Labeling and detecting method of 5-acetenyl-2'-deoxyuridine of genomic DNA of hepatitis B virus
A deoxyuridine and detection method technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of infecting host cells, restricting the research and development of the mechanism, unclear, etc., and achieves the effects of simple operation, strong signal intensity and bright color.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0060] Example 1 Establishment of Huh7-NTCP cell line
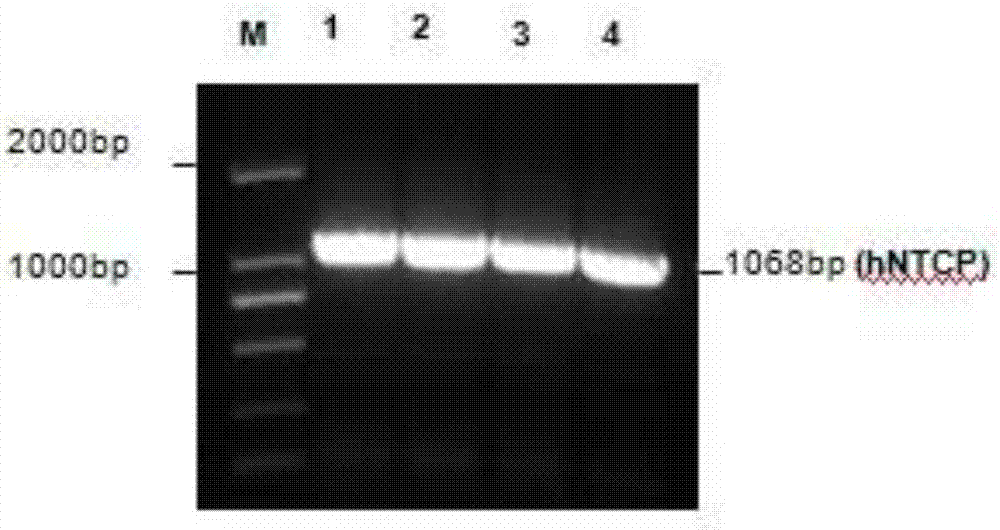
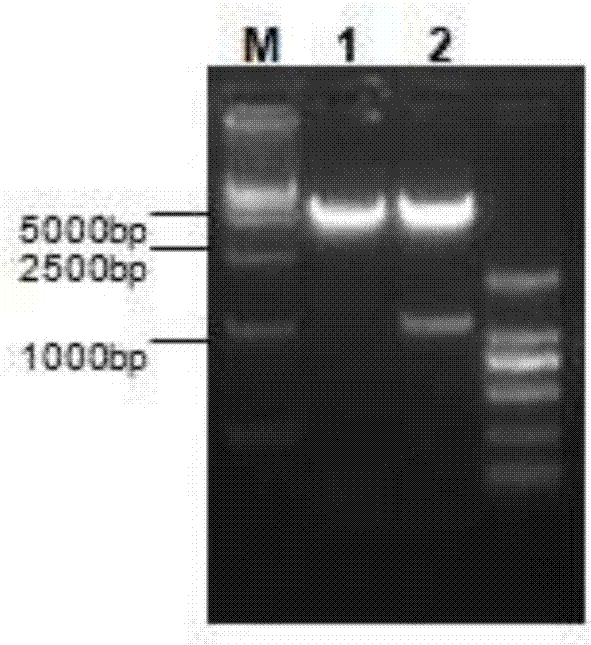
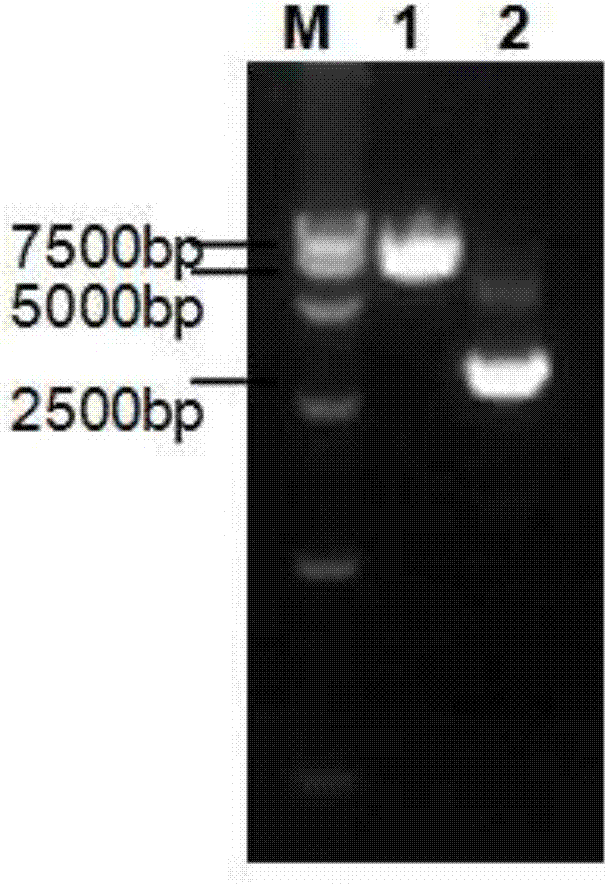
[0061] 1. Amplify the NTCP gene, insert it into the vector pcDNA3.0, and construct the NTCP eukaryotic expression plasmid pcDNA-NTCP. Specifically, the amplified NTCP gene and the vector pcDNA3.0 are subjected to HindIII and XhoI double enzyme digestion reactions respectively, The product was detected by 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis and the constructed NTCP-pcDNA plasmid was linearized using PvuI endonuclease to increase the efficiency of DNA integration and the proportion of positive cell clones; T4DNA ligase was used to connect the above-mentioned linear plasmid vector pcDNA3. 0 and NTCP genes. Primers for amplifying the NTCP gene are as follows:
[0062] pC3NTCP-F:cccAAGCTTgccaccatggaggcccacaacgcgtctg
[0063] pC3NTCP-R:ccgCTCGAGctaggctgtgcaaggggagcag
[0064] 2. Huh7 cells were transfected with pcDNA-NTCP and screened with 700ug / ml G418 for 4-6 weeks
[0065] 3. Pick G418 resistance-positive clones, detect NTC...
Embodiment 2
[0073] Example 2 Preparation of EdU-HBV
[0074] Material:
[0075] 5-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine(EdU)(Sigma)in DMSO
[0076] HepG2.2.15cell
[0077] HBV Genomic DNA Quantification Kit (QiaGen)
[0078] PEG8000 (Sigma)
[0079] step:
[0080] 1. 1x10 7 HepG2.2.15 cells were passaged in T75 culture flasks
[0081] 2. After culturing for 24 hours, replace the MEM containing 10 μM EdU and 2% FBS, collect the cell supernatant after 2 days, then add MEM containing 10 μM EdU and 2% FBS, and collect the cell supernatant again after 2 days
[0082] 3. Collect the cell supernatant for virus purification: first filter with a 0.45um filter membrane (Millipore) or centrifuge at 12000rpm for 2min to remove impurities such as cell debris
[0083] 4. Transfer the supernatant to another 50ml centrifuge tube, add PEG8000 at a final concentration of 5-10%, and mix slowly on ice for 4-6h
[0084] 5. Centrifuge at 3000-5000rpm 4°C for 20min
[0085] 6. Discard the supernatant, resuspend the ...
Embodiment 3
[0101] Example 3 virus infection
[0102] 1. Huh7-NTCP cells are passaged, and when the confluence is 50-80%, dilute EdU-HBV and HBV with DMEM containing 4% PEG8000 and 10% FBS and infect Huh7-NTCP cells (100-1000Geq / cell);
[0103] 2. After 2-12 hours of infection, discard the supernatant, wash with PBS 3 times, replace the 2% medium, detect HBsAg secretion and EdU-HBV fluorescence detection at the expected time point.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com