Brown planthopper N1MLP gene, encoded protein and application of brown planthopper NIMLP
A technology of gene coding and brown planthopper, applied in application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve the problems of human and animal harm, environmental pollution, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing the use of pesticides, good application prospects, maintaining ecological balance and sustainable development
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
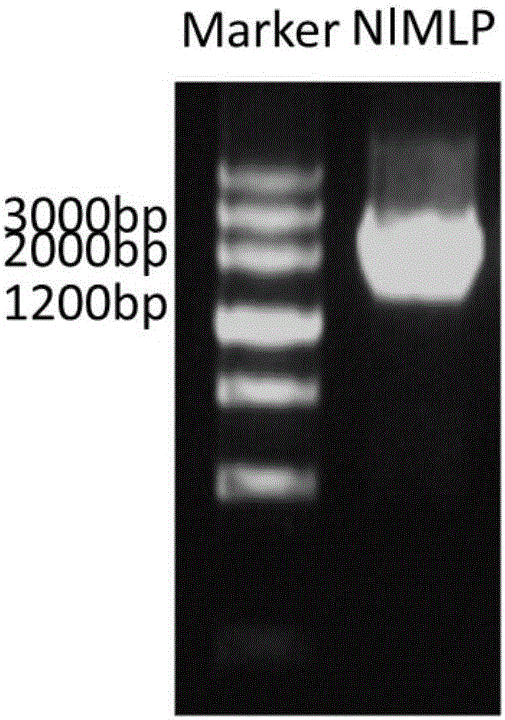
[0054] [Example 1] Cloning of the NlMLP gene of the brown planthopper
[0055] Total RNA was extracted from 20 brown planthoppers of biotype 1 and reversed to cDNA. Primers were designed based on this sequence, and the 5' and 3' end sequences of the candidate gene were obtained using TaKaRa's 5' and 3' FμL1 RACE kit, the transcription start site and termination site of the candidate gene were determined, and spliced The full-length cDNA sequence of the gene was obtained. Re-synthesize primers MLP-F, MLP-R according to the full-length cDNA sequence, amplify the full-length cDNA of N1MLP, predict ORF, and its ORF sequence is as shown in the sequence table SEQ ID NO.1 ( figure 1 ).
[0056] MLP-F: ATGAGGTGTTTCTCAGTTATCGC
[0057] MLP-R: TCAGTAGTATCCACCAAAAACCA
Embodiment 2
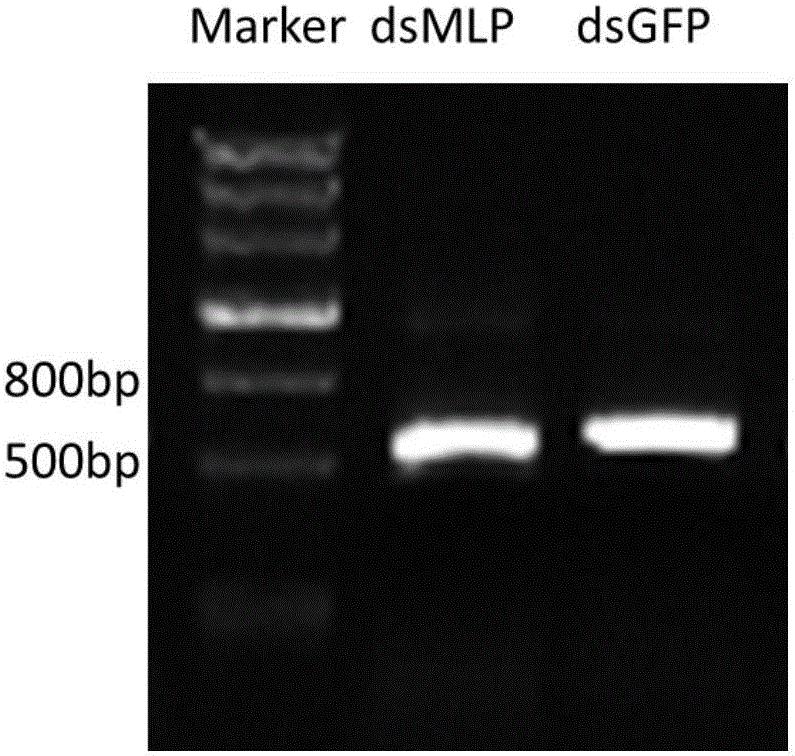
[0058] [Example 2] Preparation of the dsRNA (dsMLP) for silencing the NlMLP gene of the brown planthopper and the green fluorescent protein GFP gene dsGFP for the control
[0059] 1. Take the cDNA obtained in Example 1 as a template, and use MU-F and MU-R as primers to carry out PCR amplification to obtain a PCR amplification product.
[0060] MU-F (forward primer):
[0061] TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGA AGCCGATGTATTTCCTGTAGAT
[0062] MU-R (reverse primer):
[0063] TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGA CTACAGCAGTGTCTTCAGCCAG
[0064] The underlined region is the T7 RNA polymerase promoter sequence.
[0065] 2. Use the existing GFP-containing plasmid in the laboratory as a template, and use dsGFP-F and dsGFP-R as primers for PCR amplification to obtain PCR amplification products.
[0066] dsGFP-F (forward primer): TAATACGACTCACTATAGGG CGGACT
[0067] dsGFP-R (reverse primer): TAATACGACTCACTATAGGG CGATGC
[0068] The underlined region is the T7 RNA polymerase promoter sequence.
[...
Embodiment 3
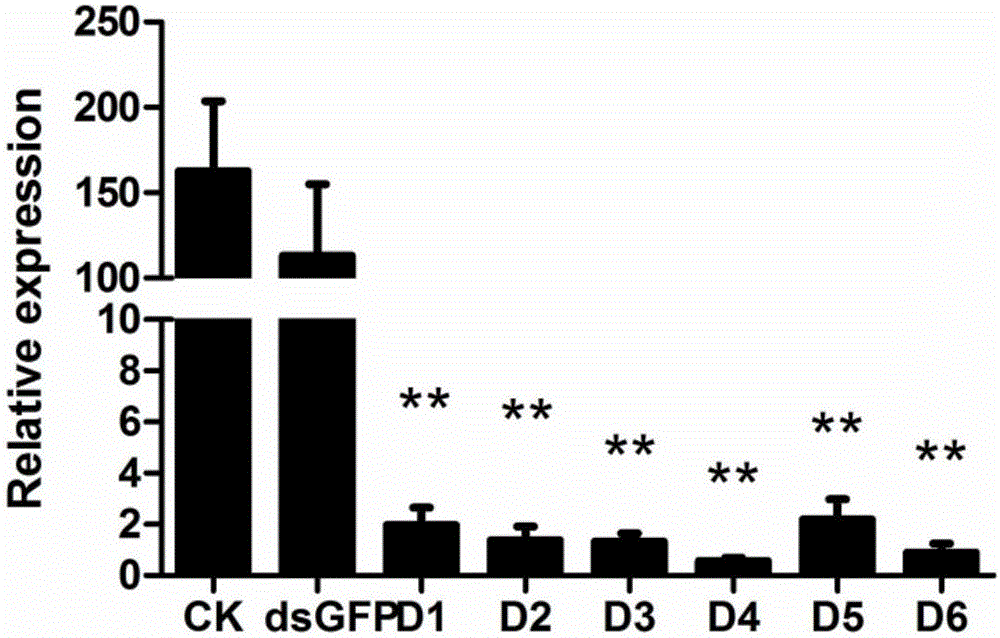
[0073] [Example 3] Microinjection and effect detection of dsMLP and dsRNA
[0074] 1. Preparation of brown planthopper: Take 30 females and 10 males in a cup with TN1 seedlings. After 24 hours, take out the adults. After hatching, it will be a fourth instar nymph after 20 days, and it will be used for injection.
[0075] 2. Plate preparation: Weigh 1.5g of agar powder and add it to 100ml of water, boil it, pour it into a glass plate, and wait for it to solidify for later use.
[0076] 3. Injection: Take 5-8 worms with similar growth in the test tube, and inject CO 2 Anesthetize for 20 seconds, do not blow on the insects when injecting CO2, to avoid collision damage caused by insects flying around. The worms were then poured onto a 1.5% agar powder plate with the abdomen facing up. Injection was performed with a Nanoliter 2010 microinjector according to the instructions. The injection site is between the front and middle chest. The injection volume was 46 nl (5 μg / μL).
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com