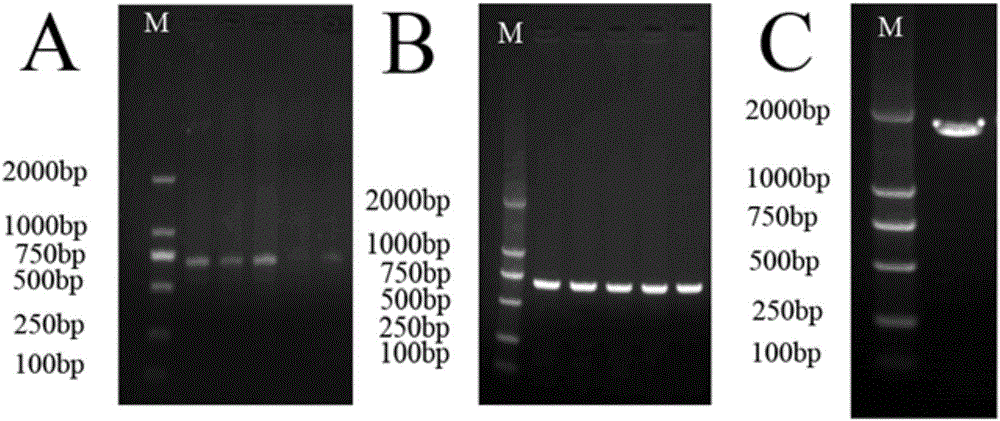
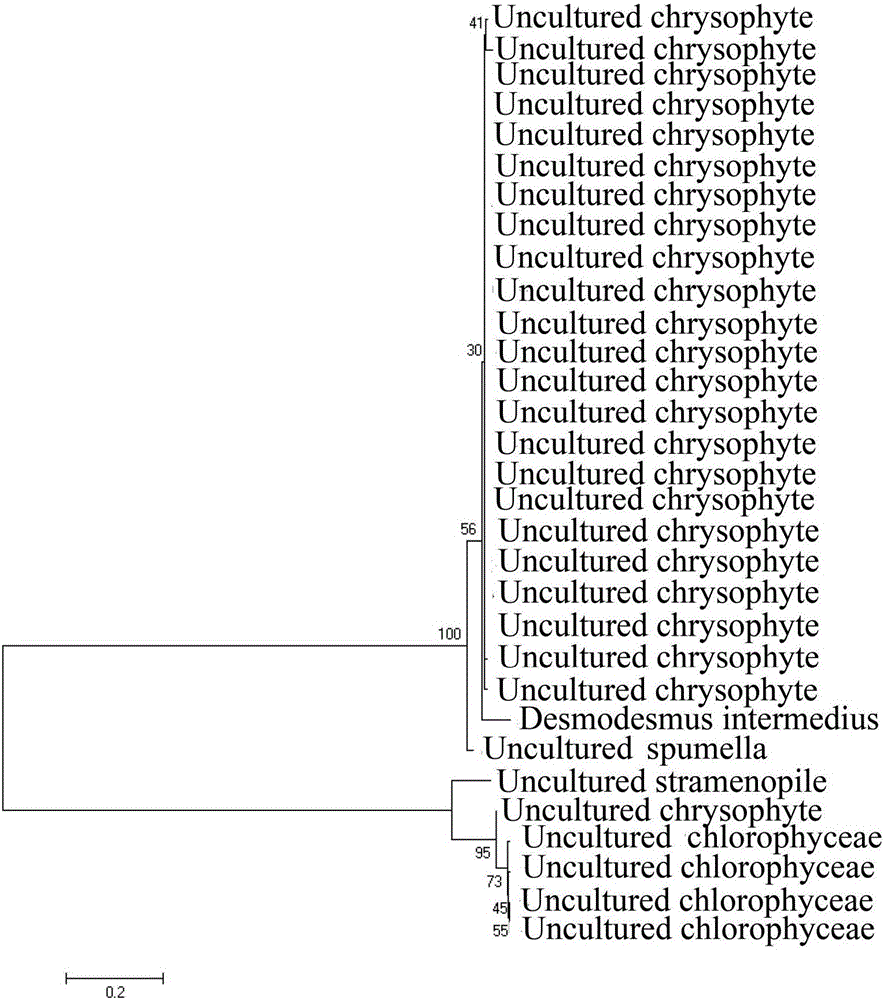
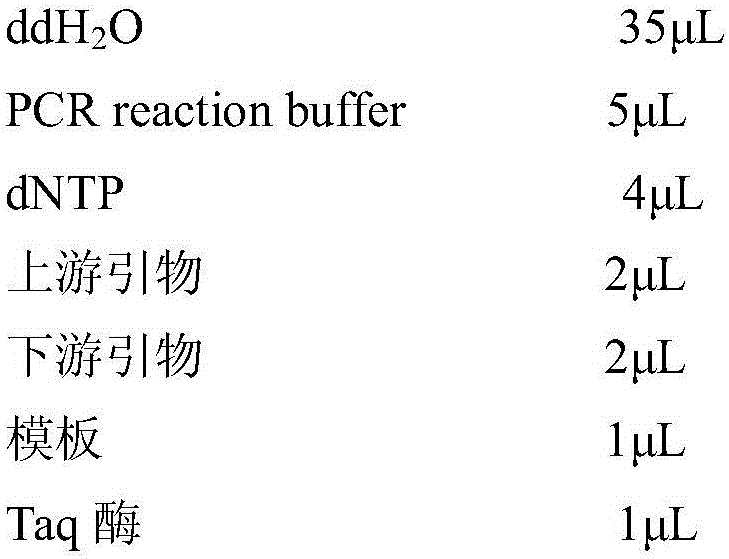
Primers and method for identifying diversity of eukaryotic algae in activated sludge of epoxypropane saponified wastewater
A technology for activated sludge and saponified wastewater, which is applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, DNA/RNA fragments, etc. It can solve the problems of inability to accurately identify and complex microbial community structure in activated sludge, etc. Achieve the effect of simple steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0060] 1. NCBI search nucleotide sequence. Log on to www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / Gen-Bank, you can get the gene sequence from Gen Bank as a template.
[0061] The target amplification group of the present invention is eukaryotic algae, according to Burki (2008) to photosynthetic eukaryote, Adl (2012) to the molecular system taxonomy of eukaryote, the target amplification group is refined as green algae (Chlorophyceae) , Porphyridium, Euglena, Charophyta, Pyrrophyta, Cryptophyceae, Haptophyta, Chlorarachniophyta, Chrysophyceae, Diatom ), brown algae (Phaeophyta), yellow algae (Xanthophyta) and other 12 eukaryotic algae. Determine the DNA sequence that needs to be amplified according to the test requirements, and know the sequence of its coding structural gene region. The specific method is as follows:
[0062] Select Nucleotide in the Search dialog box, fill in the name of the Nucleotide to be searched in the dialog box, such as input Chlorophyceae (green algae), click search to get...
Embodiment 2
[0080] The activated sludge of propylene oxide saponification wastewater described in this example is obtained from the activated sludge in the treatment process of propylene oxide saponification wastewater of Binhua Group Co., Ltd.
[0081] A method for identifying the diversity of eukaryotic algae in the activated sludge of propylene oxide saponification wastewater, comprising the steps:
[0082] (1) get propylene oxide saponification wastewater activated sludge sample, extract total DNA;
[0083] The activated sludge is taken from the activated sludge of the sewage treatment plant of Shandong Binhua Group, which is the activated sludge for the treatment of propylene oxide saponification wastewater. The fresh sludge taken from the sewage treatment plant was centrifuged at 4000r / min at 4°C for 10min, and the supernatant was discarded and stored in a refrigerator at 4°C. According to the method described in Example 1 in Chinese patent document CN103789300A (application number...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com