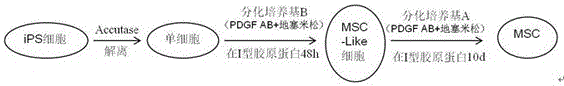Method for differentiating induced pluripotent stem cells into mesenchymal stem cells
A technology for pluripotent stem cells and pluripotent stem cells, which can be applied to artificially induced pluripotent cells, biochemical equipment and methods, animal cells, etc., and can solve the problems of long induction time, low induction efficiency, and complicated induction process.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Example 1 Inducing the differentiation of human iPSCs into MSCs
[0048] 1. Culture of human iPS cells
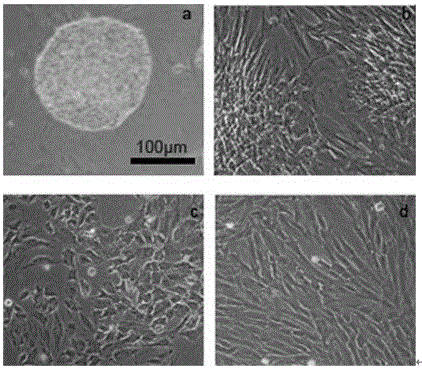
[0049] In this example, the human iPS cells (DYR0100, Cell Bank of Chinese Academy of Sciences) used were cultured on Matrigel (BD, 354277), and maintained with mTeSRTM1 (STEMCELL TECHNOLOGIES, 05850), such as figure 2 as shown in a. The specific cultivation method includes the following steps:
[0050] ①Take out the culture medium and required reagents from the refrigerator, and preheat them in a 37°C water bath for about 15 minutes;
[0051] ② Take out the cells, discard the original medium, and wash the cells once with DPBS (no calcium, no magnesium) (Invitrogen, 14190250);
[0052] ③ Add 1 mg / ml collagenase IV (dissolved in HBSS buffer, sterilized by 0.22 μm filter) (Invitrogen17104019) for digestion, place in a 37°C cell culture incubator and incubate for about 5 minutes, observe under a microscope, the edges of the clones have not rolled up yet Terminate ...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Example 2 Detection of differentiation of human iPS cells into mesenchymal cells
[0065] (1) Expression of related genes during induction and differentiation
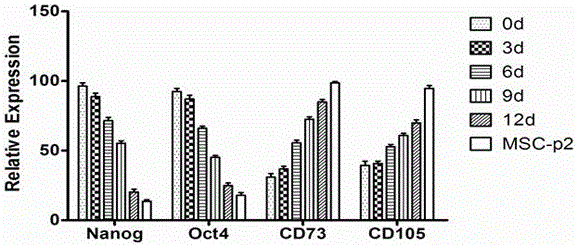
[0066] Trizol (Invitrogen) method was used to extract the total RNA of iPS-induced 0, 3, 6, 9, 12d cells and iPS-MSC-P2,
[0067] The M-MLV first-strand synthesis system (Invitrogen) was used to reverse transcribe into cDNA and SYBR Premix Ex Taq (Takara) for Realtime PCR to detect the expression of Nanog, Oct4, CD73, CD105 and the internal reference gene actin ( image 3 ). With the prolongation of induction time, the expression levels of pluripotency genes Nanog and Oct4 decreased, while the expression levels of CD73 and CD105 gradually increased. MSC-P2 only expressed a small amount of Nnaog and Oct4, while CD73 and CD105 were almost 100% expressed.
[0068] (2) MSC Surface Marker Identification
[0069] Digest the obtained MSC cells (P2) into a single cell suspension, add fluorescently labeled mouse anti-...
Embodiment 3
[0070] Example 3 Determination of the growth curve of MSC differentiated from human iPS cells
[0071] MSCs (P5) differentiated from human iPS cells were digested into a single cell suspension, counted and spread in 24-well cells at a density of 5×103 / cm2 for culture, and cells were counted in 3 wells every day after inoculation. Figure 5 It can be seen that the MSCs differentiated from human iPS cells grow in an "S" shape during the culture process, the logarithmic growth phase is 2-5 days, and enter the plateau phase on the 6th day. Can self-renew and proliferate well.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com