Confocal microscope parallel scanning device and scanning method based on scanning galvanometer and semiconductor laser
A technology of confocal microscope and scanning galvanometer, which is applied in microscopes, optics, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of exposure speed influence, low image acquisition rate, etc., and achieve the effect of increasing scanning speed and improving acquisition speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
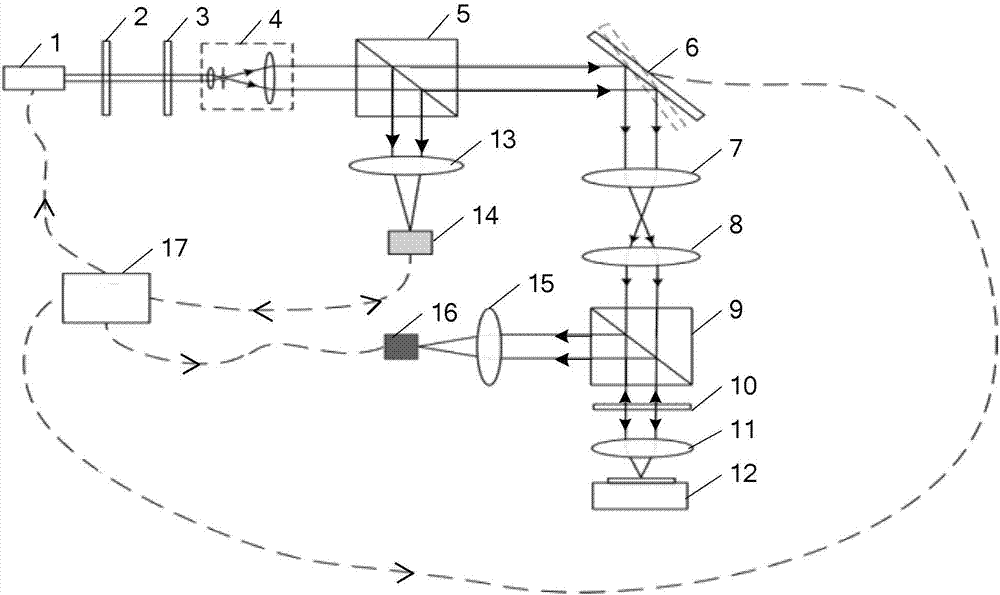
[0025] Specific implementation mode one: see figure 1 Describe this embodiment, a confocal microscope parallel scanning device based on a scanning galvanometer and a semiconductor laser described in this embodiment, it includes a semiconductor laser 1, an attenuation plate 2, a polarizer 3, a collimating beam expander system 4, a first A polarizing beam splitting prism 5, scanning galvanometer system 6, telecentric scanning lens 7, tube mirror 8, second polarizing beam splitting prism 9, 1 / 4 wave plate 10, objective lens 11, first collecting lens 13, photodetector 14, Second collecting lens 15, CCD camera 16 and controller 17;
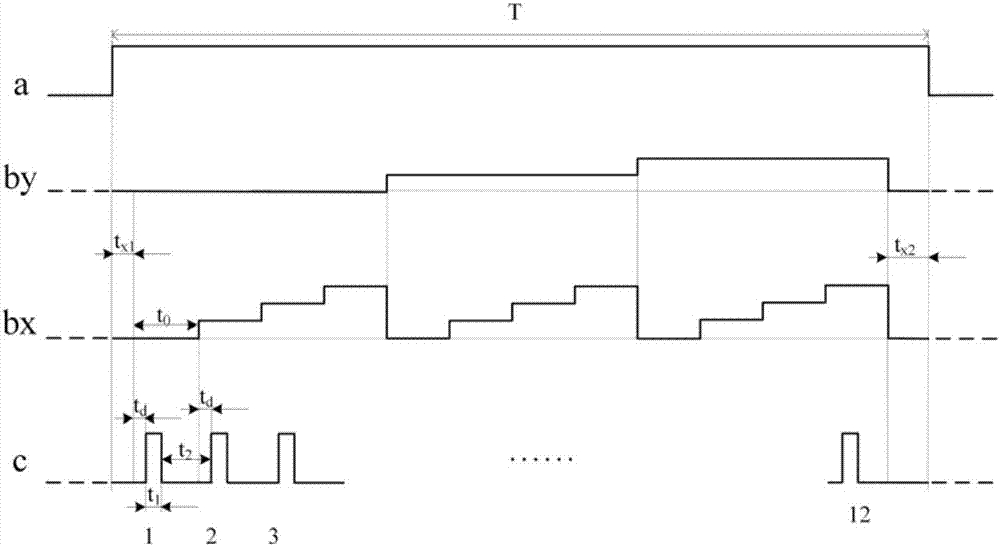
[0026] The controller 17 is used for modulating the outgoing light of the semiconductor laser 1, for controlling the photodetector 14 to perform photodetection, for controlling the exposure time of the CCD camera 16, and for controlling the scanning galvanometer system 6 to deflect;
[0027] The light emitted by the semiconductor laser 1 is transmitte...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0040] Specific implementation mode two: see figure 1 Describe this embodiment, the difference between this embodiment and the confocal microscope parallel scanning device based on the scanning galvanometer and semiconductor laser described in the first embodiment is that the 1 / 4 wave plate 10 is incident on the objective lens 11 The light is circularly polarized.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0041] Specific implementation mode three: see figure 1 Describe this embodiment, the difference between this embodiment and the confocal microscope parallel scanning device based on the scanning galvanometer and semiconductor laser described in the first embodiment is that the 1 / 4 wave plate 10 is incident to the second The light from the polarization beam splitter prism 9 is linearly polarized light.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com