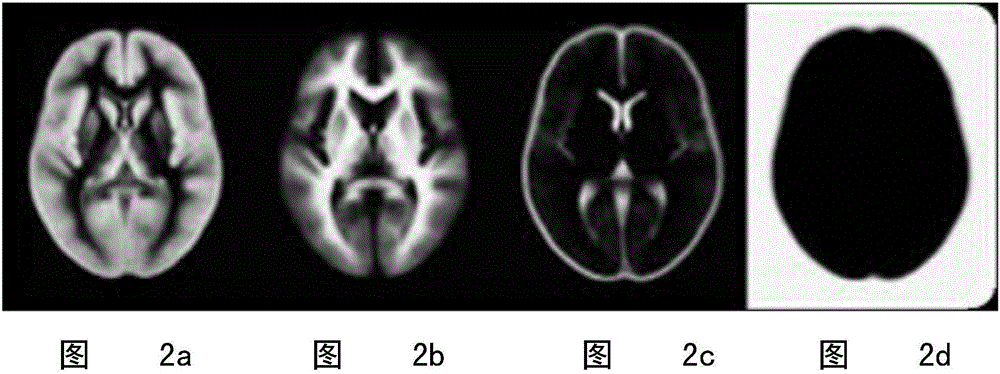
[0043] (2) Layering the NMR structural image: Using the ICBM (internationalconsortiumforbrainmapping, Human Brain Mapping Alliance) East Asian brain structure template and East Asian brain tissue probability atlas, a mixed Gau...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com