Modification method of proton exchange membrane for all-vanadium redox flow battery
A technology of all-vanadium redox flow battery and proton exchange membrane, which is applied in fuel cells, regenerative fuel cells, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of poor vanadium resistance performance and affect the electrochemical performance of all-vanadium redox flow battery, etc., and achieve good combination , vanadium ion permeability decreased, the effect of improving the overall performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
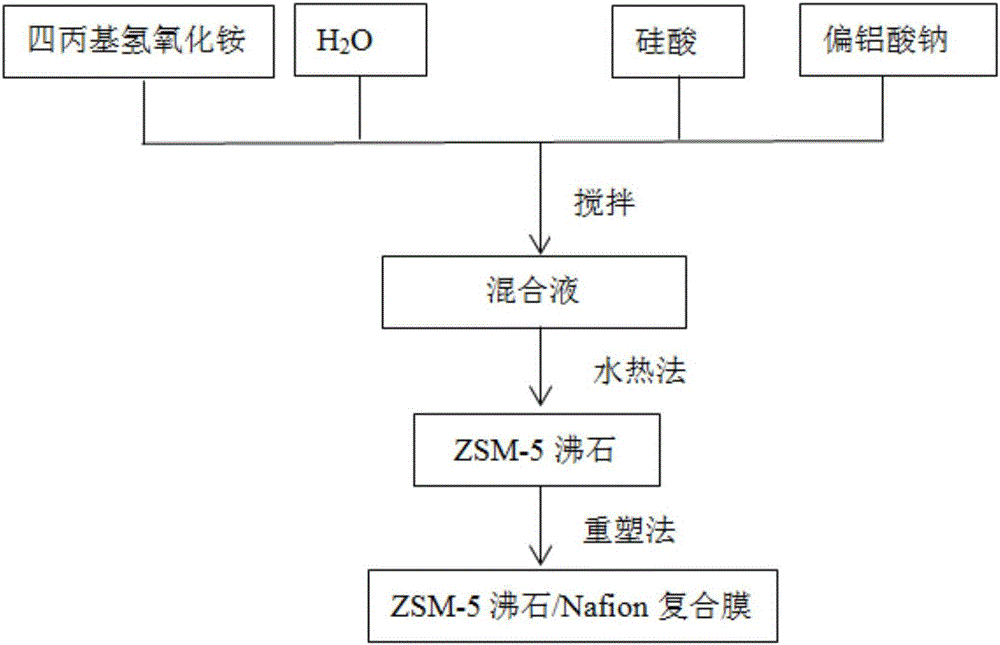
[0041] like figure 1 As shown, embodiment 1 provides a kind of modification method for the proton exchange membrane of all-vanadium redox flow battery, and it comprises the following steps:
[0042] S1. Preparation of submicron ZSM-5 zeolite: first weigh 2.185g of deionized water, add it to 5.463g (the mass ratio of deionized water to tetrapropylammonium hydroxide is 1:2.5) and the concentration is 1.0 mol / L tetrapropylammonium hydroxide (TPAOH) aqueous solution, stirring to form a uniform solution; then weigh 1.093g of silicic acid (that is, the mass ratio of silicic acid to TPAOH is 1:5), and add silicic acid to the above uniform solution; then add 0.044g of sodium metaaluminate (that is, the mass ratio of sodium metaaluminate to silicic acid is 1:25) powder into the above solution, and stir evenly to obtain a milky white solution; then the obtained milky white The solution was stirred for 24 hours to obtain a homogeneous solution, which was transferred to a 100mL Teflon-li...
Embodiment 2
[0051] The difference between the modification method of a proton exchange membrane used in an all-vanadium redox flow battery provided in Example 2 and the modification method described in Example 1 is that the quality of TPAOH in Step S1 of Example 1 is 5.463 g is replaced by: the mass of TPAOH is 6.555g, that is to say, the mass ratio of deionized water to TPAOH is 1:3, and at the same time, according to the mass ratio of silicic acid to TPAOH is 1:5, sodium metaaluminate and silicic acid The mass ratio is 1:25, add 1.311g silicic acid and 0.052g sodium metaaluminate, other content is all the same as embodiment 1, repeats no more here. The composite proton exchange membrane prepared in Example 2 is numbered A2.
Embodiment 3
[0053] The difference between the modification method of a proton exchange membrane used in an all-vanadium redox flow battery provided in Example 3 and the modification method described in Example 1 is that the quality of TPAOH in step S1 of Example 1 is 5.463 g is replaced by: the mass of TPAOH is 7.648g, that is to say, the mass ratio of deionized water to TPAOH is 1:3.5, and at the same time, according to the mass ratio of silicic acid to TPAOH is 1:5, sodium metaaluminate and silicic acid The mass ratio is 1:25, add 1.530g silicic acid and 0.061g sodium metaaluminate, other content is all the same as embodiment 1, repeats no more here. The composite proton exchange membrane prepared in Example 3 is numbered A3.
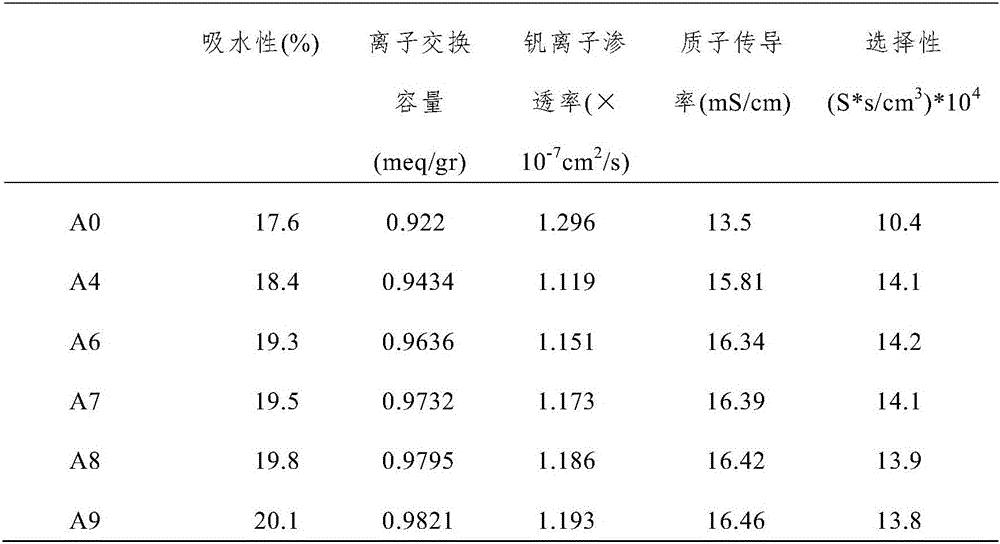
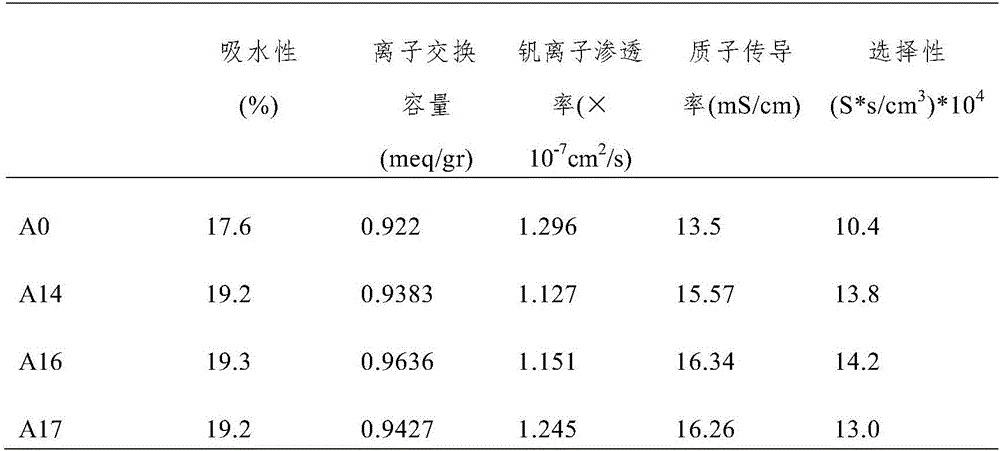
[0054] Comparing the properties of the composite proton exchange membranes prepared in Examples 1-3, it was found that the performance of the composite proton exchange membrane prepared in Example 2 was the best. In other words, the performance of the composite ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com