Indel Molecular Marker for Identification of Watermelon Seed Coat Color and Its Primers and Applications
A molecular marker and watermelon technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems that the color of the green seed coat has no effect, and the position and effect of a single gene cannot be determined, so as to speed up cloning and functional verification, improve selection efficiency and accuracy, and speed up The effect of the breeding process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] The development method of the InDel molecular marker for identifying the color of the watermelon seed coat, the specific steps are as follows:
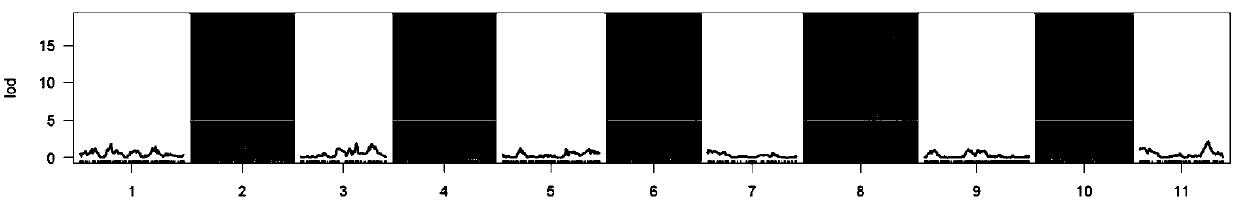
[0034] (1) Genome-wide QTL mapping for watermelon seed coat color
[0035] F obtained by crossing the female parent "ZXG01478" (jute: yellow seed coat background color, taupe-brown spots) and the male parent "14CB11" (black: black seed coat background color, no cover stripes) 2 The population has constructed a high-density genetic linkage map (Shanget al., 2016), and the parents, F 1 and F 2 Intuitive identification of seed coat color of 93 single melon seeds from the population; Combining genetic linkage map and F 2 The results of population phenotype identification, using the Rqtl-IM-binary method (Yandel et al., 2007) for initial QTL mapping ( figure 1 ), only one major QTL (sc8) for seed coat color was identified in LG8, its peak LOD was 17, which explained 90% of the phenotypic variation, and the corresponding confidenc...
Embodiment 2
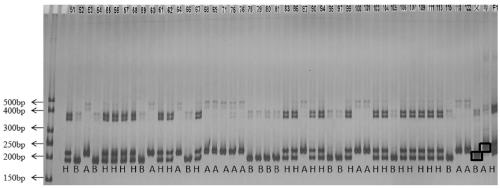
[0041] Watermelon F 2 Population molecular marker analysis, comprising the following steps:
[0042] (1) Utilize the CTAB method to extract the total DNA of leaves, the specific steps are as follows:
[0043] ①Put 1g of fresh leaves into a mortar, add liquid nitrogen to grind into powder, then transfer to a centrifuge tube with 1ml of CTAB extraction solution, mix the two thoroughly, and then place them in a constant temperature water bath at 65°C for 60 minutes, during which time they are mixed upside down 2-3 times;
[0044] ②After taking it out from the water bath, centrifuge at 8000rpm for 1min;
[0045] ③Take the supernatant and put it in another centrifuge tube, add an equal volume of chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (24:1, V / V), invert gently to mix well;
[0046] ④Centrifuge at 10000rpm for 5min, take the supernatant (try not to get the middle sediment);
[0047] ⑤ Add 0.7 times the volume of isopropanol (need to pre-cool for 30 minutes in advance), mix well and freeze at ...
Embodiment 3
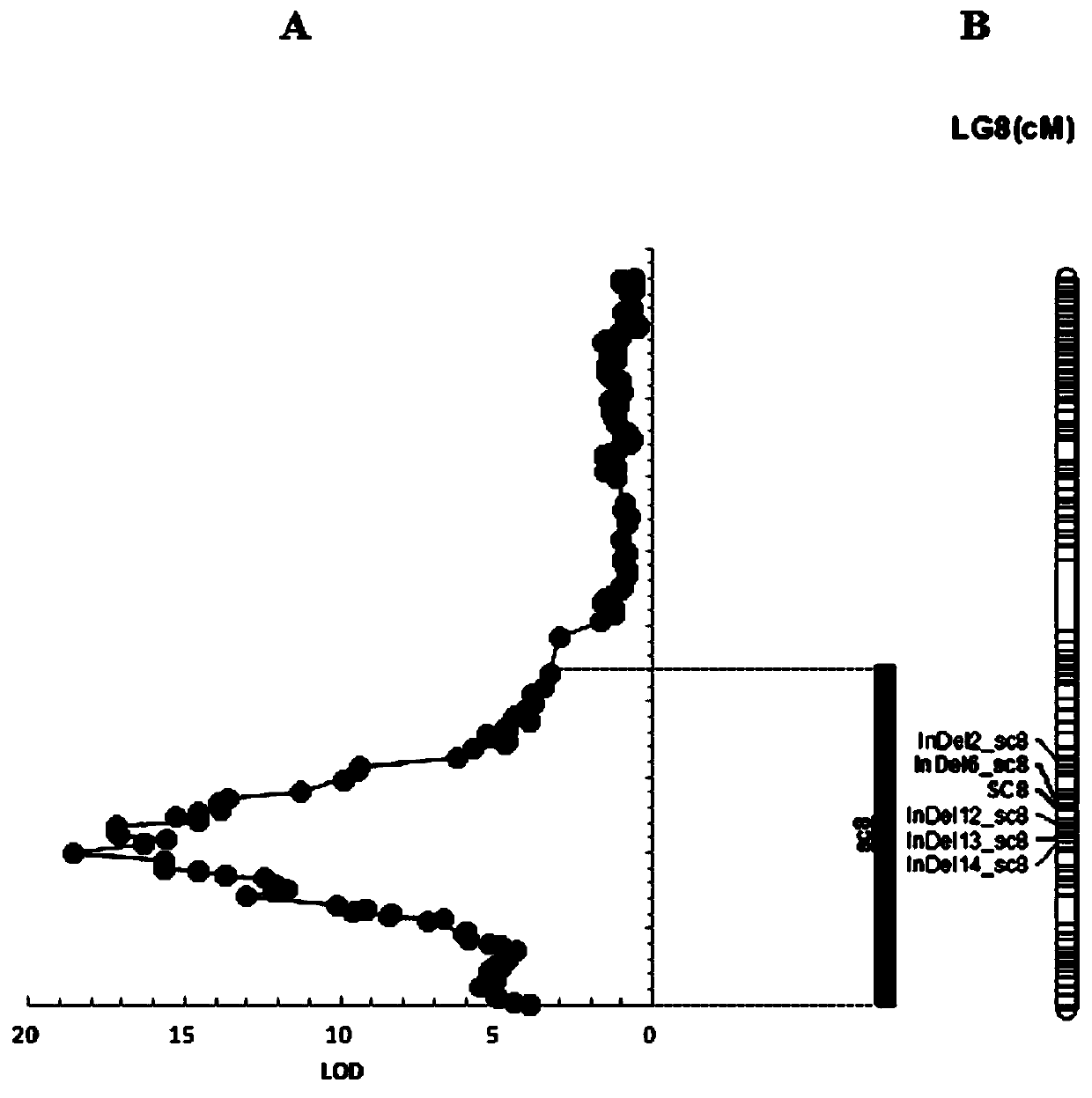
[0084] f 2 The reconstruction of population genetic linkage map, the steps are as follows: First, use the testa color morphological marker (SC8), the newly developed InDel marker and other SNP markers on LG8 to conduct linkage analysis with Joinmap4.0 software, and find that SC8 is located in the main QTL sc8 The confidence interval of , and it is relatively close to the QTL peak position, the genetic distance between InDel6_sc8 and SC8, one of the newly developed markers, is very close, only 1cM ( figure 2 ). So far, we have developed the co-dominant molecular marker InDel6_sc8 that is most closely linked to the testa color QTL (sc8), which corresponds to a 17bp indel at 22640623bp on chromosome 8, its sequence is ATATGAGCCCGTAGAGG, and its primer sequence is, InDel6_sc8F: AAATCACAGTAATAGAATGCTT ; InDel6_sc8R:TTAGAAGCTACACTCGTCCT. The amplified product of this primer in the female parent (jute) is 197bp, and the amplified product in the male parent (black) is 180bp. The ge...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com