Use of xanthohumol in prevention and treatment of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome
A technology for acute respiratory distress and acute lung injury, applied in the field of medicine, can solve the problems of reducing mortality and complicated pathogenesis, and achieve the effect of obvious clinical symptoms, good therapeutic effect and high cure rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment example 1
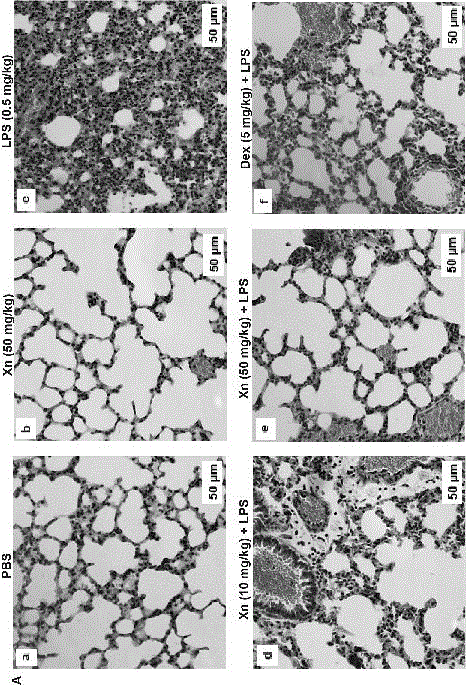
[0033] Therapeutic effect of xanthohumol on mice with acute lung injury in vivo
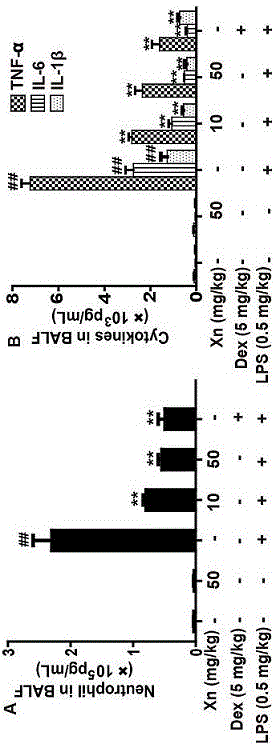
[0034] Establishment of acute lung injury model in mice: 60 male C57 / B mice (6-8 weeks old, 18-20g) were randomly divided into 6 groups, 10 mice in each group: blank group, LPS (0.5 mg / kg) group, Xanthohumol administration group (50 mg / kg), xanthohumol (10, 50 mg / kg) + LPS group, dexamethasone (5 mg / kg) + LPS group were used as positive control groups. Operation method: First, dilute xanthohumol and dexamethasone with normal saline and intraperitoneally inject mice, and the blank group and LPS group intraperitoneally inject equal volumes of normal saline. One hour after administration, LPS nasal instillation was used to establish the model, and mice in the blank group and xanthohumol-administered group were instilled with equal volumes of normal saline in the nasal cavity. After 12 hours of LPS instillation, the mice were sacrificed, and the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and lung tissues o...
experiment example 2
[0038] In vitro anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities of xanthohumol and regulation of signaling pathways
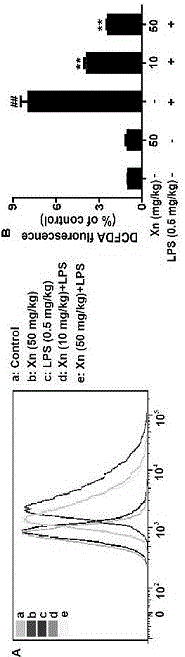
[0039] Cell model establishment: the RAW 264.7 cells in the logarithmic growth phase were plated in a 96-well culture plate, and after 24 hours of culture, different concentrations of xanthohumol were added for 1 hour, and then LPS (1 μg / ml) was given for 24 hours. MTT was used to detect cytotoxicity; cells were plated in 24-well culture plates, and the treatment method was the same as above. (a) collected supernatants for ELISA to detect cytokines, collected cells for Western Bloting to detect the expression levels of iNOS, COX-2 and HMGB1; (b) prepared DCFH-DA (final concentration: 10 μM) was added to each well, placed in a 37 °C incubator for 30 min to detect ROS products.
[0040] The cells were spread in a 6-well culture plate, and after 24 hours of culture, they were treated with different concentrations of xanthohumol for 18 hours or treated with xanthohumo...
experiment example 3
[0044] Mechanisms of anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects in vivo and in vitro
[0045] Establishment of acute lung injury model in vivo: In order to further explore the protective mechanism of xanthohumol on LPS-induced acute lung injury, wild-type (WT) and Nrf2 knockout (Nrf2 - / - ) mice to construct an LPS-induced mouse acute lung injury model (the modeling method is the same as above), and the lung tissue and alveolar lavage fluid (BALF) of the mice were collected for the following related experiments.
[0046] Experimental results: The protective mechanism of xanthohumol on mice with acute lung injury is as follows: Figure 7-10, xanthohumol significantly inhibited oxidative stress-induced Txinp activation and Trx-1 depletion, inhibited NLRP3 inflammasome and NF-κB inflammatory signaling pathways; significantly activated Nrf2, AMPK and GSK3β; significantly inhibited TNF-α, IL -6, IL-1β and ROS production, but in Nrf2 - / - Attenuated inhibition in mice; Nrf2 - / - In m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com