Application of interferon kappa in preparation of anti-enveloped virus medicines
An interferon and envelope technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of public health safety hazards, inability to determine IFN-κ enveloped virus, inconsistent replication mechanism, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
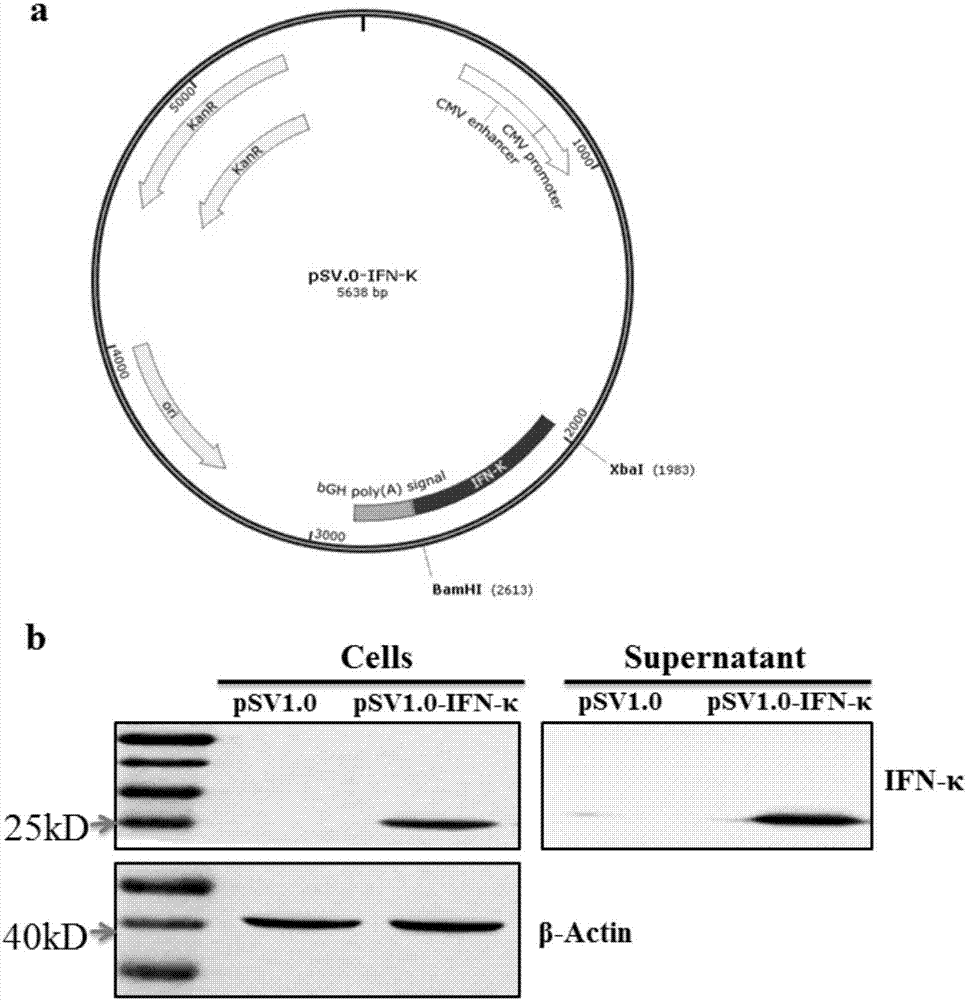
[0014] Example 1: Construction of pSV1.0-IFN-κ overexpression plasmid
[0015] The present invention has cloned IFN-κ from the human genome, the nucleotide sequence of its coding gene is shown in SEQ ID No.1, the full-length amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.2, and the IFN-κ described in the present invention Belonging to the type I interferon family, it has only 30% homology with IFN-α and IFN-β.
[0016] In order to study the function of IFN-κ, we constructed the eukaryotic expression vector of IFN-κ, and eukaryotically expressed the mature secreted protein in cell lines in vitro, and then detected the effect of IFN-κ protein on the replication of influenza virus and Zika virus influences. First, we used the eukaryotic expression vector pSV1.0 to construct the IFN-κ eukaryotic expression plasmid. The construction method was as follows: the cDNA generated by reverse transcription of RNA extracted from A549 cells was used as a template, and the corresponding primers w...
Embodiment 2
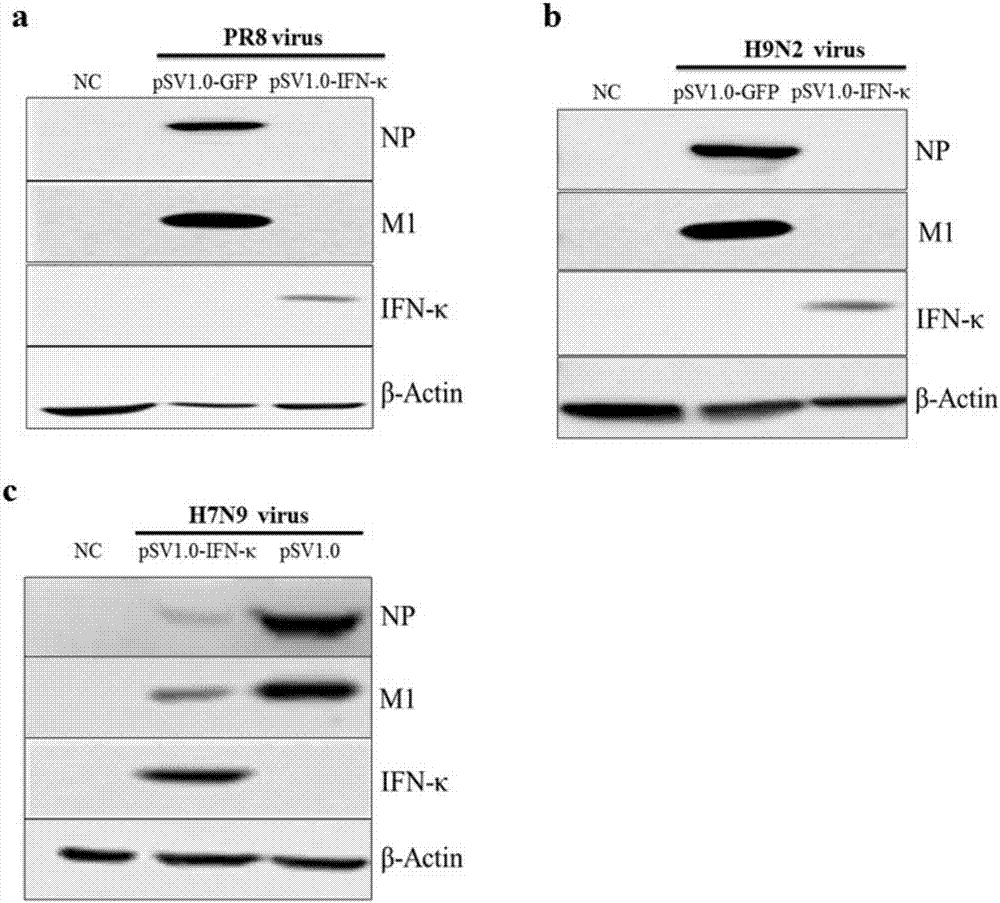
[0020] Example 2: IFN-κ inhibits the replication of influenza viruses H7N9, PR8 and H9N2
[0021] The lung epithelial cell line A549 is derived from human non-small cell lung cancer epithelial cells, which is the main cell model for studying influenza virus infection. In order to verify the effect of IFN-κ on different subtypes of influenza virus infection, this example uses 12-well plates The pSV1.0-IFN-κ overexpression plasmid and the control plasmid pSV1.0-GFP were transfected in the A549 cell line. After 24 hours, 100 μL of three influenza virus PR8 ( figure 2 a), H9N2 ( figure 2 b), and H7N9 ( figure 2 c), the average number of virus-infected particles per cell (MOI) is 1. in CO 2 After continuing to incubate in the incubator for 2 hours, discard the virus solution, wash it twice with PBS, add DMEM complete medium and continue to culture for 48 hours, then collect the cells, and analyze the expression of IFN-κ and the expression of influenza virus nucleoprotein NP a...
Embodiment 3
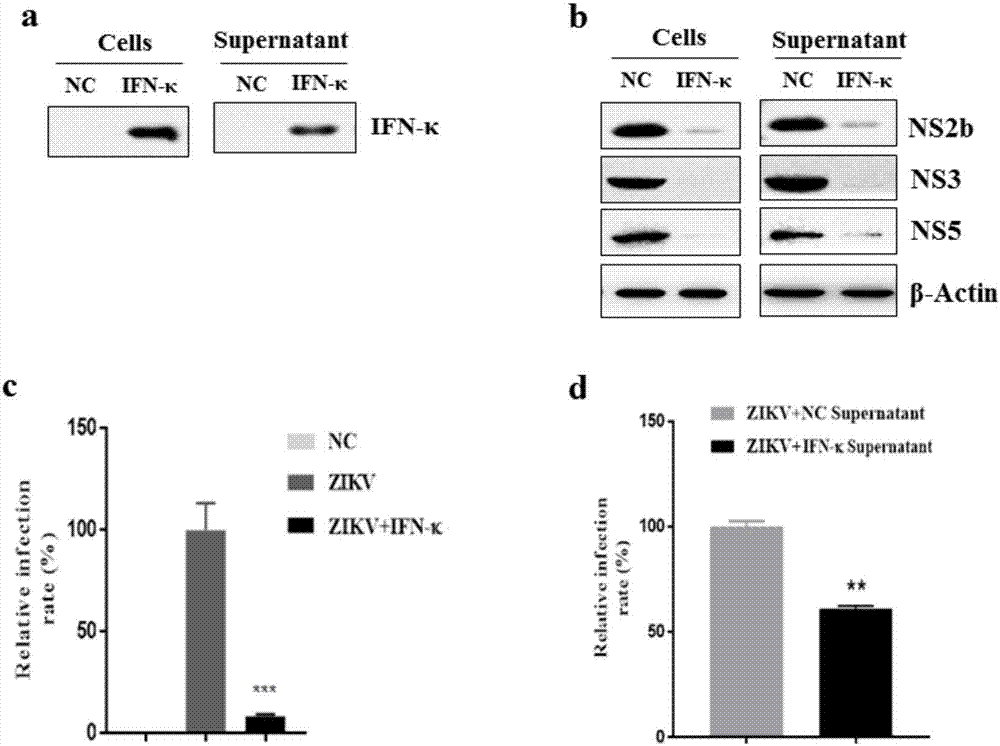
[0023] Example 3: IFN-κ inhibits the replication of Zika virus
[0024] Astrocyte U-251 cells are one of the main target cells of Zika virus infection. In order to verify the effect of IFN-κ on Zika virus infection, U-251 cells were used to transfect control plasmids pSV1.0 and pSV1.0-IFN-κ plasmids. After 36 hours of transfection, cells in some wells were harvested to detect IFN in the cells -κ protein expression level ( image 3 a-left). The remaining cells were infected with Zika virus at a multiplicity of infection (MOI = 2), infected at 37 °C for 2 h, washed twice with PBS, and replaced with fresh DMEM medium containing 2% FBS to continue culturing. After 36 hours of Zika virus infection, the cells were harvested, and a part of the cells were used for western blot (WB) analysis of the expression levels of Zika virus non-structural proteins (NS2b, NS3, NS5) in U-251 cells ( image 3 b-left). Another part of cells was analyzed by immunofluorescence staining technique to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com