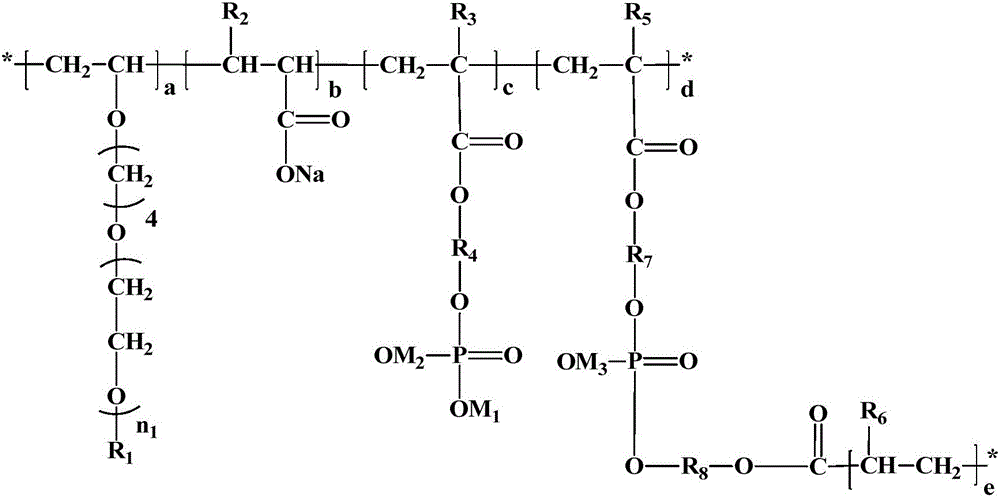
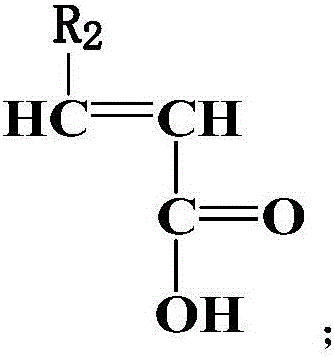
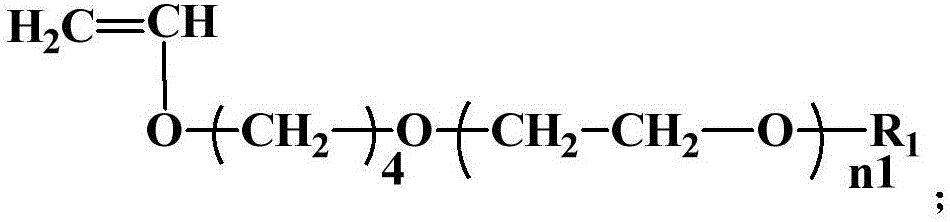Cross-linking type low-sensitivity polycarboxylate water reducing agent and preparation method thereof
A low-sensitivity, polycarboxylic acid technology, applied in the field of building materials, can solve the problems of water reducing agent dosage sensitivity, dosage sensitivity has not been improved, etc., to achieve good anti-intercalation effect, excellent low-sensitivity performance, slow water The effect of speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] (1) Dissolving 180 g of VPEG-type monomer 4-hydroxybutyl vinyl polyoxyethylene ether with a number-average molecular weight of 2000 in 180 g of deionized water, and adjusting its temperature to 15 ° C, obtains the first solution;
[0044] (2) acrylic acid 26g and mercaptopropionic acid 1.5g are dissolved in 20g deionized water, then 10g 30% potassium hydroxide solution is added to carry out partial neutralization to obtain the second solution;
[0045] (3) 0.6g sodium formaldehyde sulfoxylate is dissolved in 30g deionized water to obtain the third solution;
[0046] (4) drip 22g of the second solution into the first solution, and keep the temperature at 15°C;
[0047] (5) 3 g of 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphate and 1 g of di(hydroxyethyl acrylate) phosphate are added to the remaining second solution;
[0048] (6) 0.05g ferrous sulfate and 2.5g hydrogen peroxide (30%) are successively added to the material obtained in step (4), and then the material obtained in step (5)...
Embodiment 2
[0050] (1) Dissolving 180g of VPEG-type monomer 4-hydroxybutyl vinyl polyoxyethylene ether with number-average molecular weight of 2400 in 180g deionized water, and adjusting its temperature to 15°C, obtains the first solution;
[0051] (2) 24g of acrylic acid and 1.4g of thioglycolic acid are dissolved in 20g of deionized water, and then 9g of 30% sodium hydroxide solution is added for partial neutralization to obtain the second solution;
[0052] (3) 0.6g FF6 is dissolved in 30g deionized water to obtain the third solution;
[0053] (4) drip 20g of the second solution into the first solution, and keep the temperature at 15°C;
[0054] (5) 2 g of 2-methacryloyloxypropyl phosphate and 1 g of di(hydroxyethyl acrylate) phosphate are added to the remaining second solution;
[0055] (6) successively adding 0.055g ferrous sulfate and 2.5g hydrogen peroxide (30%) to the material obtained in step (4), then adding dropwise the material obtained in step (5) and the third solution, whe...
Embodiment 3
[0057] (1) dissolving 180 g of VPEG-type monomer 4-hydroxybutyl vinyl polyoxyethylene ether with a number-average molecular weight of 3000 in 180 g of deionized water, and adjusting its temperature to 14 ° C to obtain the first solution;
[0058] (2) 20g of acrylic acid and 1.2g of mercaptoethanol are dissolved in 20g of deionized water, and then 8g of 30% sodium hydroxide solution is added for partial neutralization to obtain the second solution;
[0059] (3) 0.5g sodium hypophosphite is dissolved in 30g deionized water to obtain the third solution;
[0060] (4) drip 15g of the second solution into the first solution, and keep the temperature at 14°C;
[0061] (5) adding acryloyloxyethyl phosphate 3g and phosphoric acid di(hydroxyethyl acrylate) 1.2g to the remaining second solution;
[0062] (6) 0.045g ferrous sulfate and 2.0g sodium persulfate are successively added in the material of step (4) gained, then dropwise the material of step (5) gained and the third solution, wh...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com