Superconducting nanowire single-photon detector with suppressed polarization sensitivity
A single-photon detector and superconducting nanowire technology, which is applied in the field of light detection, can solve the problems of low absorption efficiency, influence of absorption efficiency, and high polarization sensitivity, so as to avoid the influence of absorption efficiency, avoid long-distance focusing, and reduce polarization Correlation Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
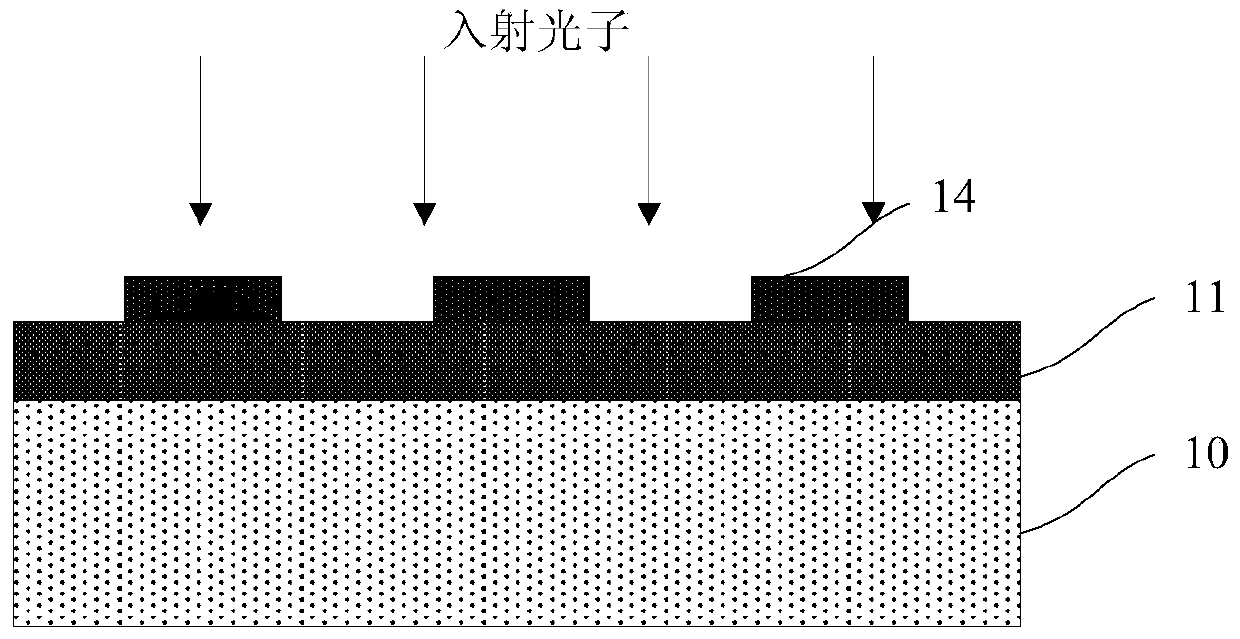
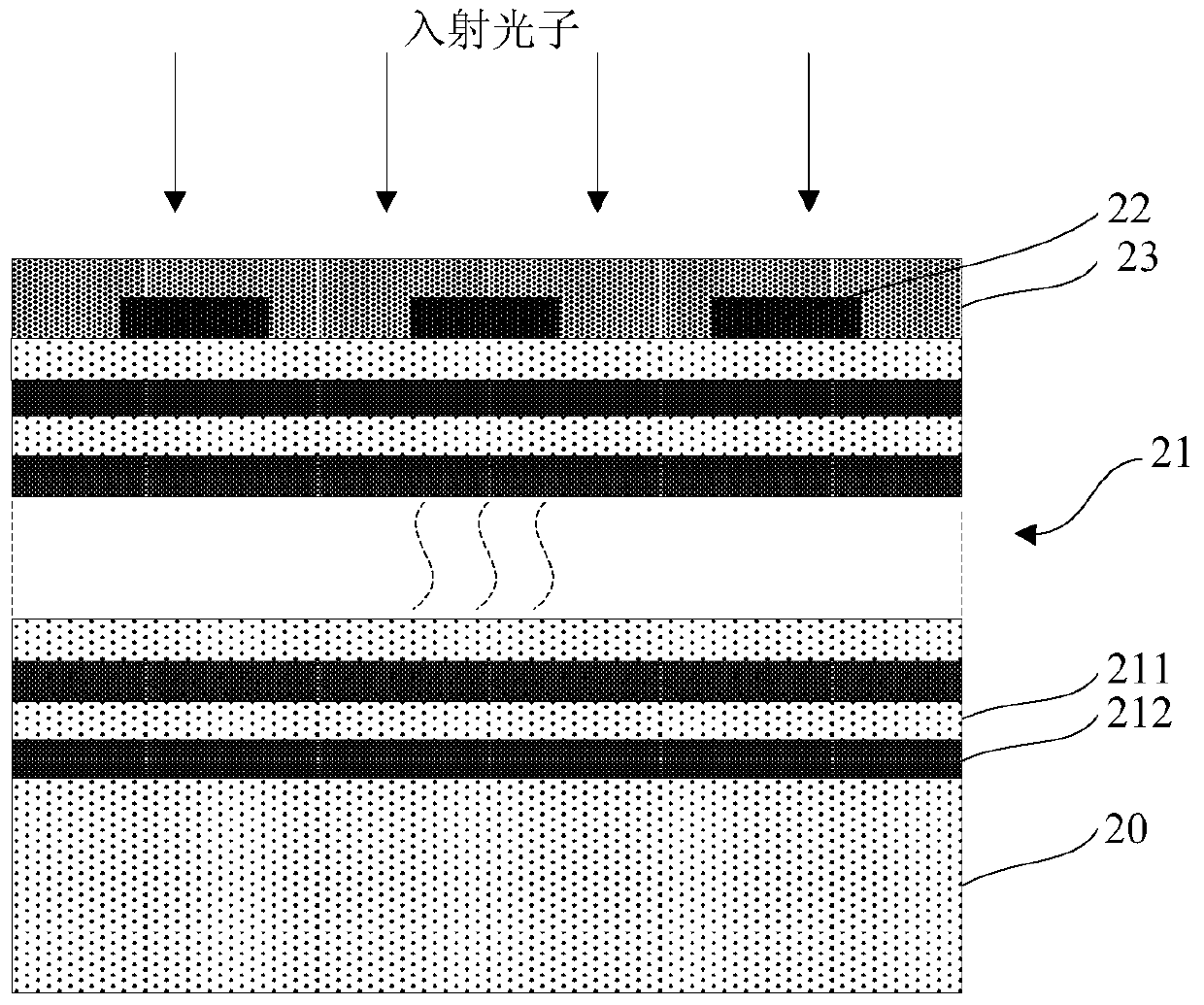
[0048] Such as image 3 As shown, the present embodiment provides a superconducting nanowire single photon detector that suppresses polarization sensitivity, including:
[0049] substrate 20;
[0050] A high reflection film 21 located on the surface of the substrate 20;
[0051] Superconducting nanowires 22, located on the surface of the high reflection film 21;
[0052] The dielectric layer 23 is located on the surface of the high reflection film 21 and covers the superconducting nanowires 22, and is suitable for reducing the polarization sensitivity of the superconducting nanowires 22 to light absorption.
[0053] As an example, the superconducting nanowire single photon detector with suppressed polarization sensitivity in this embodiment is a superconducting nanowire single photon detector with a front incident structure.
[0054] As an example, the substrate 20 includes a silicon substrate, an MgO substrate or a sapphire substrate, and the thickness of the substrate 20 is...
Embodiment 2
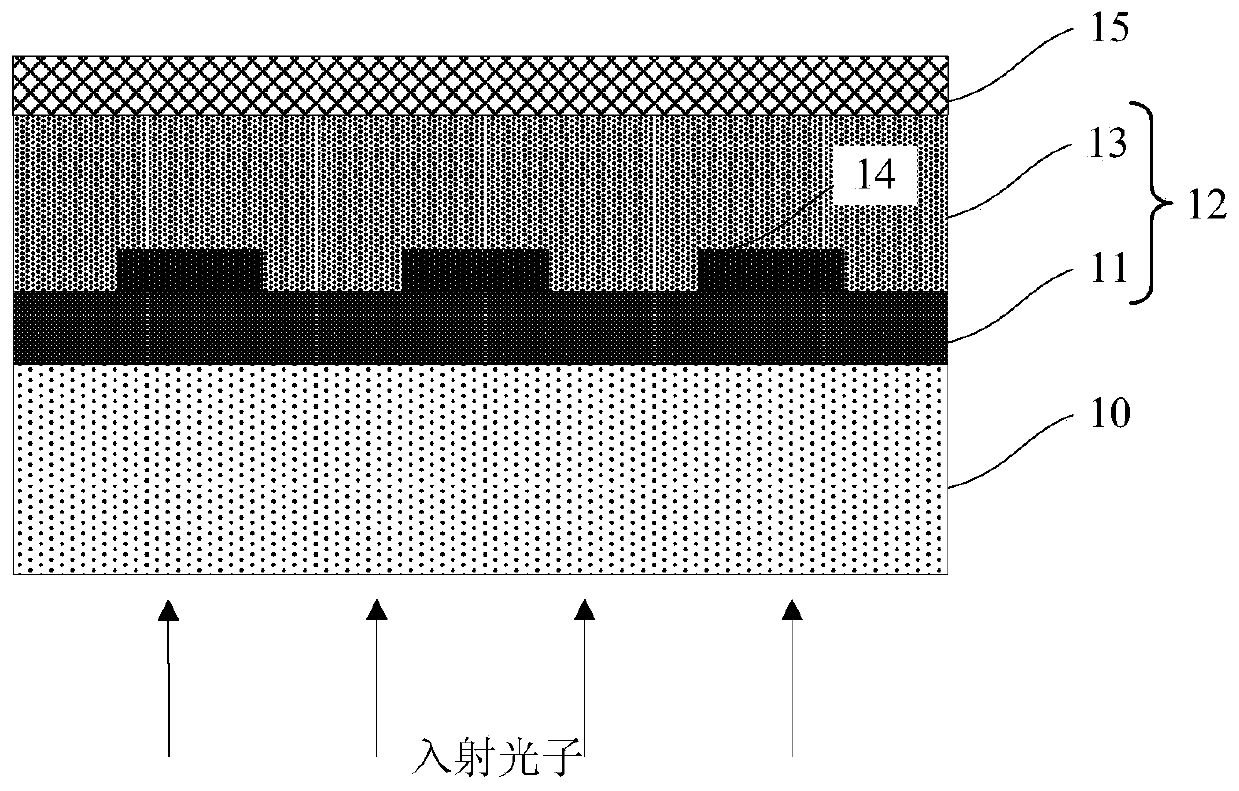
[0063] Such as Figure 4 As shown, this embodiment also provides a superconducting nanowire single-photon detector that suppresses polarization sensitivity. In this embodiment, the basic structure of the superconducting nanowire single-photon detector that suppresses polarization sensitivity is basically the same as in Embodiment 1. , the difference between the two is that the high reflection film 21 in the first embodiment is alternately stacked SiO 2 thin film layer 211 and Si thin film layer 212; and the high reflection film 21 described in this embodiment is alternately stacked SiO 2 Thin film layer 211 with TiO 2 Thin film layer 213 . The high reflection film 21 can be the SiO 2 The thin film layer 211 is located on the surface of the substrate 20, the TiO 2 Thin film layer 213 is located on the SiO 2 Above the thin film layer 211; also can be as Figure 4 As shown in the TiO 2 The thin film layer 213 is located on the surface of the substrate 20, the SiO 2 Thin f...
Embodiment 3
[0065] Such as Figure 5 As shown, this embodiment provides a superconducting nanowire single-photon detector that suppresses polarization sensitivity. The basic structure of the superconducting nanowire single-photon detector that suppresses polarization sensitivity is basically the same as in Embodiment 1. The difference between the two is that the high reflection film 21 described in the first embodiment is alternately stacked SiO 2 thin film layer 211 and Si thin film layer 212; and the high reflection film 21 described in this embodiment is alternately stacked SiO 2 Thin film layer 211 and Ta 2 o 5 film layer 214 . The high reflection film 21 can be the SiO 2 The thin film layer 211 is located on the surface of the substrate 20, the Ta 2 o 5 Thin film layer 214 is located on the SiO 2 Above the thin film layer 211; also can be as Figure 5 Ta 2 o 5 The thin film layer 214 is located on the surface of the substrate 20, the SiO 2 Thin film layer 211 is located on...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com