Crystalline oxides, preparation thereof and conductive pastes containing the same
A technology of conductive coatings and oxides, applied in conductive coatings, conductive materials dispersed in non-conductive inorganic materials, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of inability to provide pulling force, insufficient density of electrode structure, and inability of electrodes to form ohmic contact, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
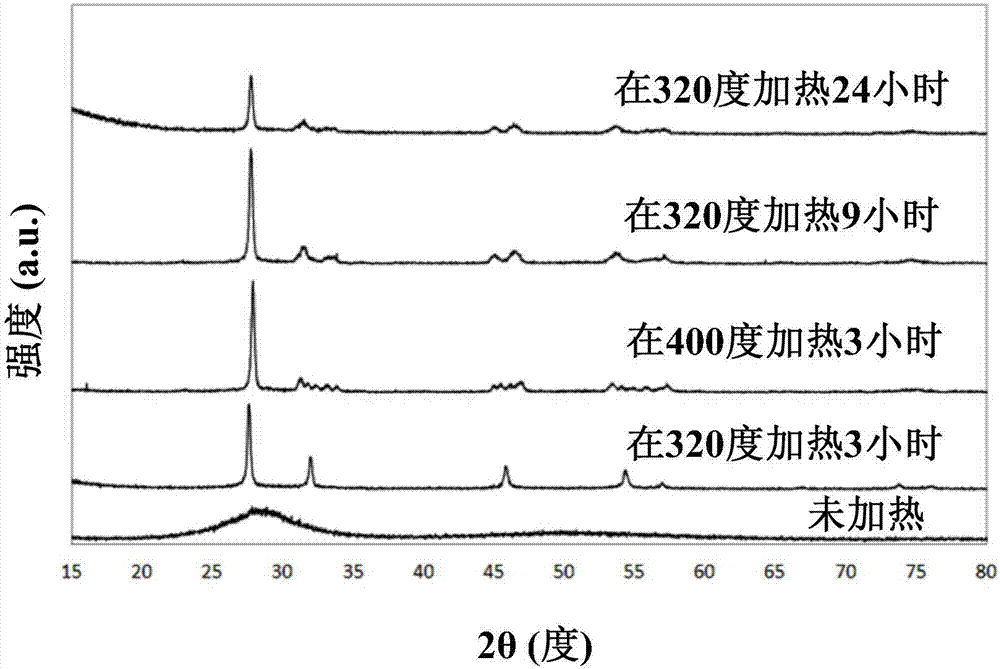
[0047] Another aspect of the present application is to provide a method for preparing oxide crystals, especially the preparation of lead-tellurium-bismuth-oxide crystals. In one embodiment, the application provides a lead-tellurium-bismuth-oxide crystal preparation method comprising the following steps: (i) providing PbO-TeO 2 -Bi 2 o 3 For the substrate glass, (ii) subjecting the glass to its crystallization temperature for about 3 to 24 hours. In step (i) PbO-TeO 2 -Bi 2 o 3 The glass as the base will be in the form of powder, block, powder, etc., but preferably in the form of glass powder. In (i) step, the glass may be placed at its crystallization temperature for 6, 8, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21 hours. According to this application, for PbO-TeO 2 -Bi 2 o 3 The crystallization temperature of the glass used as the substrate for heat treatment in step (ii) must be higher than its Tg glass transition temperature (glass transition temperature). In one embodiment, for PbO-TeO i...
experiment example
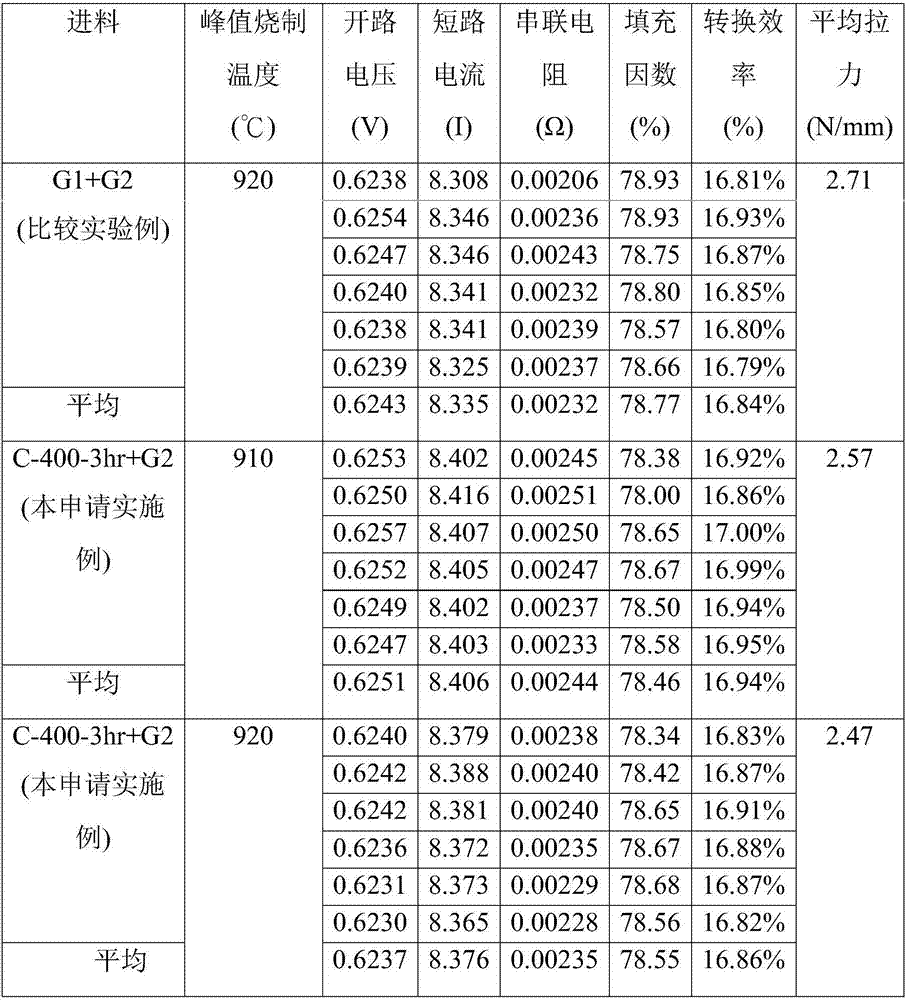
[0073] Preparation of lead-tellurium-bismuth-oxide crystals
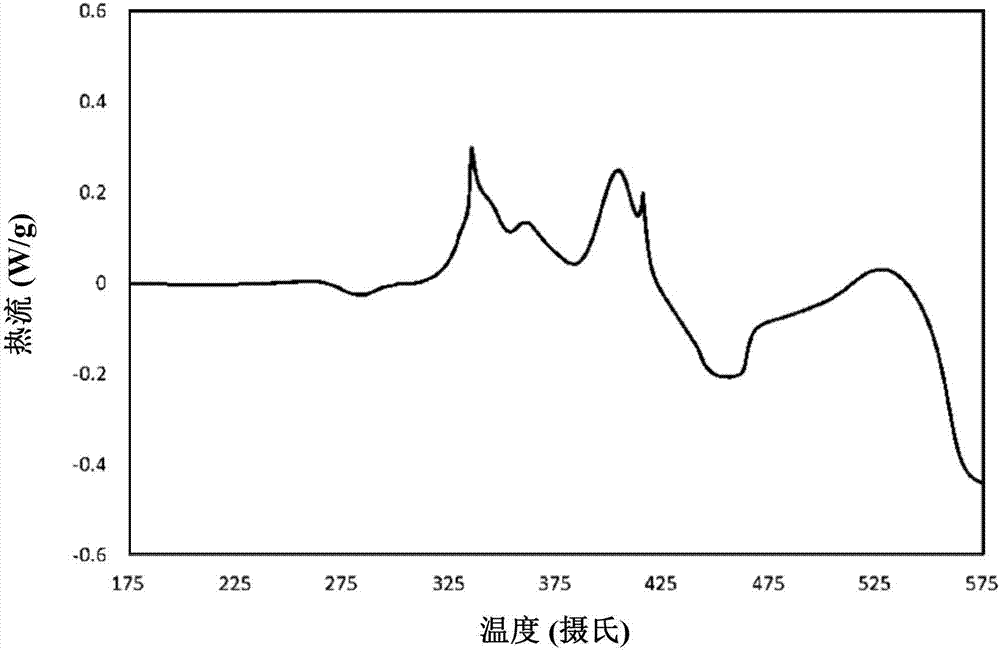
[0074] First, the differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) was used to examine the PbO-TeO 2 -BiO 2 is the crystallization temperature of the glass powder of the substrate. To measure the crystallization temperature, 20 mg of PbO-TeO 2 -BiO 2 The glass powder used as the substrate was heated from room temperature to 600°C at a heating rate of 20°C per minute, and then cooled using nitrogen as a carrier gas. The analysis results of the differential calorimetry scanning method are shown in Fig. 1 .
[0075] According to the analysis result of differential calorimetry, PbO-TeO 2 -BiO 2 The glass transition temperature of the glass as the substrate is about 266 degrees Celsius, and at least two crystal phases exist, because there are two crystallization temperature peaks (ie about 320 degrees Celsius and 400 degrees Celsius).
[0076] Then, the PbO-TeO 2 -BiO 2 The glass powder used as the base is heat-treated...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com