Hybridoma cell lines (my-c-cc0c2-259-1 a4) and use thereof for producing a monoclonal antibody against human cardiac myosin binding protein c (c-protein, mybpc3, cmybp-c or my-c)
A hybridoma cell line and monoclonal antibody technology, applied in the direction of anti-animal/human immunoglobulin, immunoglobulin, fusion cells, etc., can solve problems such as cardiac troponin deficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Preparation of hybridoma cell lines
[0025] Spleens from mice immunized with cCOC2 of My-C in a known manner were removed under aseptic conditions using RPMI 1640 medium (Life Technologies TM , Karlsruhe) flushed and diluted the splenocytes from the splenic capsule using a syringe. Splenocytes were pelleted (10 minutes, 300xg), washed three times with RPMI 1640 medium, and resuspended in RPMI 1640 medium. Then, it was fused with the myeloma cell line P3X63Ag8.653 (ATTC CPL 1580). For this purpose, cultured myeloma cells in log phase of growth were likewise pelleted and washed three times. Will 1x 10 8 Splenocytes and 5x 10 7 Myeloma cells were pipetted into a centrifuge tube, mixed thoroughly and centrifuged, and the centrifuge tube was rotated continuously at 37°C, and 1.5ml of preheated 50% polyethylene glycol 1500 (Roche, Basel) was added dropwise within one minute. in the cell pellet. The fusion reaction was then incubated at 37°C for an additional minute. P...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Selection of antibody-producing clones
[0028] All growing clones or their antibodies were tested for reactivity by ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay). The immunosorbent used was the immunogen, recombinant cCOC2 domain of My-C (approximately 2 μg / ml). ELISA protocol:
[0029] 1. Coat a microtiter plate (Costar, high binding capacity) with 50 μl of immunogen solution per well overnight at 4°C;
[0030] 2. Wash the microtiter plate (MTP), wash 3 times with TBS (TRIS-buffered saline) pH 7.4;
[0031] 3. Block MTP, 200 μl blocking agent (Boehringer, Mannheim) per well, 37°C, 1 hour;
[0032] 4. Wash MTP, wash 3 times with NaCl-Tween 20;
[0033] 5. Use the hybridoma culture supernatant to incubate; 50 μl per well, dilute about 1:2 with TBS-Tween 20;
[0034] 6. Wash MTP, wash 3 times with NaCl-Tween 20;
[0035]7. Incubate with peroxycyclase-coupled anti-mouse Ig antibody, 50 μl per well, at room temperature for 1 hour;
[0036] 8. Wash MTP, wash 3 times with...
Embodiment 3
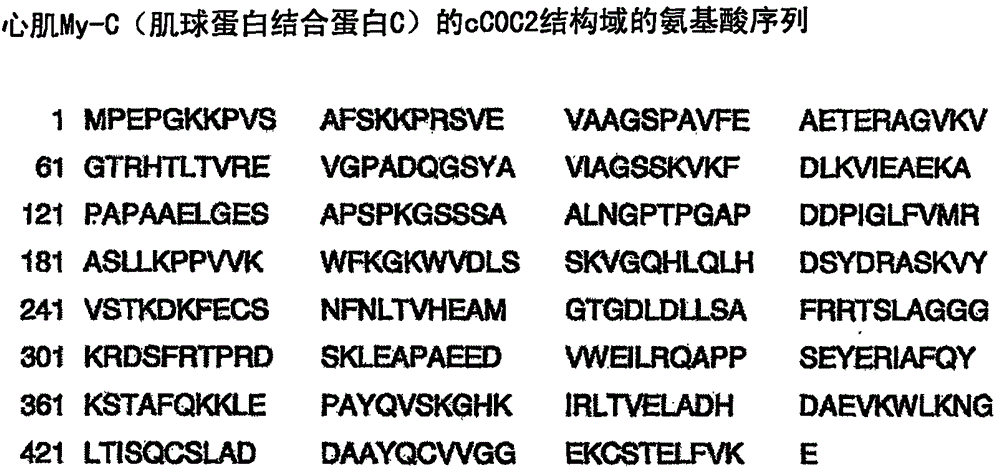
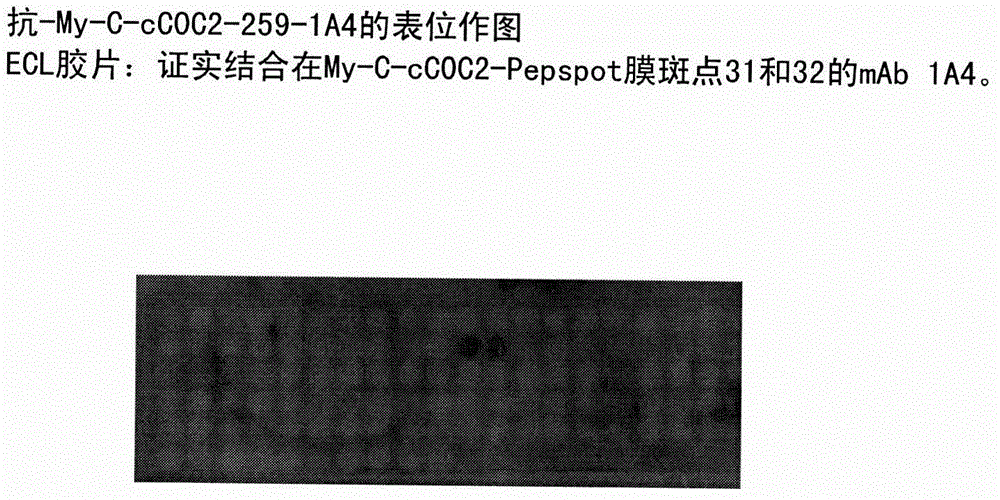
[0040] Epitope mapping of monoclonal antibody 1A4 in human cardiac-specific My-C
[0041] Identification of the binding site of mAb 1A4 using a peptide scanning method. To this end, the entire amino acid sequence of the human cCOC2 domain of My-C used for immunization was divided into a total of 111 mutually overlapping amino acid sequences with a length of 15 amino acids. These sequences were synthesized directly on cellulose membranes as individual peptides in spots. The membranes were incubated with antibody-containing hybridoma culture supernatants, and antibody binding sites were visualized by incubation with peroxidase-conjugated anti-mouse Ig antibodies. For this, after three washes with TBS-Tween, the membrane was placed between replica films and then exposed to ECL TM (enhanced chemiluminescence) detection reagent (Amersham, Braunschweig) was incubated for 3 minutes. The film (Hyperfilm-ECL) that will be placed next TM [RPN 2103 HAmersham, Braunschweig]) exposure ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com