Alkali-activated cementing material and preparation method thereof
A cementitious material, alkali-activated technology, applied in cement production, etc., can solve problems affecting the appearance of materials, adverse effects on construction, difficulties in surface plastering, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing frosting and ensuring strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0024] An embodiment of the present invention provides a method for preparing an alkali-activated gelling material, comprising the following steps:
[0025] (1) Weighing raw materials: the raw materials include powders, aqueous solutions of liquid activators and calcium-containing zeolites, wherein the powders are calcined bauxite dressing tailings and slag powder according to the mass ratio of 7-8 : 3-2 mixed, the aqueous solution of the liquid activator is Na 2 The mass of O is 4-5% of the mass of the powder, and the calcium-containing zeolite is 1-5% of the mass of the powder;
[0026] (2) mixing the raw materials to obtain the alkali-activated gelling material;
[0027] The mass ratio of water to solid raw materials in the raw materials is 0.4-0.5.
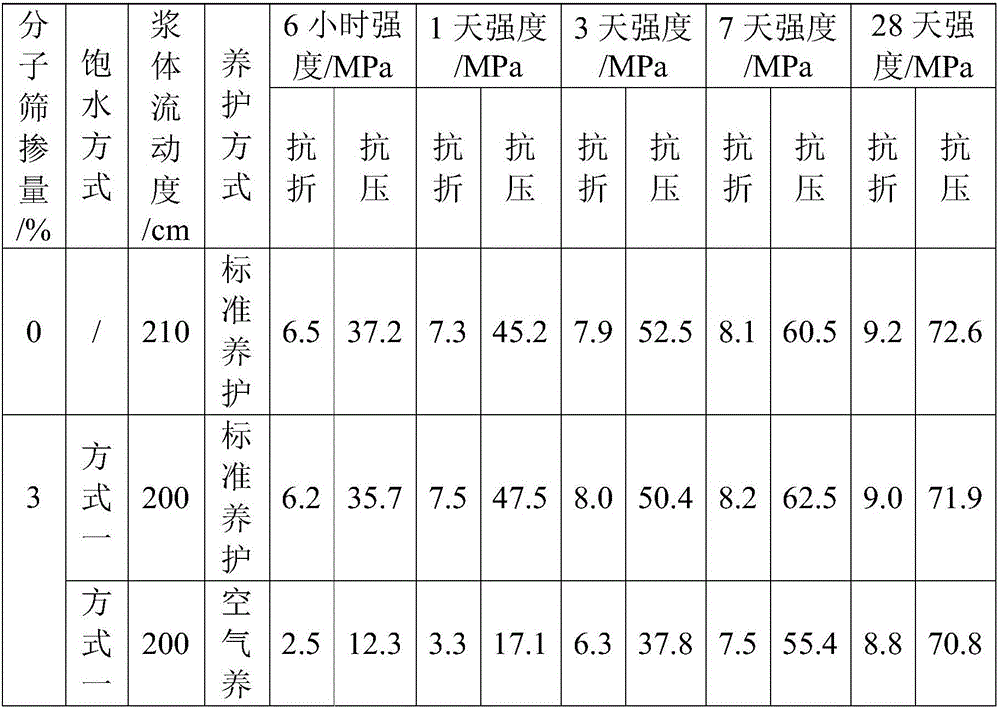
[0028] The above scheme can already complete the preparation of the alkali-activated gelling material. On this basis, the optimal scheme is given below, which has achieved the purpose of better and effectively inhibiting its...
Embodiment 1
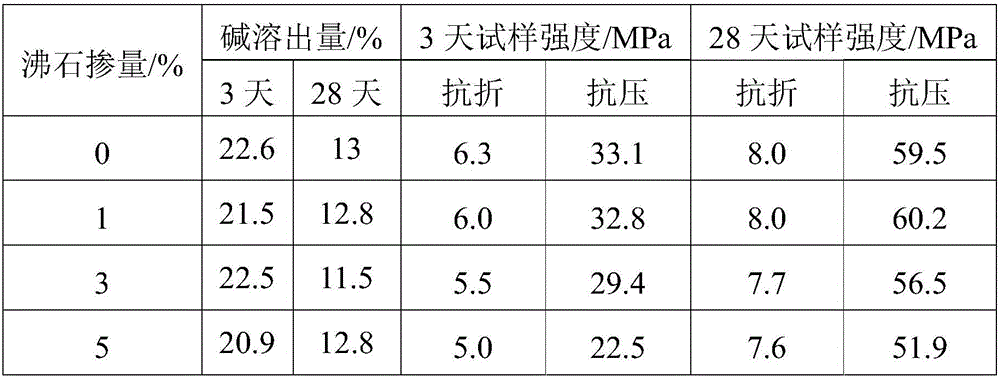
[0040] Table 1 shows the effect of synthetic zeolite (molecular sieve) and natural stilbite (a kind of sodium zeolite) on the alkali dissolution of alkali-activated gelling materials. In the cementitious material, the powder is composed of 80% tailings+20% slag powder, and the quality of water glass is 5% of the powder quality (in terms of Na 2 In terms of O, it accounts for the mass percentage of tailings and slag powder; the modulus is 2.2). The zeolite is mixed into the powder body composed of 80% tailings and 20% slag powder, and the dosage is 1%, 3%, 5%. The curing conditions of the samples are standard curing, that is, 95±5%RH, 20±2°C.
[0041] Table 1
[0042]
[0043] It can be seen from the results that the unmodified zeolite is rich in sodium ions, so its ability to exchange bases to excite sodium ions in the gelling material solution is limited. According to the existing research results, the ion exchange capacity of zeolite can only be released effectively in...
Embodiment 2
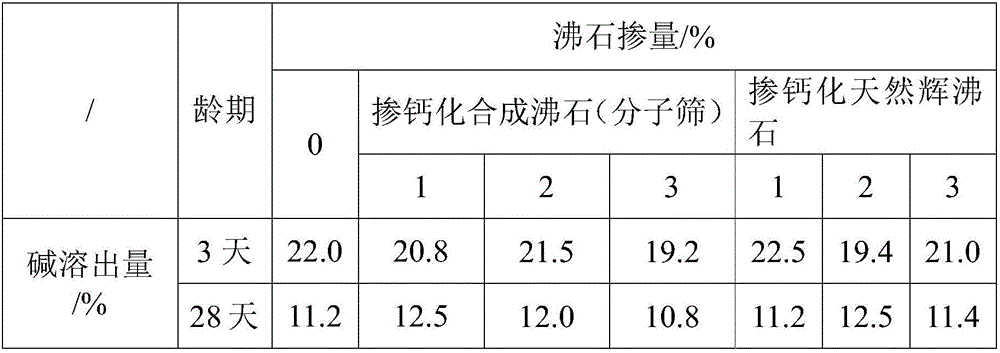
[0047] According to the results of Example 1, in order to use the ion exchange capacity of zeolite to achieve the purpose of bonding alkali to excite the alkali metal ions in the gelling material, the zeolite must be modified into a calcium type.
[0048] The modification method of zeolite is in 25% NH 4 In the boiling solution of Cl, it is modified into ammonium type zeolite, and the zeolite is modified at 2mol / LCaCl 2 Carry out ammonium-calcium exchange in hot solution (90° C.), and finally obtain calcium-type zeolite, which is dried for later use.
[0049] Table 2 shows the effect of calcified zeolite on alkali dissolution inhibition of alkali-activated gelling materials. The cementitious material proportioning is that the powder in the cementitious material is made up of 70% tailings+30% slag powder, and the quality of water glass is 4% of the powder mass (in the form of Na 2 In terms of O, it accounts for the mass percentage of tailings and slag powder; the modulus is 2...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com