Infrared dim small target detection method based on first-order partial derivatives in multiple directions
A technology of weak and small targets and detection methods, applied in image data processing, instruments, calculations, etc., can solve the problems of sensor noise non-uniformity interference, high false alarm rate, cluttered and strong edges, etc., to achieve broad market prospects and application value, The effect of improving detection accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0046] In order to better understand the technical solutions of the present invention, the implementation manners of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
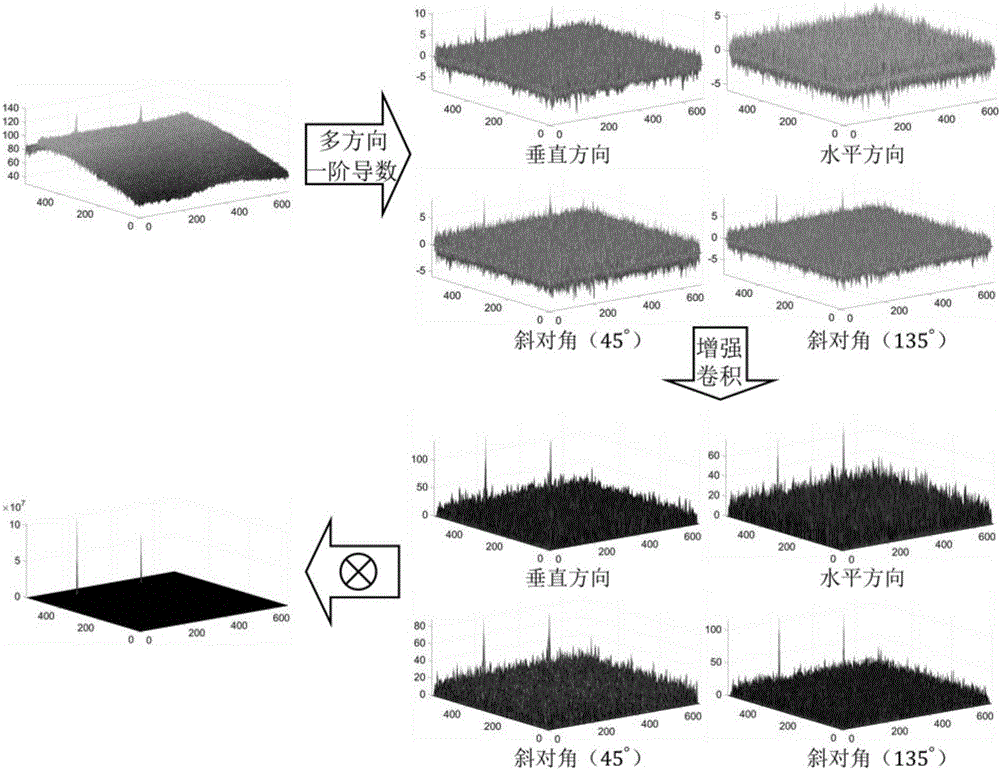
[0047] The present invention is a detection method of small and weak infrared targets using multi-direction first-order partial derivatives. The principle block diagram is as follows: figure 1 As shown, the specific implementation steps are as follows:
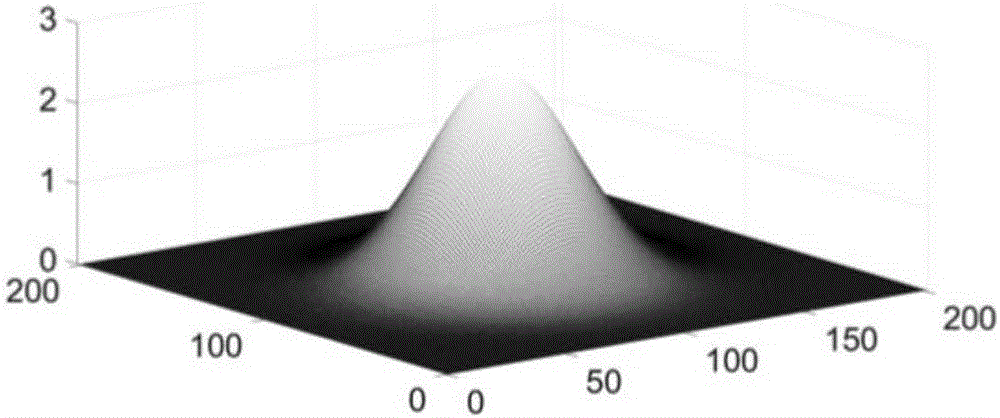
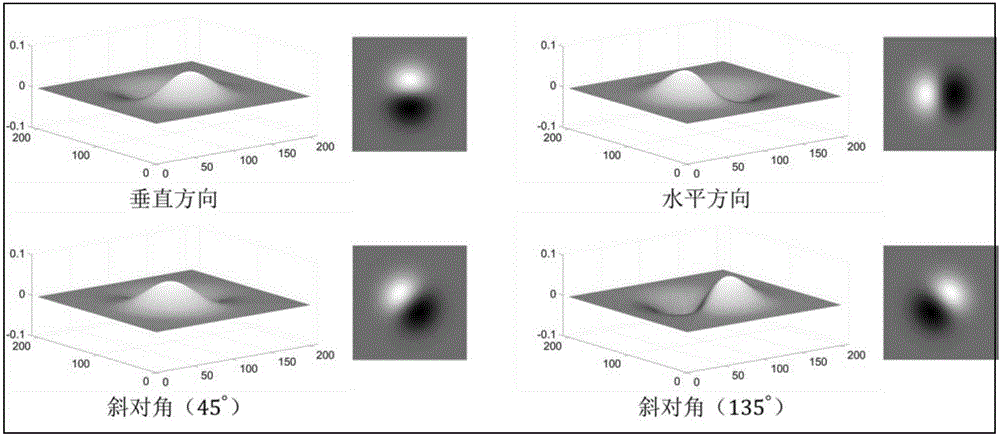
[0048] Step 1: Use the facet model to construct a bivariate cubic function of image grayscale in a small range, solve the first-order partial derivatives in each direction in the central area, and design the convolution template of the required coefficients. Each operation coefficient can be directly obtained from the volume obtained from the accumulated image.
[0049] The facet model uses least squares to fit polynomial equations in a small range, transforming discrete gray values into continuous function...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com