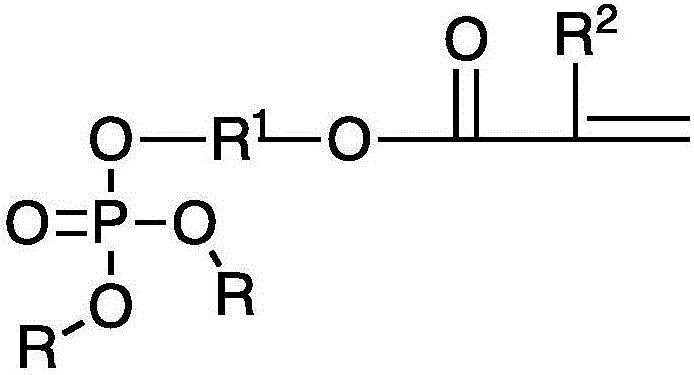
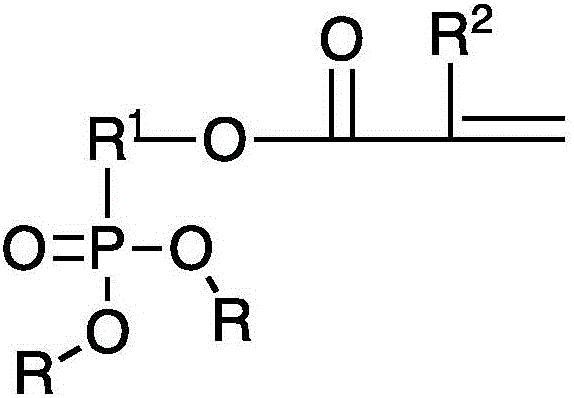
Flame-retardant copolymers of dialkyl (meth) acryloyloxyalkyl phosphate or dialkyl (meth) acryloyloxyalkyl phosphonate monomers and polymer foams based made therefrom
A technology of acryloyloxyalkyl esters and methyl methacrylates, applied in the field of foams containing those copolymers, can solve the problems of additive sensitivity and limited material types, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0069] Example 1 and Foam Examples F-1 to F-5
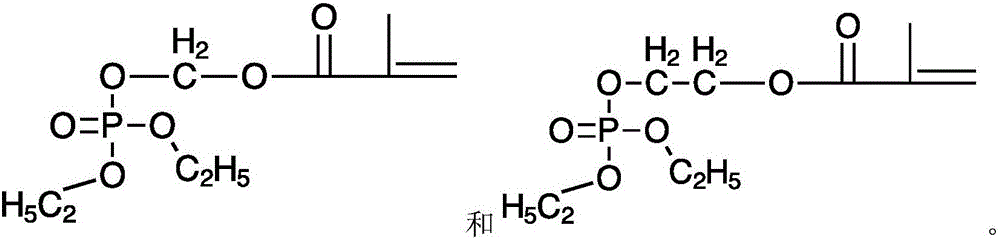
[0070] 2-Hydroxyethyl methacrylate (13 g), triethylamine (12.3 g) and copper(I) chloride (0.15 g) were dissolved in 55 mL of ether, cooled in an ice bath, and flushed with nitrogen. Diethyl chlorophosphate (17.25 g) was added dropwise over 1.5 hours. The mixture was then stirred at about 0°C for one hour, and then at room temperature for two days. The precipitated triethylamine monochloride was removed by filtration. The solvent was then removed by rotary evaporation, yielding 21.5 g of diethyl methacryloxyethyl phosphate (DEMEP) in the form of a pale yellow liquid. The crude product was purified by column chromatography using silica gel medium and a mixture of hexane and ethyl acetate as eluent. Final product purity was determined by gas chromatography and 31 PNMR about 98%.
[0071] A phosphorus-containing copolymer of DEMEP and methyl methacrylate (Example 1) was prepared by mixing 45.6 parts of methyl methacrylate, 34.4 ...
example 2
[0084] DEMEP copolymers were prepared in the general manner described in Example 1, except that the ratios of the monomers were changed. This copolymer contained 7.8% phosphorus, had a weight average molecular weight of 150,000 g / mol and had a glass transition temperature of 17°C. This DEMEP copolymer was blended with the random methyl methacrylate / butyl acrylate copolymer described in Example 1 to produce a blend containing 3% phosphorus. The blend exhibited a glass transition temperature of 17°C and another of 98°C, corresponding to those of the two polymer components. Foam was made from this blend in the manner described according to Example F1 above. The foam had an average cell size of 1900 nm and a porosity of 71%.
example 3
[0086] Diethyl hydroxymethyl phosphonate (118 g) and triethylamine (98 mL) were dissolved in 400 mL of anhydrous dichloromethane, cooled in an ice bath, and flushed with nitrogen. Acryloyl chloride (56.9 g) was added dropwise in 10 mL of dichloromethane. The mixture was then stirred at about 0°C for three hours, and then at room temperature under nitrogen for 24 hours. The precipitated triethylamine monochloride was removed by filtration. The solvent was then removed by rotary evaporation. Phenothiazine (400 mg) and hydroquinone (350 mg) were added. The product was distilled under vacuum at 108°C, yielding 109.6 g of diethyl acryloyloxymethyl phosphonate (DEAMPn) in the form of a colorless liquid. Final product purity was determined by gas chromatography and 31 PNMR about 98%.
[0087] A portion of DEAMPn was copolymerized with methyl methacrylate in the general manner described in Example 1 to produce a phosphorus-containing random copolymer having a molecular weight of ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com