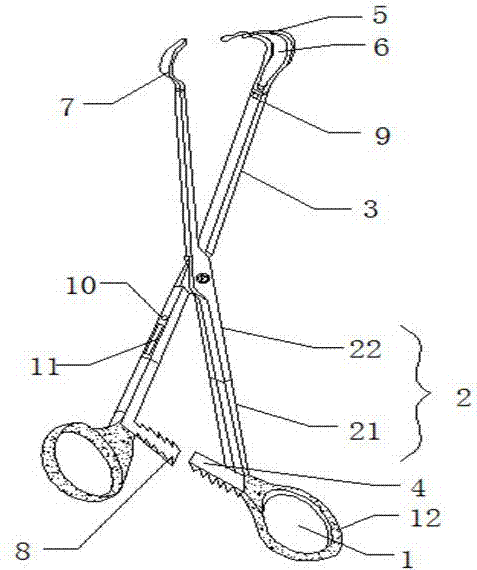
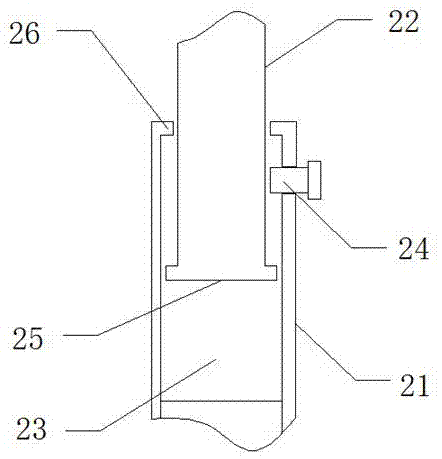
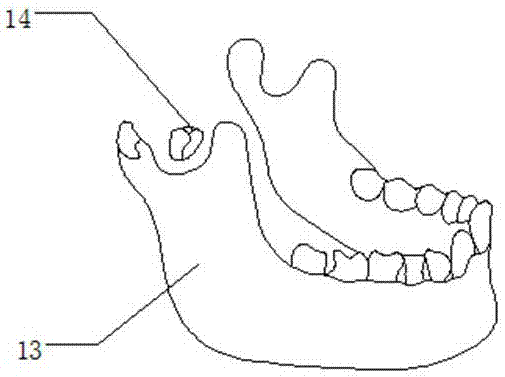
Novel forceps for reduction of sagittal fracture of mandibular condyle and production method of jaws of novel forceps
A technology of sagittal fractures and fixation forceps, which is applied in the field of medical equipment, can solve the problems of limited application range, complicated production process, hidden health and safety hazards, etc., to reduce the risk of secondary injury, increase mechanical strength, and prevent line of sight from being blocked Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] A preparation method for the clamp head of a new type of condylar sagittal fracture reduction and fixation forceps, the forceps head is composed of the following raw materials, by weight percentage: 92% of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene, 6% of nano-ZnO , nano-chitosan is 0.5% and sintering aid micron Ni is 1.5%; The preparation method of described pliers comprises the following steps:
[0047] (1) Weigh the ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene powder, nano-ZnO powder and nano-chitosan powder in proportion, and use an appropriate amount of absolute ethanol as the dispersion medium to prepare ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene suspension, ZnO suspension and chitosan Suspension, then fully stirred with a stirrer, and ultrasonically dispersed for 15-30min;
[0048] (2) Mix the ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene suspension, ZnO suspension and chitosan suspension obtained above to obtain a multi-phase suspension, then add micron Ni as a sintering aid...
Embodiment 2
[0052] A preparation method for the clamp head of the new type of condylar sagittal fracture reduction and fixation forceps, the forceps head is composed of the following raw materials, by weight percentage: 80% of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene, 15% of nano-ZnO %, nano-chitosan is 4% and sintering aid micron Ni is 1%; The preparation method of described clamp head comprises the following steps:
[0053] (5) Weigh the ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene powder, nano-ZnO powder and nano-chitosan powder in proportion, and use appropriate amount of absolute ethanol as the dispersion medium to prepare ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene suspension, ZnO suspension and chitosan Suspension, then fully stirred with a stirrer, and ultrasonically dispersed for 15-30min;
[0054] (6) Mix the ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene suspension, ZnO suspension and chitosan suspension obtained above to obtain a multi-phase suspension, then add micron Ni as a sintering ai...
Embodiment 3
[0058] A preparation method for the clamp head of a new type of condylar sagittal fracture reduction and fixation forceps, the forceps head is composed of the following raw materials, by weight percentage: 86.5% of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene, 10% of nano-ZnO , nano-chitosan is 3% and sintering aid micron Ni is 0.5%; The preparation method of described clamp head comprises the following steps:
[0059] (9) Weigh ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene powder, nano-ZnO powder and nano-chitosan powder in proportion, and use appropriate amount of absolute ethanol as the dispersion medium to make ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene suspension, ZnO suspension and chitosan Suspension, then fully stirred with a stirrer, and ultrasonically dispersed for 15-30min;
[0060] (10) Mix the ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene suspension, ZnO suspension and chitosan suspension obtained above to obtain a multi-phase suspension, then add micron Ni in proportion as a sin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com