High voltage generator, X ray generation device and control method thereof
A high-voltage generator and X-ray tube technology, applied in the field of X-ray control, can solve the problem of high consistency requirements, and achieve the effect of improving adaptability, flexibility and diversity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
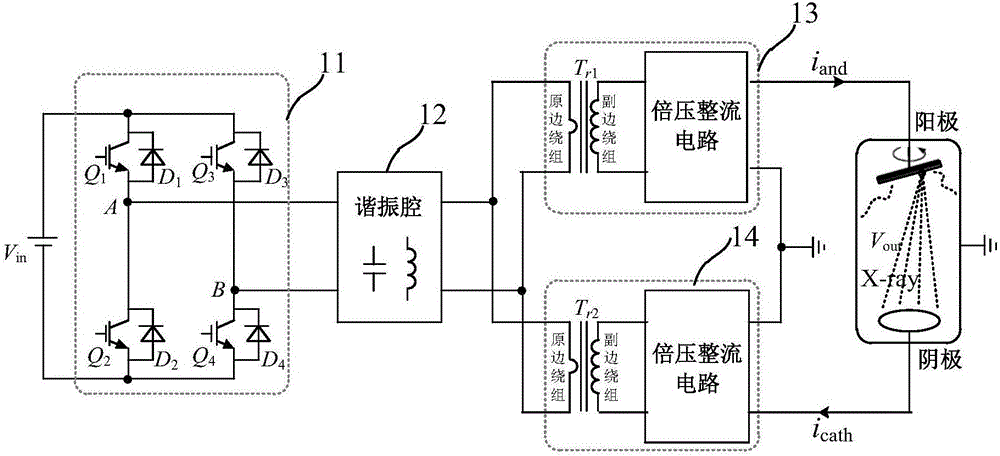
[0047] figure 2 It is a schematic diagram of the circuit structure of an X-ray high voltage generator according to an embodiment of the present invention. The high-voltage generator includes an inverter (circuit), a resonant cavity, a transformer, a voltage doubler rectifier circuit and control components.
[0048] The inverter circuit is composed of a first switching device Q1, a second switching device Q2, a third switching device Q3, a fourth switching device Q4, a first capacitor C1, and a second capacitor C2. Wherein, the first switching device Q1 and the second switching device Q2 are connected in series to form a first bridge arm (leading bridge arm) 21; the third switching device Q3 and the fourth switching device Q4 are connected in series to form a second bridge arm (lag bridge arm) 22; The first capacitor C1 and the second capacitor C2 are connected in series to form a third bridge arm (common bridge arm), and the third bridge arm is arranged between the first bri...
Embodiment 2
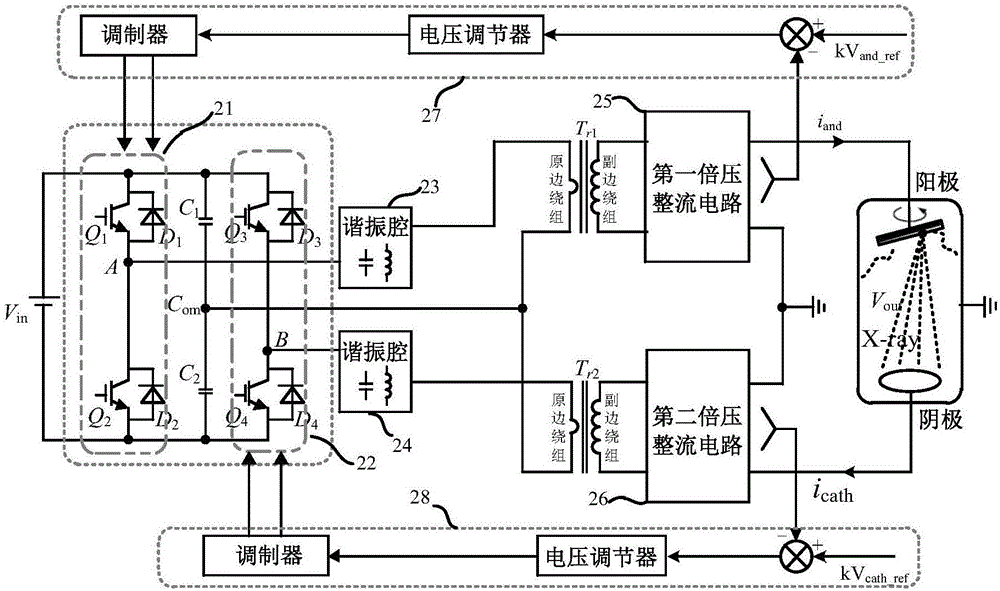
[0067] The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment lies in that the third bridge arm includes active devices. Such as image 3 Shown is the schematic diagram of the circuit structure of the X-ray high voltage generator of the second embodiment, the third bridge arm (common bridge arm) of the inverter circuit includes the fifth switching device Q5 and the sixth switching device Q6 connected in series, in the fifth switch A reverse diode D5 is connected in parallel at both ends of the device Q5, a reverse diode D6 is connected in parallel at both ends of the sixth switching device Q6, and the midpoint Com of the third bridge arm is electrically connected to the transformer T r output terminal of the primary winding. The modulator contained in the first control component 37 is a PWM modulator, and the modulator contained in the second control component 38 is a PWM modulator. It should be noted that the transformer used in this embodiment is a transformer wit...
Embodiment 3
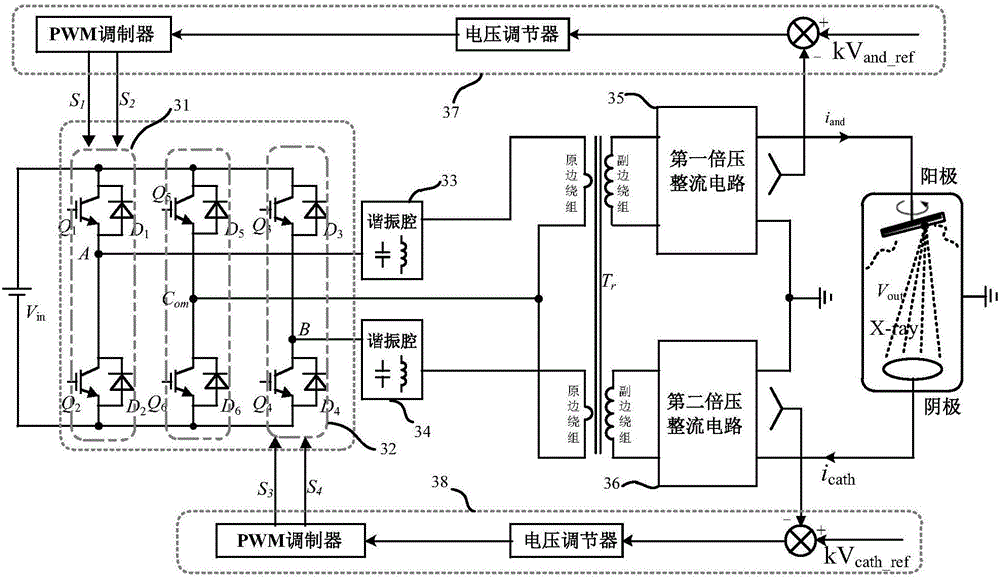
[0083] The difference between this embodiment and the second embodiment lies in the control mode of each switching device in the inverter circuit. Such as Figure 5 As shown, the modulator contained in the first control component 57 is a PFM modulator, the modulator contained in the second control component 58 is a PWM modulator, and a frequency synchronization circuit 59 is connected between the PFM modulator and the PWM modulator. The PFM modulator connects the base poles of the switching devices in the first bridge arm 51 and the third bridge arm simultaneously, and performs PFM modulation on the first bridge arm 51 and the third bridge arm; the PWM modulator connects the switching devices in the second bridge arm 52 The base is used to perform PWM modulation on the second bridge arm 51 , and the frequency synchronization circuit 59 adjusts the adjustment frequency or operating frequency of the PWM modulator and the PFM modulator to be the same.
[0084] The anode inverter...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com