ALS (Acetolactate Synthetase) mutant type gene of japonica rice as well as protein and application thereof
A mutant and gene technology, applied in the field of plant protein and plant herbicide resistance, can solve the problem that no one has reported herbicide resistance, it is difficult to predict the herbicide resistance of ALS protein in advance, and the mechanism of herbicide action is not determined, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
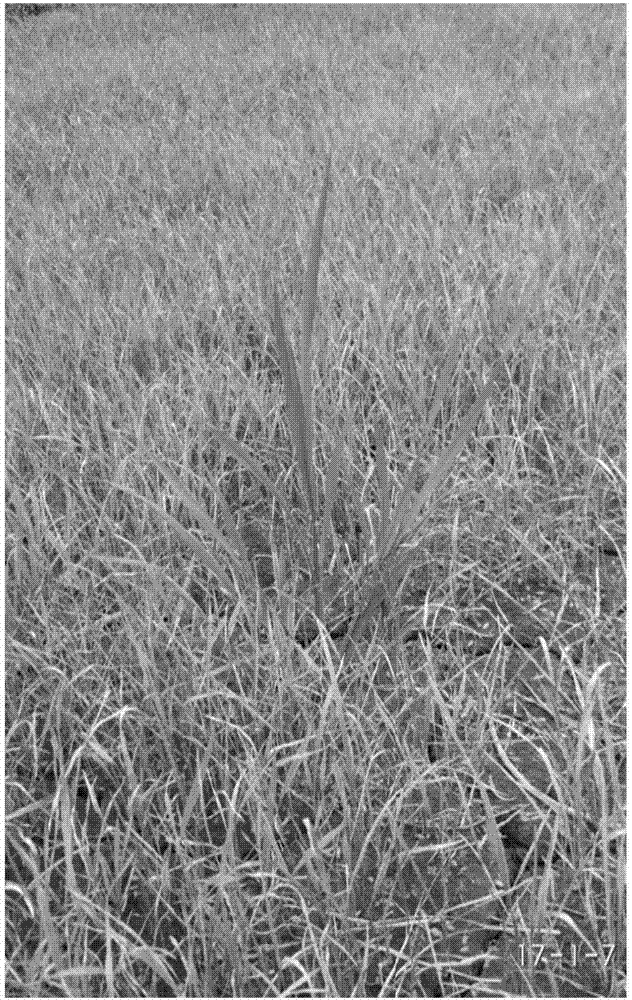
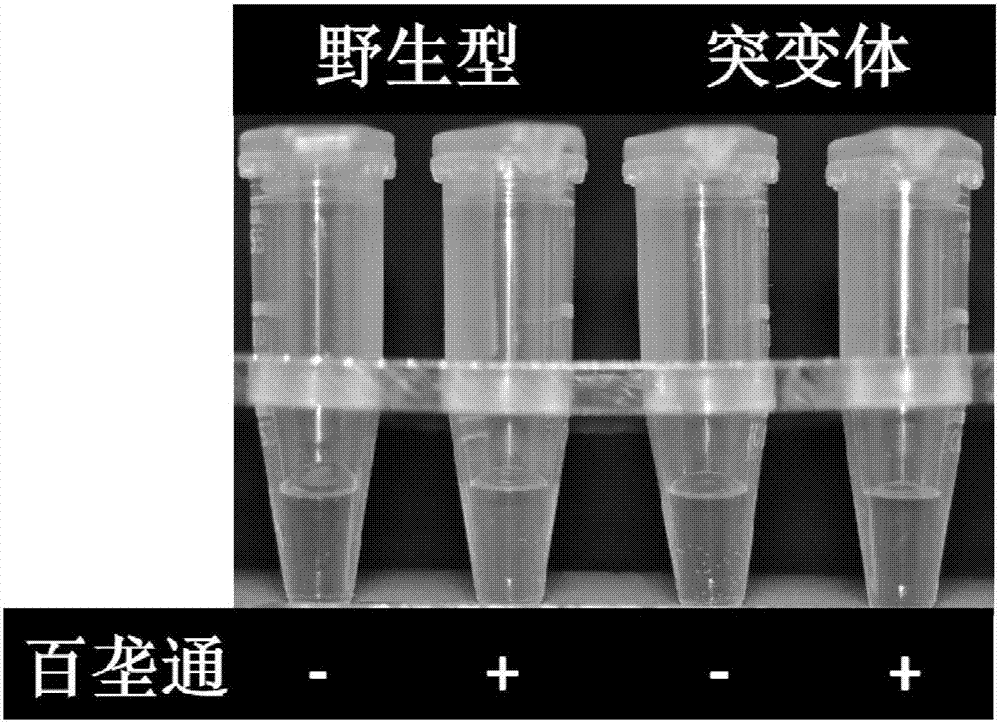
[0036] Example 1: The process of obtaining the imidazolinone herbicide-resistant mutant of japonica rice Zhendao 18 (Bailongtong)
[0037]Regular japonica rice seed Zhendao 18 (purchased from the Agricultural Germplasm Resources Protection and Utilization Platform of Jiangsu Province) (this is M0, soaked in water for 2 hours) 150kg was divided into 6 times with 0.5-1.0% (w / w) methanesulfonic acid Soak in ethyl ester (EMS) at room temperature for 6-9 hours, shake the seeds every 1 hour during this period; discard the EMS solution, soak the seeds 5 times in tap water, 5 minutes each time, then rinse the seeds with tap water overnight, and sow in the field the next day , and carry out conventional fertilizer and water management (this is M1). After the plants are mature, the seeds are mixed, dried, and stored for the winter. Sow in the field the following year. When the rice (this is M2) seedlings grow to the 3-4 leaf stage, spray 3mL Bailongtong / L water ("Bailongtong" is a wat...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2: Analysis of mutation sites of japonica rice mutants resistant to imidazolinone herbicides
[0039] The herbicide-resistant japonica rice mutant plants obtained in the above-mentioned Example 1 were taken to select the leaves of the mutant plants, and the genomic DNA was extracted respectively, and sent to Shanghai Hanyu Biotechnology Co., Ltd. for genome sequencing. Comparing the sequencing results with the reference gene sequence of japonica rice (https: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / nuccore / XM_015770973.1), it was found that the above herbicide-resistant japonica rice mutant had one locus in the ALS gene Mutation, wherein the herbicide-resistant mutant plants have a mutation at the 406th base of the ALS gene, changing from G to T, resulting in a change from glycine to threonine at the 136th position of the corresponding encoded amino acid sequence, that is, herbicide resistance The nucleotide sequence of the ALS gene of the agent mutant plant is shown in SEQ ID NO....
Embodiment 3
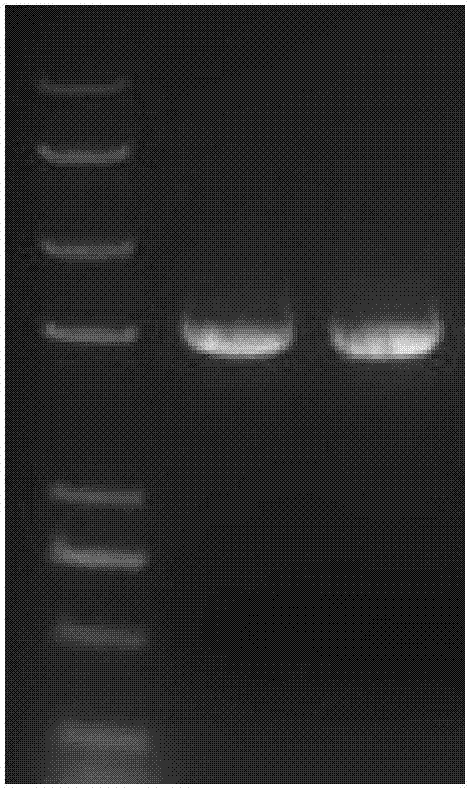
[0040] Example 3 Cloning of the ALS gene of the japonica rice mutant resistant to imidazolinone herbicides
[0041] The leaves of the above-mentioned herbicide-resistant japonica rice mutant zhen9 were taken, and the genomic DNA of the mutant zhen9 was extracted respectively. According to the chromosomal sequence of the rice wild-type ALS gene (such as Genbank accession number XM_015770973.1), the specific primers for amplifying the ALS gene are: forward primer F5'-ATCCGAGCCACACATCGCCTCAC-3', reverse primer R 5'-CTCTTTATGGGTCATTCAGGTCAA-3 '.
[0042] Using OneTaq TM Quick 2×Master Mix (purchased from NEB Company, article number: M0483L) amplifies the 5' end sequence and 3' end sequence of the ALS gene, and the reaction system is as follows:
[0043]
[0044] The PCR amplification reaction program adopts a two-step method, annealing and extension are combined together, and 68 degrees are used.
[0045] The program is as follows: pre-denaturation: 98°C for 3min; 35 cycl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com