Chaotropic agent and method for extracting genomic DNA by using chaotropic agent
A chaotropic agent and genome technology, applied in the field of chaotropic agent for rapid separation of histones and genomic DNA, and DNA extraction, it can solve the problems of poor experimental repeatability and stability, high chlorine valence, and strong oxidative properties of reagents. Avoid prolonged digestion, high purity, and high DNA yield effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0029] Wherein, as a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the sample containing histone and genomic DNA contains cell lysate.
[0030] Wherein, the method may further include: pretreating the eukaryotic biological material to obtain biological material containing histone and genomic DNA suitable for lysing directly. The pretreatment operation includes at least one of washing, drying, shredding, grinding, freezing and freeze-thawing. The pretreatment operation can be performed in a conventional manner in the art, for example, according to the contents recorded in the "Molecular Cloning Experiment Guide".
[0031] Wherein, the eukaryotic biological material may include at least one of tissues, organs, individuals and symbionts. The biological material may include at least one of oral mucosal epithelial cells, blood and artificially cultured cells.
[0032] Wherein, the method further includes: precipitating, washing and redissolving the DNA. Wherein, the reagent use...
Embodiment 1
[0035] This example is used to illustrate the operation of extracting DNA from saliva samples using two different methods.
[0036] (1) Sample pretreatment: centrifuge saliva at 2000 g for 10 min, discard the supernatant, suspend oral mucosal epithelial cells with 1 mL of normal saline, centrifuge at 2000 g for 10 min, and discard the supernatant.
[0037] (2) Add 400 μL of cell lysate to the Eppendorf (EP) tube, and mix thoroughly until there is no obvious cell mass. The cell lysate formula is: 10 mmol / L Tris-HCl (pH8.0), 30 mmol / L EDTA (pH8.0), 0.5% SDS, RNase A (20 μg / mL).
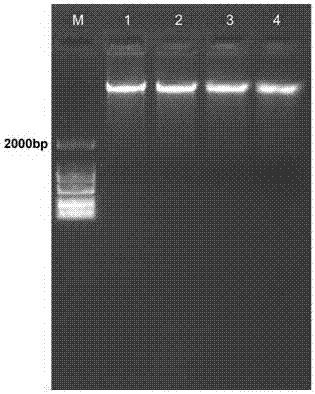
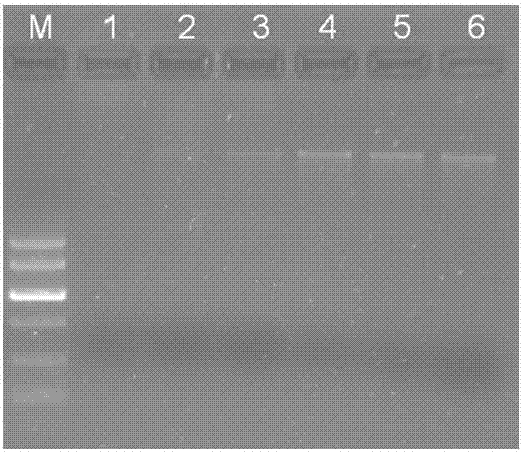
[0038] (3) Genomic DNA was extracted by proteinase K method and sodium bromate method respectively. Proteinase K method: Add proteinase K with a final concentration of 100 μg / mL to the EP tube in step (2), mix well, and place at 56 °C for 40 min, mixing from time to time. Sodium bromate method: Add chaotropic agent sodium bromate with a final concentration of 1 mol / L to the EP tube in step (2), and mi...
Embodiment 2
[0044] This example is used to illustrate the operation of extracting DNA from oral mucosal epithelial cells collected by oral swab method using two different methods.
[0045] (1) Sample pretreatment: Cut out the material carrying oral mucosal epithelial cells and place it in an Eppendorf (EP) tube.
[0046] (2) Add 400 μL of cell lysate to the EP tube, and mix well until there is no obvious cell mass. The cell lysate formula is: 10 mmol / L Tris-HCl (pH8.0), 30 mmol / L EDTA (pH8.0), 0.5% SDS, RNaseA (20 μg / mL).
[0047] (3) Genomic DNA was extracted by proteinase K method and sodium bromate method respectively. Proteinase K method: Add proteinase K with a final concentration of 100 μg / mL to the EP tube in step (2), mix well, and place at 56 °C for 40 min, mixing from time to time. Sodium bromate method: Add chaotropic agent sodium bromate with a final concentration of 1 mol / L to the EP tube in step (2), and mix well. The rest of the steps are the same.
[0048] (4) Add an e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com