Adaptive biasing radio frequency power amplifier
A technology of adaptive bias and RF power, applied in the direction of power amplifiers, RF amplifiers, amplifiers, etc., to achieve the effects of reducing on-resistance and on-voltage drop, reducing phase distortion, and increasing output power
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
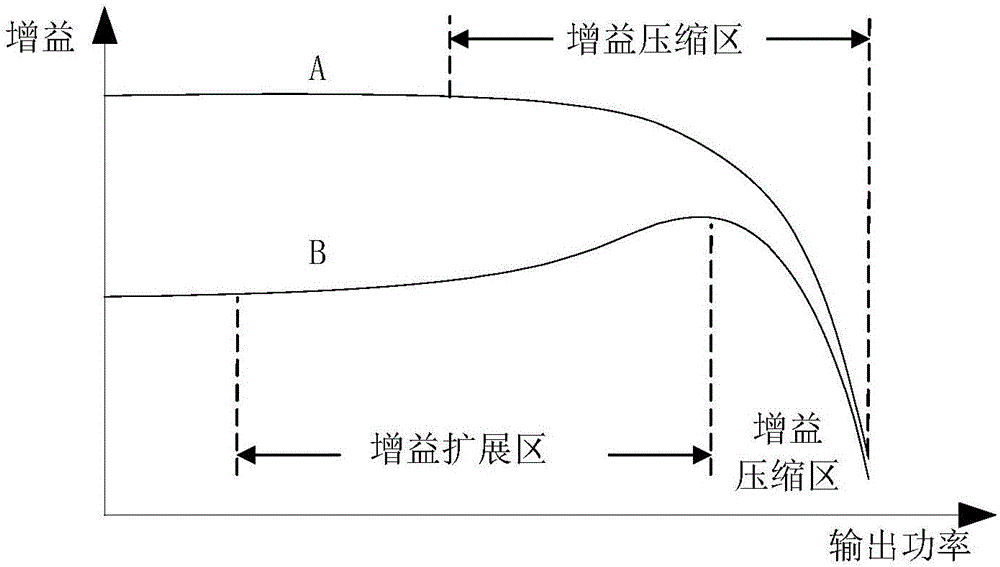
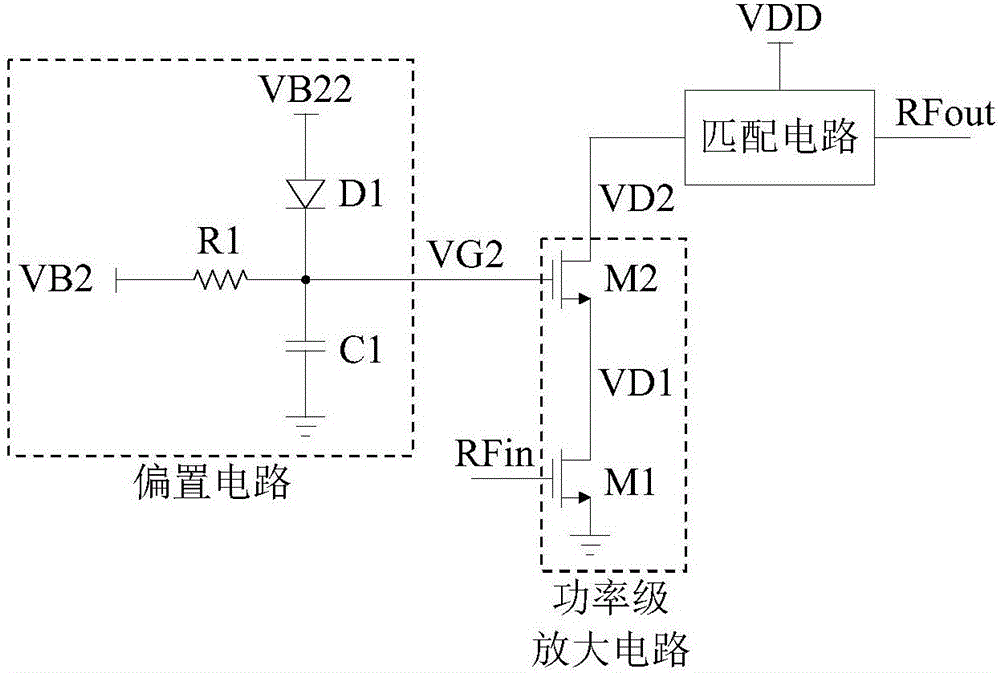
[0030] see image 3 , which is Embodiment 1 of the radio frequency power amplifier provided in this application. The radio frequency power amplifier includes a bias circuit and a power stage amplifying circuit. For clarity, image 3 The matching circuit is also schematically shown in .
[0031] The bias circuit includes a resistor R1, a diode D1 and a capacitor C1, which are used to provide a dynamic bias voltage for the transistor M2 in the power stage amplifier circuit. The working voltage VB2 is connected to one end of the resistor R1, and the other end of the resistor R1 serves as the output terminal of the bias circuit to provide a dynamic bias voltage for the transistor M2. The dynamic bias voltage includes a static working voltage VB2 and a dynamic voltage generated by a dynamic current passing through the resistor R1, and the dynamic current refers to a DC component of the current flowing through the resistor R1. The gate voltage VG2 of the transistor 2 M2 is the c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com