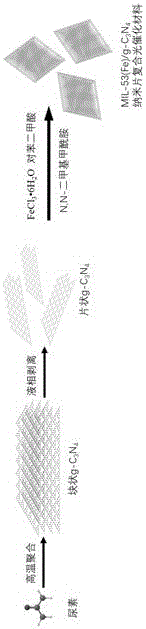
Preparation method of MIL-53(Fe)/g-C3N4 nanosheet composite photocatalysis material
A technology of composite photocatalysis and nanosheets, which is applied in the field of photocatalytic materials, can solve the problems of small specific surface area and easy composite, and achieve the effect of simple and easy process, mild conditions and suitable for large-scale production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] 1) g-C 3 N 4 Preparation of nanosheets
[0030] Weigh 10 g of urea and place it in a crucible with a lid, wrap the crucible with aluminum foil, place it in a box furnace for heating under a nitrogen atmosphere (introduce nitrogen at a flow rate of 1.5 L / min), and heat up to 550 °C at a heating rate of 5 °C / min. ~600℃, keep it warm for 2h, cool down to room temperature naturally, and get block g-C 3 N 4 ;Weigh 150mg of synthetic block g-C 3 N 4 , add 150mL of water, use an ultrasonic instrument with a power of 300W for 3 hours, then let it stand for 1 hour, use a dropper to carefully remove the top layer of liquid, and centrifuge at 7000 rpm for 10 minutes to obtain g-C 3 N 4 Nanosheet, its morphology and XRD spectrum see figure 2 .
Embodiment 2
[0032] 1) Preparation of MIL(Fe)-53
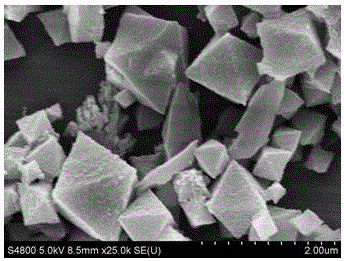
[0033] First, 2mmol FeCl 3 •6H 2 O and 2 mmol of terephthalic acid were dissolved in 40 mL of N,N-dimethylformamide, stirred magnetically for 60 min, then transferred to a hydrothermal kettle, heated at 150°C for 15 h, and cooled naturally to room temperature at 4000 rpm / min speed, centrifuged for 5min, then washed twice with DMF and methanol respectively, and finally vacuum-dried at 80°C for 12h to obtain the MIL(Fe)-53 (abbreviated as M53). For its morphology and XRD spectrum, see image 3 and Figure 7 .
[0034] 2) Photocatalysis experiment
[0035] Put 80 mg of the prepared M53 photocatalyst into potassium dichromate solution (100 mL) with a concentration of 50 ppm. Catalytic reaction. Get a certain amount of potassium dichromate solution at regular intervals, test the absorption spectrum of the solution with a UV-visible spectrophotometer, and calculate the degradation rate of the potassium dichromate solution by the change in ...
Embodiment 3
[0037] 1) MIL(Fe)-53 / g-C 3 N 4 Preparation of -20
[0038] First, weigh 20 mg of g-C synthesized in Example 1 3 N 4 Nanosheets were dispersed in 40mL of DMF at room temperature, ultrasonicated for 15-30 min, and then added with 2mmol FeCl 3 •6H 2 O and 2 mmol terephthalic acid, magnetically stirred for 60 min, transferred to a hydrothermal kettle, heated at 150°C for 15 h, naturally cooled to room temperature, centrifuged at 4000 rpm / min for 5 min, and then washed twice with DMF and methanol respectively. times, and finally vacuum dried at 80°C for 12h to obtain the MIL(Fe)-53 / g-C 3 N 4 -20 (referred to as M53 / g-C 3 N 4 -20) Composite photocatalytic material, its morphology and XRD spectrum refer to Figure 4 and Figure 7 .
[0039] 2) Photocatalysis experiment
[0040] The prepared M53 / g-C 3 N 4 Put 80mg of -20 composite photocatalytic material into potassium dichromate solution (100 mL) with a concentration of 50ppm. Under the condition of magnetic stirring, a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com