Catalytic cracking method for treating residual oil and ultra-heavy oil raw material
A catalytic cracking and residual oil technology, which is applied in the treatment of hydrocarbon oil, hydrocarbon oil treatment products, refining and cracking process treatment only in multi-stage series, etc. The problems such as the increase in the amount of coke generated in the cracking unit, to achieve the effect of low residual carbon and sulfur and nitrogen content, maximized utilization, and high saturated hydrocarbon content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0061] Example 1. Treatment of Daria vacuum residue with a hydrotalcite catalyst with a magnesium-aluminum ratio of 2.5
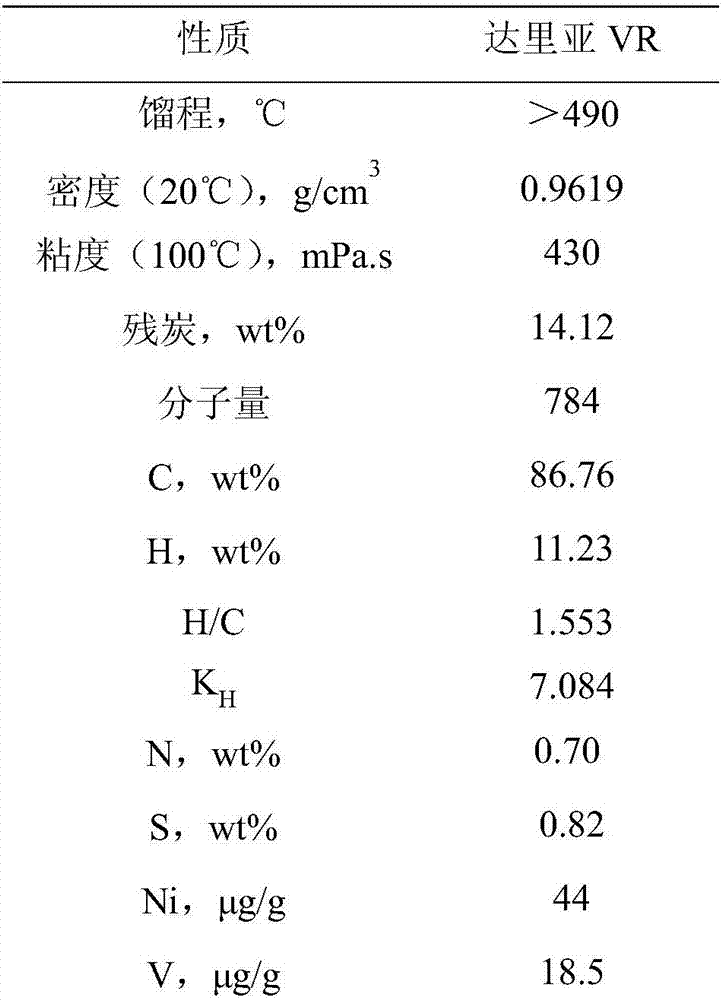
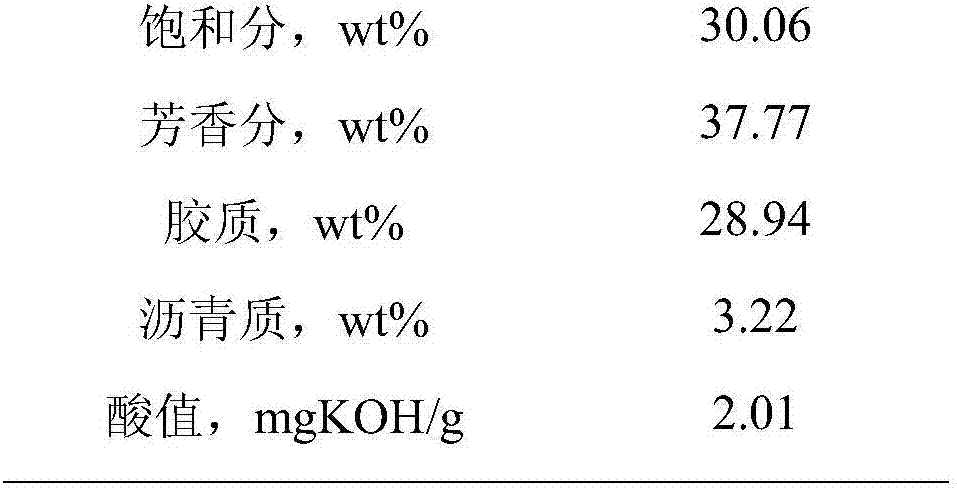
[0062] The basic properties of Daria vacuum residue are shown in Table 1.
[0063] Table 1 Daria Vacuum Residue
[0064]
[0065]
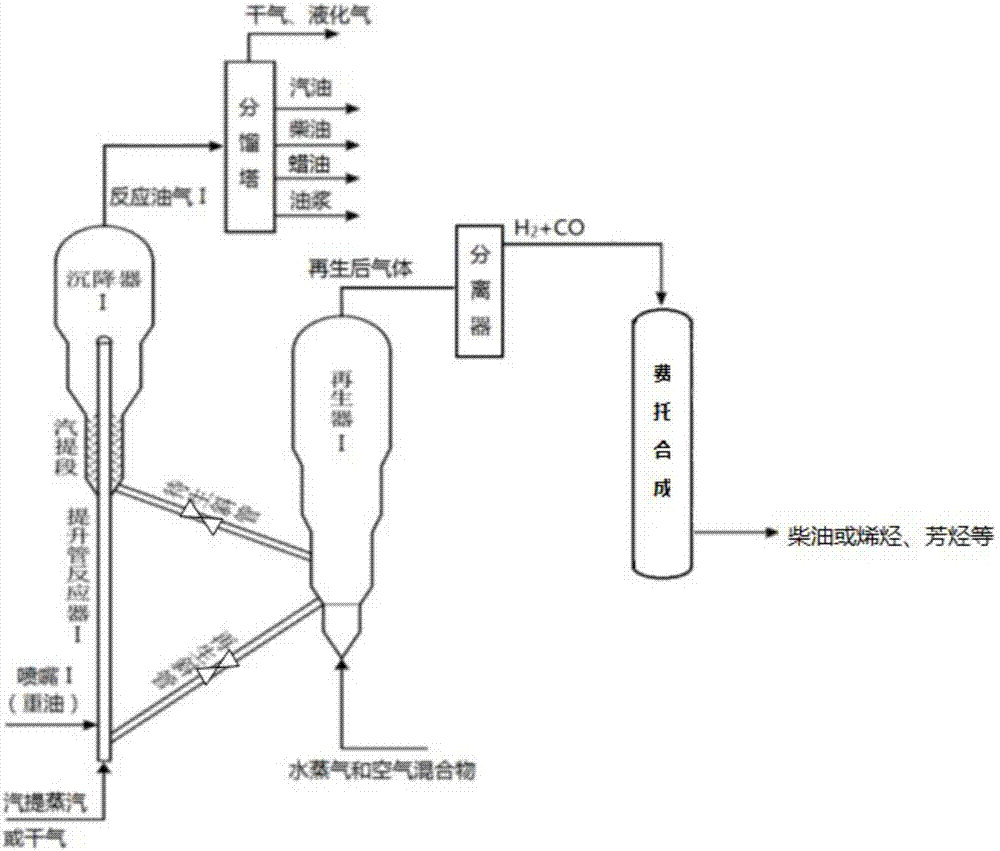
[0066] according to figure 1 The process shown is carried out, and the steps are as follows:
[0067] Use dry gas to lift the vacuum residue, and carry out catalytic cracking in the riser reactor, where the temperature is 525°C, the ratio of agent to oil is 5, and the pressure is 0.2Mpa. Then, the oil and gas in the spent catalyst are stripped through the stripping section, and the oil and gas are separated from the spent catalyst in a settler to obtain the spent catalyst and reaction oil and gas.
[0068] The catalyst to be regenerated enters the regenerator through the inclined pipe to be regenerated. The regeneration gas is a mixture of water vapor and air (the volume ratio of the two is 1:5.5), the temperature is 8...
Embodiment 2
[0079] From the data in Table 4, it can be seen that the residual carbon content in the wax oil is low, and it is a high-quality raw material for conventional catalytic cracking. Example 2, treating Penglai vacuum residue with a hydrotalcite catalyst with a magnesium-aluminum ratio of 3
[0080] The basic properties of Penglai vacuum residue are shown in Table 5.
[0081] Table 5 Penglai vacuum residue
[0082]
[0083]
[0084] according to figure 1 The process shown is carried out, and the steps are as follows:
[0085] Use dry gas to lift the vacuum residue, and carry out catalytic cracking in the riser reactor, where the temperature is 530°C, the ratio of catalyst to oil is 6, and the pressure is 0.2Mpa. Then, the oil and gas in the spent catalyst are stripped through the stripping section, and the oil and gas are separated from the spent catalyst in a settler to obtain the spent catalyst and reaction oil and gas.
[0086] The catalyst to be regenerated enters th...
Embodiment 3
[0099] Example 3: Continue conventional catalytic cracking with the wax oil obtained in Example 2, using HY molecular sieve catalyst, the reaction temperature is 515°C, the solvent-to-oil ratio is 6, and the pressure is 0.2Mpa.
[0100] The conditions for the regeneration of the catalyst to be regenerated are: air is used as the regeneration gas, the temperature is 580°C, the pressure is 0.3MPa, and the regeneration flue gas is discharged outside.
[0101] The distribution of products obtained by acid catalyst catalytic cracking is shown in Table 9.
[0102] Table 9 Distribution of products obtained by acid catalytic cracking
[0103] product Yield (wt%) dry gas, liquefied gas 19.1% gasoline 43.9% diesel fuel 28.7% oil slurry 3.5% coke 4.8%
[0104] As can be seen from the data in Table 9, the yield of gasoline and diesel reaches more than 72%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com