Plant endophyte capable of degrading PAEs and application of plant endophyte in PAEs polluted soil repair
A plant endophyte and phytoremediation technology, which is applied in the field of plant endophytes to achieve the effects of avoiding crop pollution risks, avoiding pollution risks, and simple operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Plant samples were collected from the constructed wetland, and the endophyte isolation and screening test was carried out immediately. Conventional endophyte isolation methods were used. After cleaning the collected fresh plant material samples with sterile water, cut them into 1cm-long segments with sterile scissors, and perform surface sterilization in the ultra-clean bench according to the following procedures, 3% H 2 o 2 Rinse for 2.5 minutes, rinse with sterile water for 4 times, rinse with 70% alcohol for 3 times, rinse with sterile water for 3 times, rinse with 3% NaClO solution for 5 minutes, rinse with sterile water for 3 times, and take the sterile water used for the last rinse of plant materials respectively 100 μL and surface-sterilized plant samples were transferred to LB solid medium (peptone 10g, yeast extract 5g, NaCl 10g, agar powder 1.8%, constant volume 1000mL, pH 7.0, sterilized at 121°C) plates and cultured at 30°C for 24h, No microorganisms grow ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Plant samples were collected from the constructed wetland, and the endophyte isolation and screening test was carried out immediately. After cleaning the collected fresh plant material samples with sterile water, cut them into 1cm-long pieces with sterile scissors, completely immerse the plant material in a stoppered Erlenmeyer flask or a beaker with a cover filled with 150mL-200mL sterile water, and ultrasonically Sterilize for 25 minutes, with a working frequency of 20KHz and a power of 150W; put the plant material in a sterile mortar, add 2g of sterile quartz sand and 10mL of sterile phosphate buffer (pH7.2), grind and pulverize until homogenized, and take Supernatant 0.5mL, inoculated in 100mL inorganic salt liquid medium containing DBP as the only carbon source, 30 ℃, 150rpm, dark shaker culture, every 7 days as a cycle, gradually increase the initial concentration of DBP, 100mg / Gradient acclimatization from L to 800mg / L; -6 Spread it on a plate containing 1000mg...
Embodiment 3
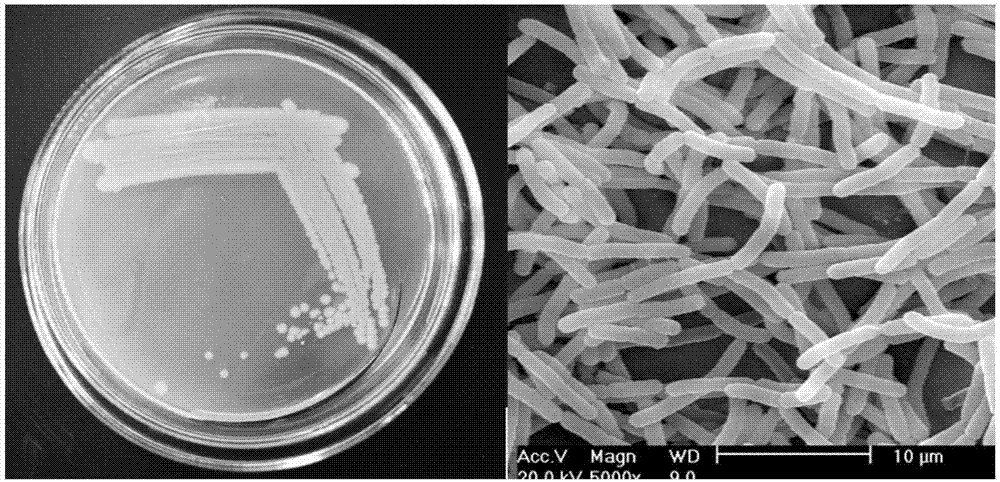
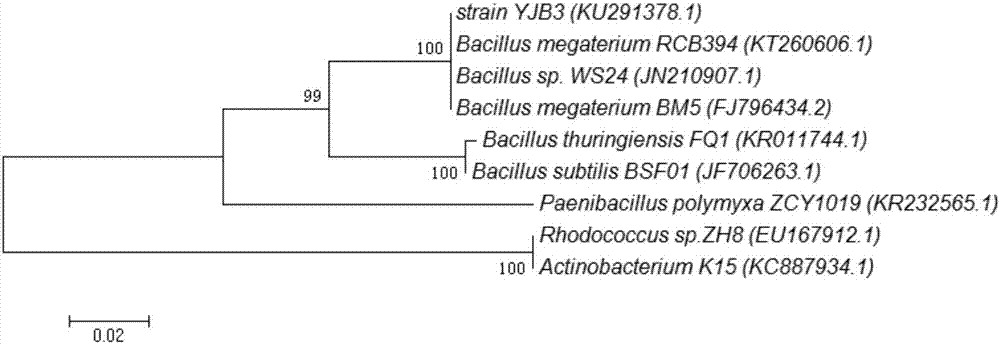
[0041] (1) Identification of strain morphological characteristics: Streak inoculation of strain YJB3 in LB solid medium, place the plate upside down in a constant temperature incubator, and incubate at a constant temperature of 30°C for 12-18 hours, observe the colony shape, the colony is smooth, light yellow, with neat edges, easy to pick Gram staining of the strain, Gram-positive bacteria, using scanning electron microscope observation, the strain is a long bacillus, 1.5-2.0 μm wide, 5.2-7.8 μm long, see figure 1 .
[0042] (2) Physiological and biochemical tests related to bacterial strains
[0043] Methyl red experiment, urease experiment, catalase experiment, sugar fermentation experiment, starch hydrolysis experiment, citrate experiment, H 2 S test, Voges-Proskauer test, indole test, gelatin hydrolysis test and a series of related physiological and biochemical tests, detailed results are shown in Table 1.
[0044] Table 1 The results of physiological and biochemical te...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com