rAAV8-CRISPR-SaCas9 system and application of system in preparing hepatitis B therapeutics
A drug, hepatitis B virus technology, applied in the field of gene mutation and genetic engineering, can solve the problem of not being able to effectively inhibit HBV replication and so on
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Example 1 Construction of the CRISPR-SaCas9 system with different targets
[0044] 1. CRISPR-SaCas9 target selection
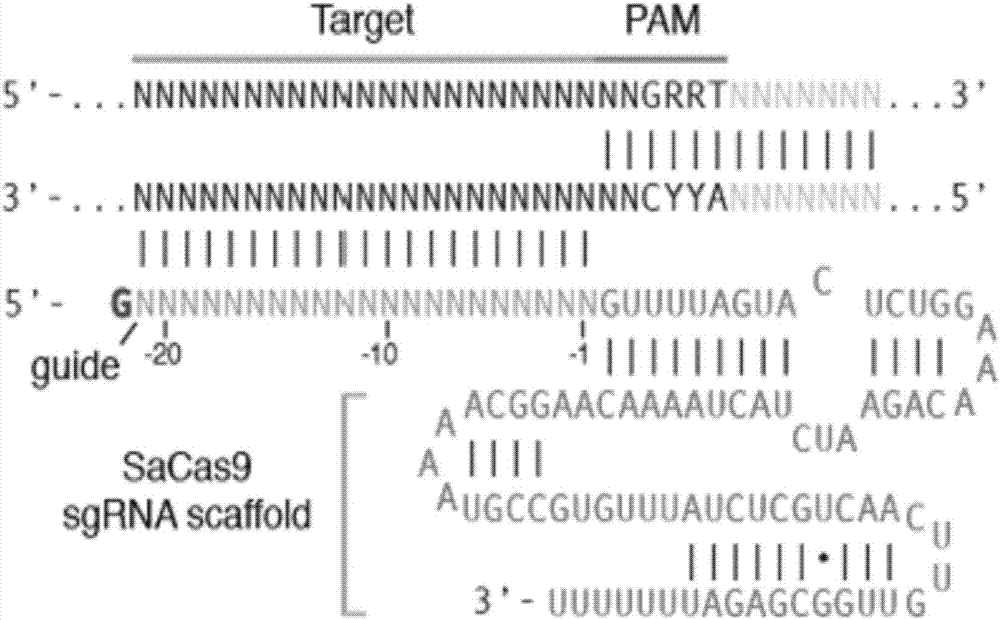
[0045] Find the region with the "NNGRRT" PAM original in the HBV sequence, and try to stay away from the GC-rich region to avoid the possible impact of CpG methylation on gRNA recognition. Select the first 21-23bp of the PAM original as the gRNA sequence, and the first base is G is the best (see the structure of the gRNA figure 1 ). Add a Bsa I restriction site before the screened gRNA sequence: add AAAC at the 3' end and CCAC at the 5' end.
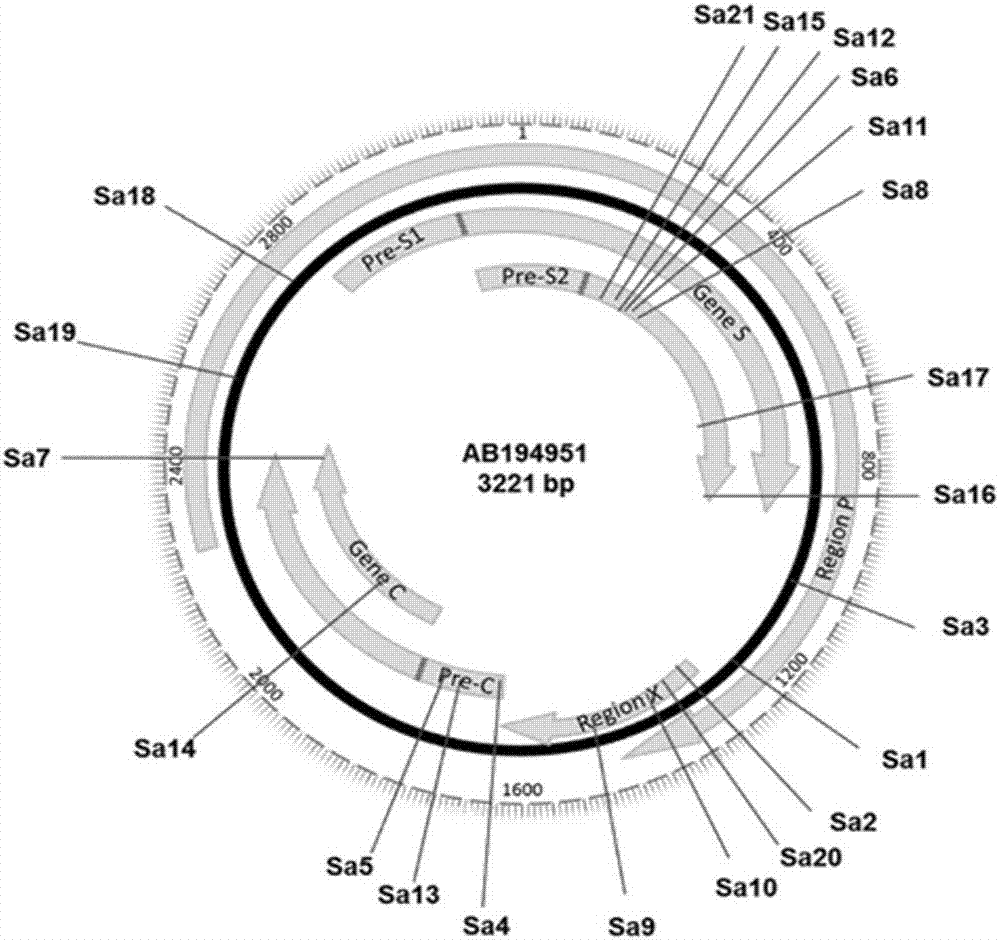
[0046] According to the principle of target site screening, the target site of CRISPR-SaCas9 was finally determined by comparing the HBV sequences of each genotype and searching for the "NNGRRT" PAM motif in the conserved region. Through screening, we obtained 21 target sites located in different genes of the HBV genome. The sequence information of each site is shown in Table 1. The position of each site on the...
Embodiment 2
[0104] Example 2. Observation of the Inhibition Efficiency of CRISPR-SaCas9 Systems with Different Targets to Intracellular HBV
[0105] The 21 sets of CRISPR-SaCas9 systems containing different targets obtained in Example 1 were co-transfected into 293T cells with the HBV expression vector pGL3-HBV1.2, and the cell culture supernatant was collected on the 3rd day after transfection, and tested by ELISA The content of HBsAg and HBeAg in the cell supernatant was detected by the method. The detection results of HBsAg are as follows: Figure 5 As shown, compared with the control group transfected with gRNA-empty, five sets of systems including Sa-4, Sa-6, Sa-10, Sa-16 and Sa-20 among the 21 sets of CRISPR-Cas9 systems were able to express the cells on The average content of HBsAg in the serum was reduced by more than 2 / 3.
[0106] The detection results of HBeAg content in the cell supernatant are as follows: Figure 6 As shown, compared with the control group transfected with ...
Embodiment 3
[0107] Example 3. CCK-8 method to observe the effect of CRISPR-SaCas9 system with different targets on cell activity
[0108] In order to detect whether the inhibition of HBV by the above 8 sets of CRISPR-SaCas9 systems is caused by the inhibition of cell activity, the cell activity was detected by the CCK-8 method. The experiments were divided into 11 groups: transfection of the CRISPR-SaCas9 expression vector px601 without the target, 8 sets of CRISPR-SaCas9 systems that could effectively inhibit HBsAg or HBeAg in the cell supernatant in the previous experiment, and only transfection reagent LTX group and no treatment group, each set three parallel wells. After 48 hours of transfection, the absorbance value was detected at a wavelength of 450nm, and the results were as follows: Figure 7 shown. Compared with the control group, except for Sa-6 and Sa-20, other targets had no significant effect on cell viability (p>0.05).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com