Method for realizing carbon dioxide cycle power generation based on waste heat from cement plant
A technology of cycle power generation and carbon dioxide, applied in cement production, waste heat treatment, machine/engine, etc., can solve problems such as inappropriateness, and achieve the effects of reducing pollution, efficient recovery, and extensive energy utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
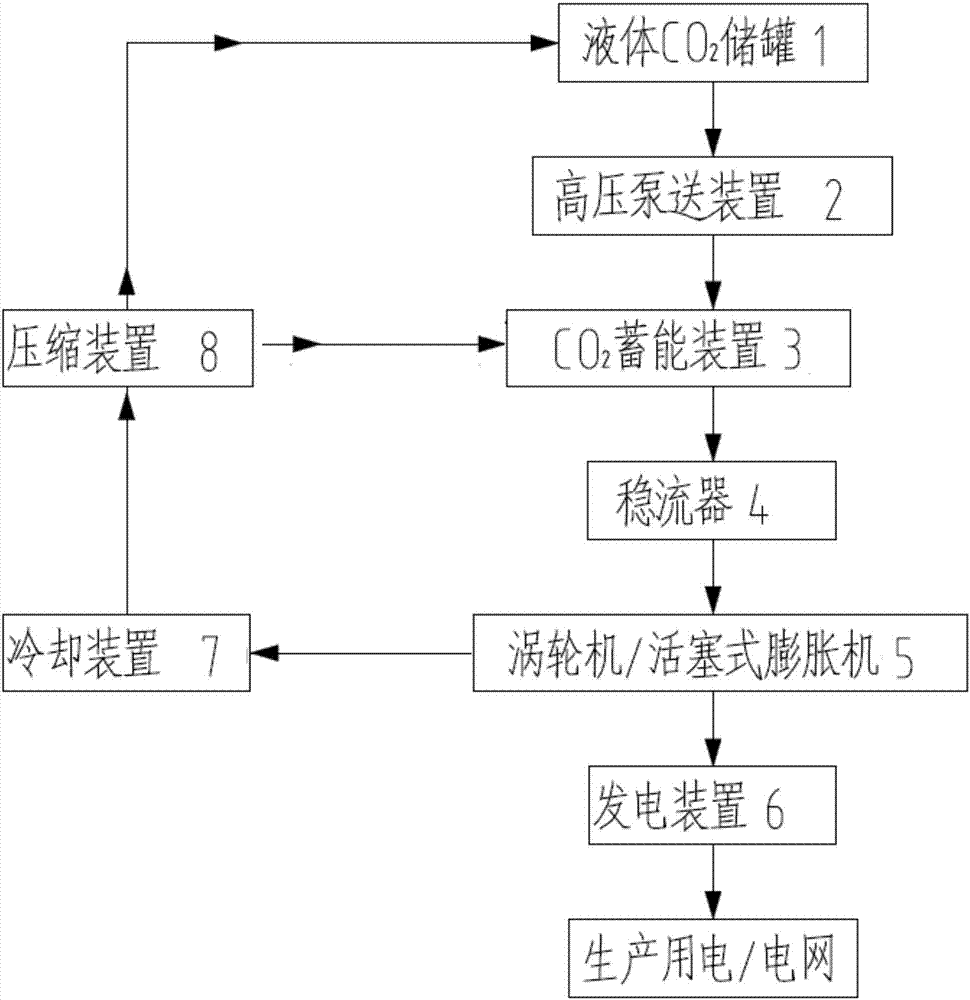
[0040] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention provides a method for utilizing the waste heat of a cement plant to realize carbon dioxide cycle power generation, and the CO captured during the production and emission reduction process of the cement plant 2 Stored in liquid CO for liquefaction of working fluid 2 In the storage tank 1, the liquid CO is pumped by the high-pressure pumping device 2 2 Low pressure liquid CO in storage tank 1 2 Fluid continuously pressed into CO 2 In the energy storage device 3;
[0041] CO 2 The energy storage device 3 is a liquefied CO 2 The fluid directly absorbs the waste heat of waste gas or high-temperature thermal energy generated by the cement production line and converts it into high-pressure thermal supercritical CO 2 Fluid device, the device is provided with CO 2 Fluid energy storage mechanism, the mechanism takes CO 2 Fluid is the working medium; CO 2The fluid energy storage mechanism is set on the side wall or the top ...
Embodiment 2
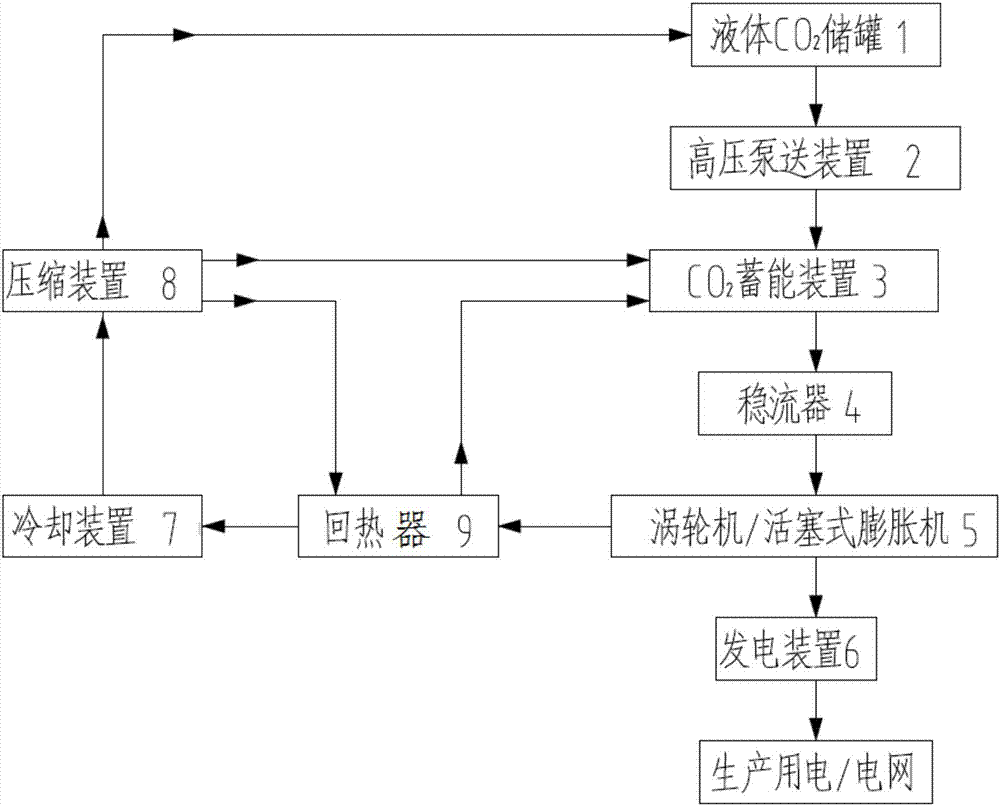
[0045] like figure 2 As shown, the difference from Example 1 is that the method also includes heat recovery, which is manifested as: the low-pressure liquid CO is discharged after the turbine / piston expander 5 performs work and energy release. 2 After the fluid recovers the waste heat through the regenerator 9, the low-pressure liquid CO 2 After the fluid is cooled by the cooling device 7 and compressed by the compression device 8, the compressed fluid is sent into the liquid CO 2 The storage tank 1 is used for circulation; or the low-pressure liquid CO is discharged after the turbine / piston expander 5 releases energy 2 After the waste heat is recovered by the regenerator 9, the fluid is cooled by the cooling device 7 and compressed by the compression device 8, and the compressed fluid enters the recirculator 9 again to absorb the waste heat and then is sent to CO 2 Circulating energy storage power generation in the energy storage device 3;
[0046] Or discharge the low-pr...
Embodiment 3
[0048] The difference from Example 1 is that CO 2 The energy storage device adopts a specific kiln hood with built-in CO 2 Energy storage device and high temperature section of kiln carcass radiate CO 2 energy storage device; both devices are equipped with CO 2 Fluid energy storage mechanism, the mechanism takes CO 2 Fluid is the working medium; CO 2 The fluid energy storage mechanism is respectively arranged on the side wall or roof of the kiln hood and kiln body. Waste heat or radiant heat comes from the kiln hood and kiln body. Specifically, it can be the 100-500 ℃ clinker discharged from the grate cooler for cooling. Waste waste heat, radiant heat and conduction heat at 800°C to 1500°C in the kiln hood, conduction and radiation heat at 300°C to 500°C in the high temperature section of the rotary kiln body, conduction and radiation heat at 150°C to 300°C in the low temperature section of the rotary kiln body; These four different waste heat or radiant heat are replaced ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com