Method for reinforcing waste biomass sodium carbonate pretreatment by utilizing lignin-degrading bacteria
A technology for lignin degrading bacteria and waste biomass, which is applied in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., to achieve the effects of reduced strength, less secondary pollution, and short processing time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
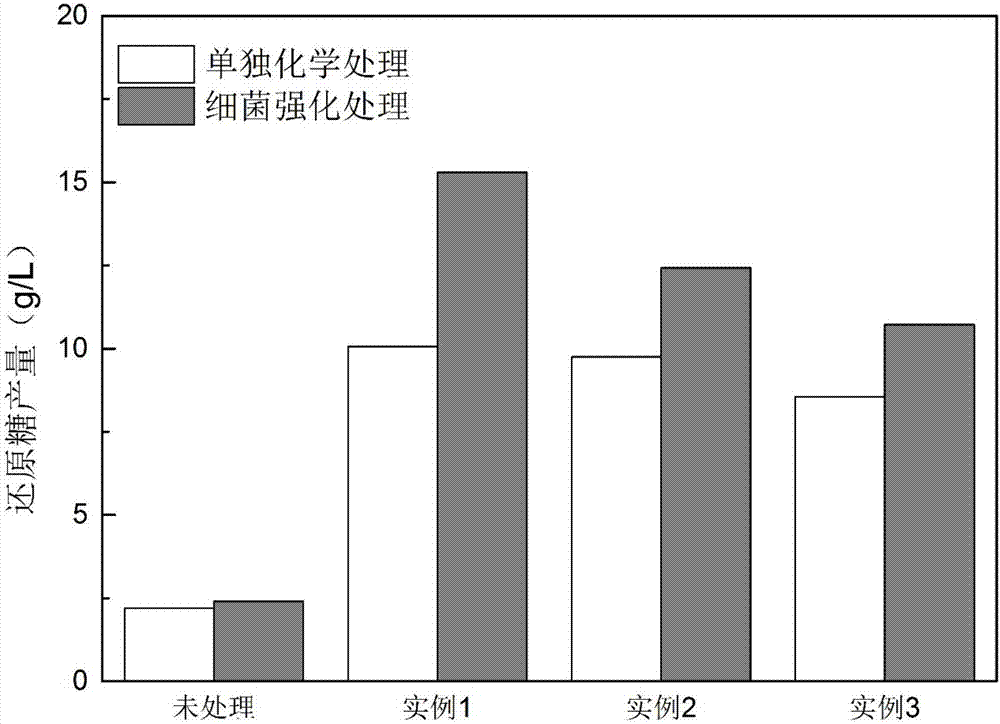
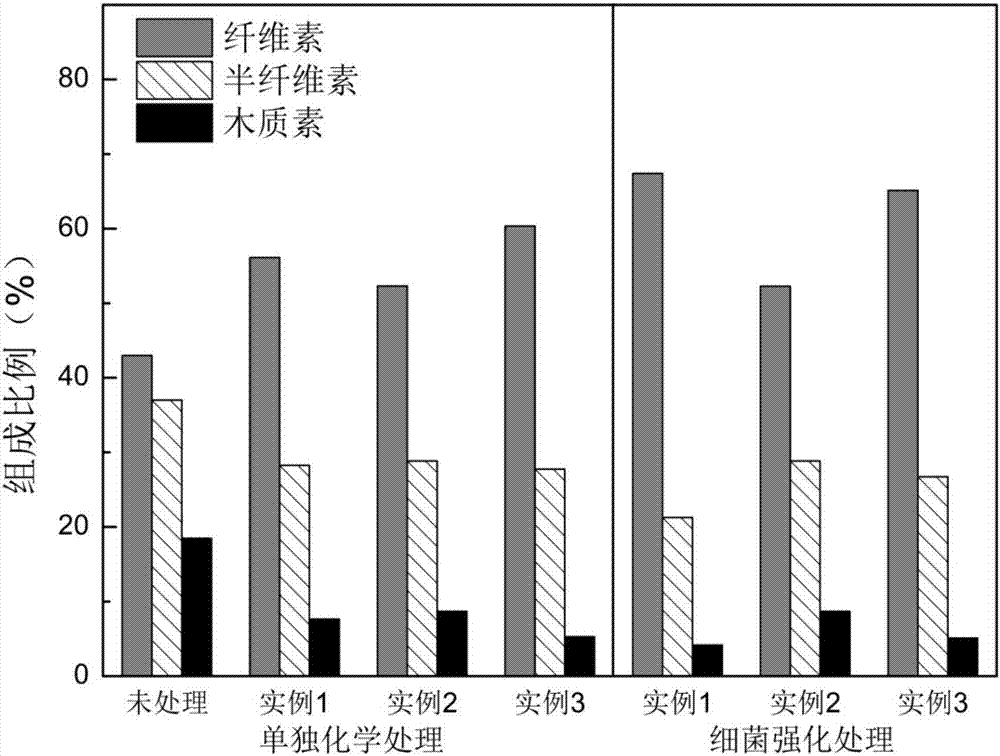
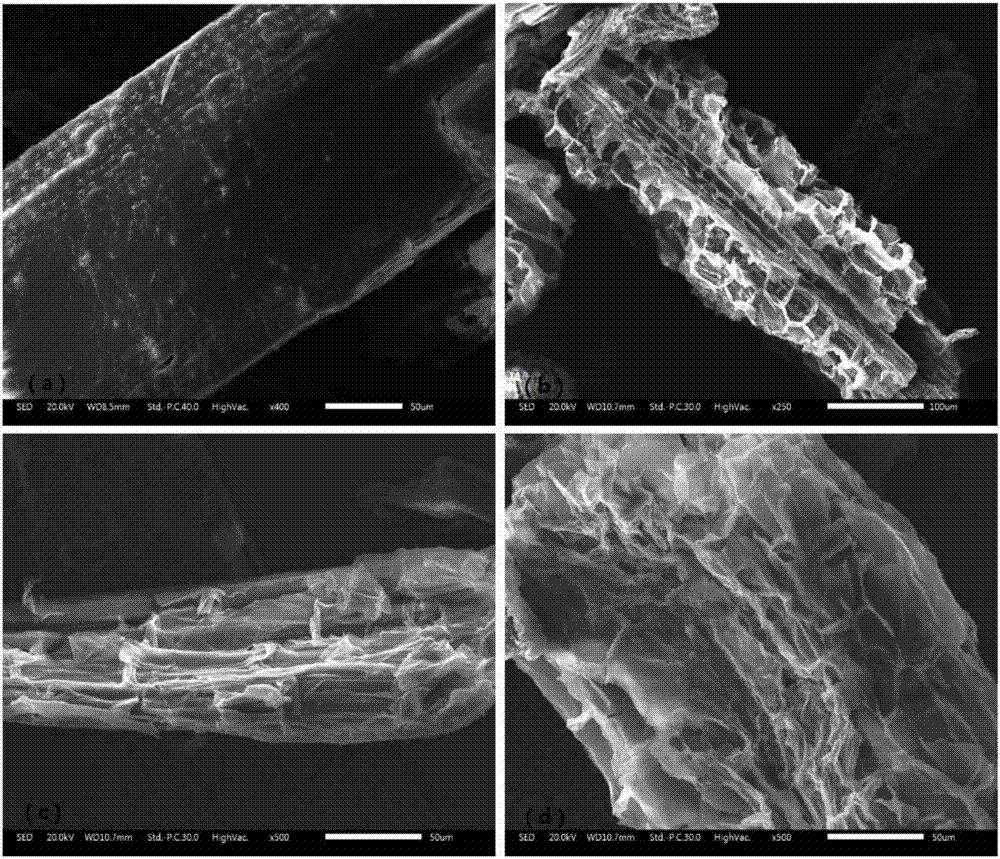
[0032] (1) The rice straw was crushed and sieved with 60 meshes, washed twice with ultrapure water, and dried at 60°C until constant weight.
[0033] (2) Put the waste biomass in a container of appropriate size, and add Na at a concentration of 8% according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:10 (g / ml). 2 CO 3 The solution was left to stand in a constant temperature environment of 80° C. for 3 hours, and then filtered to obtain a wet residue A.
[0034] (3) Rinse the wet residue A obtained by filtering and separating with distilled water repeatedly until the pH of the washing liquid is neutral, and dry at 60° C. to a constant weight to obtain dry residue B.
[0035] (4) Inoculate the Cupriavidus basilensis B-8 bacteria stored on the LB slope into LB liquid medium, and culture at 30°C for 18 hours (the optical density at 600nm reaches 0.8-1.0) to obtain the seeds of Cupriavidus basilensis B-8 Liquid; wherein said LB liquid culture medium each composition ratio is: peptone 10g, ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] (1) The rice straw was crushed and sieved with 60 meshes, washed twice with ultrapure water, and dried at 60°C until constant weight.
[0043] (2) Put the waste biomass in a container of appropriate size, and add Na at a concentration of 6% according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:10 (g / ml). 2 CO 3 The solution was left to stand in a constant temperature environment of 80° C. for 3 hours, and then filtered to obtain wet residue A.
[0044] (3) Rinse the wet residue A obtained by filtering and separating with distilled water repeatedly until the pH of the washing liquid is neutral, and dry at 60° C. to a constant weight to obtain dry residue B.
[0045] (4) Inoculate the Cupriavidus basilensis B-8 bacteria stored on the LB slope into LB liquid medium, and culture at 30°C for 18 hours (the optical density at 600nm reaches 0.8-1.0) to obtain the seeds of Cupriavidus basilensis B-8 Liquid; wherein said LB liquid culture medium each composition ratio is: peptone 10g, ye...
Embodiment 3
[0052] (1) The rice straw was crushed and sieved with 60 meshes, washed twice with ultrapure water, and dried at 60°C until constant weight.
[0053] (2) Put the waste biomass in a container of appropriate size, and add Na at a concentration of 4% according to the solid-liquid ratio of 1:10 (g / ml). 2 CO 3 The solution was left to stand in a constant temperature environment of 80° C. for 3 hours, and then filtered to obtain a wet residue A.
[0054] (3) Rinse the wet residue A obtained by filtering and separating with distilled water repeatedly until the pH of the washing liquid is neutral, and dry at 60° C. to a constant weight to obtain dry residue B.
[0055] (4) Inoculate the Cupriavidus basilensis B-8 bacteria stored on the LB slope into LB liquid medium, and culture at 30°C for 18 hours (the optical density at 600nm reaches 0.8-1.0) to obtain the seeds of Cupriavidus basilensis B-8 Liquid; wherein said LB liquid culture medium each composition ratio is: peptone 10g, yea...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com