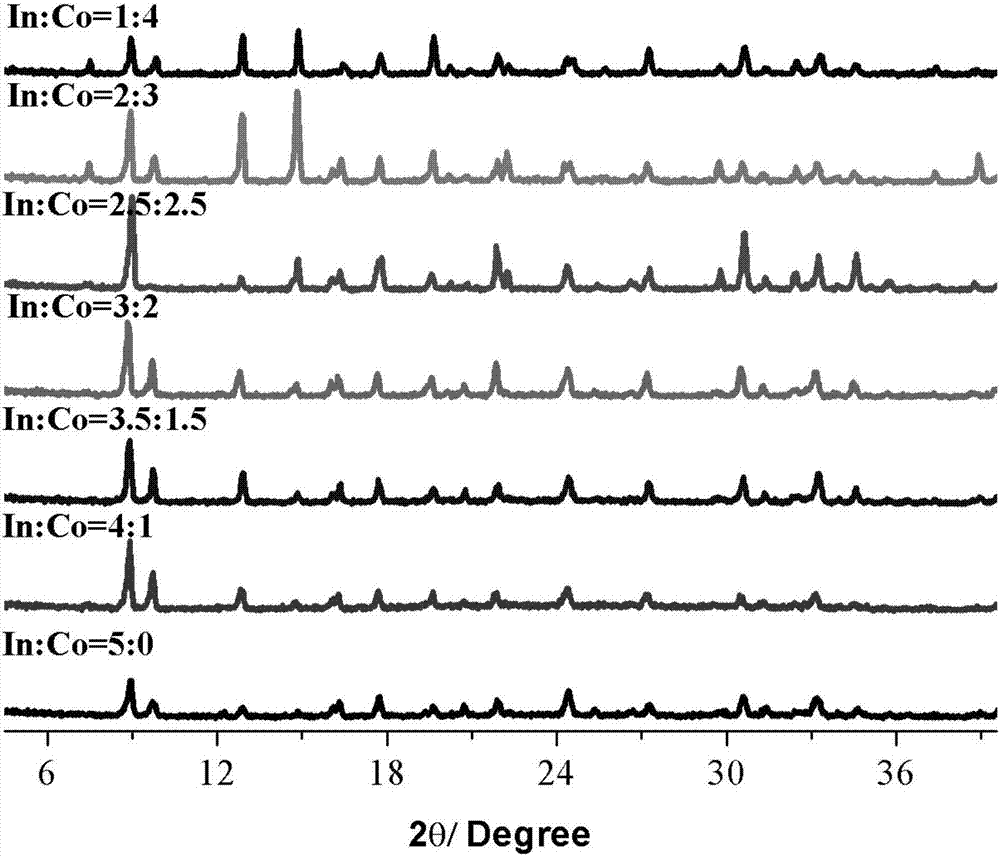
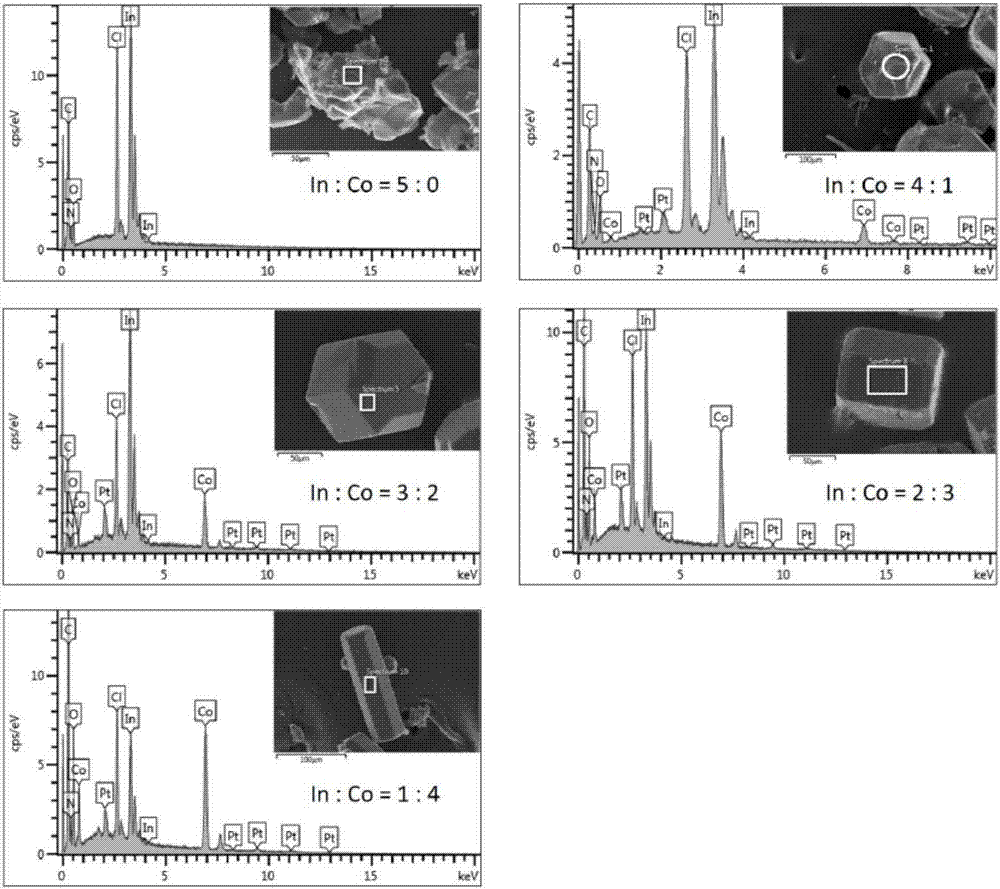
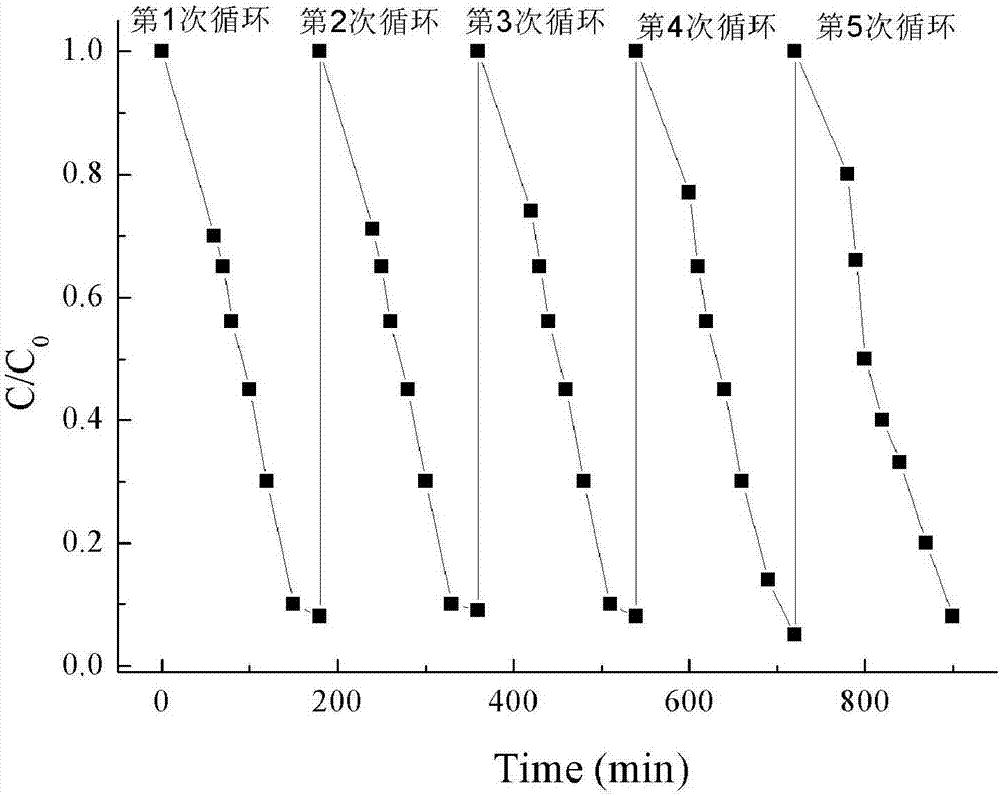
Method for removing low-concentration antibiotics in water through In-Co-contained MOFs adsorption and excitation persulphate synergism
A technology for activating persulfate and persulfate, applied in the field of environmental pollution control, can solve the problems of difficult treatment, low antibiotic concentration, large energy consumption, etc., and achieves the effect of simple process flow, broad application prospects, and improved activation efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] A method for synergistic removal of low-concentration antibiotics in water by adsorption of In-Co MOFs and activation of persulfate, the specific steps are as follows:
[0036] (1) Prepare 100 μmol / L sulfadiazine solution at room temperature, take 100ml of the solution in a 250ml reactor, add 0.05g of In-Co-containing MOFs, and stir for 1h;
[0037] (2) Add 0.1g K to the reaction system 2 S 2 o 8 Continue stirring for 2h;
[0038] (3) After the reaction is completed, the purpose of solid-liquid separation is achieved after simple filtration, and the In-Co-containing MOFs are collected and dried at 60°C for later use.
[0039] The adsorption capacity (indicated by the adsorption rate) of the stirred solution obtained in step (1) to In-Co MOFs was tested, and the final degradation rate was tested with the stirred solution obtained in step (2). The experimental results are shown in Table 1. , the results in Table 1 show that different ratios of In-Co-containing MOFs ha...
Embodiment 2
[0049] A method for synergistic removal of low-concentration antibiotics in water by adsorption of In-Co MOFs and activation of persulfate, the specific steps are as follows:
[0050] (1) Prepare a 100 μmol / L acetaminophen solution at room temperature, take 100ml of the solution in a 250ml reactor, add 0.05g of In-Co-containing MOFs, and stir for 1 hour;
[0051] (2) Add 0.1g K to the reaction system 2 S 2 o 8 Continue stirring for 2h;
[0052] (3) After the reaction is completed, the purpose of solid-liquid separation is achieved after simple filtration, and the In-Co-containing MOFs are collected and dried at 60°C for later use.
[0053] The adsorption capacity of In-Co MOFs (indicated by adsorption rate) was tested with the stirred solution obtained in step (1), and the final degradation rate was tested with the stirred solution obtained in step (2). The experimental results are shown in Table 2 , the results in Table 2 show that different proportions of In-Co-containin...
Embodiment 3
[0063] A method for synergistic removal of low-concentration antibiotics in water by adsorption of In-Co MOFs and activation of persulfate, the specific steps are as follows:
[0064] (1) Prepare a 100 μmol / L norfloxacin solution at room temperature, take 100ml of the solution in a 250ml reactor, add 0.05g of In-Co MOFs, and stir for 1h;
[0065] (2) Add 0.1g K to the reaction system 2 S 2 o 8 Continue stirring for 4h;
[0066] (3) After the reaction is completed, the purpose of solid-liquid separation is achieved after simple filtration, and the In-Co-containing MOFs are collected and dried at 60°C for later use.
[0067] The adsorption capacity (indicated by the adsorption rate) of the stirred solution obtained in step (1) to In-Co MOFs was tested, and the final degradation rate was tested with the stirred solution obtained in step (2). The experimental results are shown in Table 3 , the results in Table 3 show that the removal rate of norfloxacin with different proporti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com