Method for quickly detecting polyaromatic hydrocarbons in seawater or marine sediments by utilizing gene expression change
A technology for marine sediments and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, which is applied in the field of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollution, can solve problems such as low sensitivity and long cycle, and achieve the effects of high reliability, stable and reliable quality, and easy large-scale promotion and application.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] 1. Experimental organisms
[0020] A 120-day-old adult mullet goby was used as the experimental organism. The experimental fish were cultured in a recirculating aquaculture system with a water temperature of 26°C and a salinity of 20°C. Artemia nauplii and compound feed were fed once a day, and half of the water was changed every week. 24 hours before the start of the experiment, the experimental fish were selected for temporary raising in still water. During the temporary raising, the temperature was controlled at 26±0.5°C, the salinity was 20±1, and the dissolved oxygen was above 60% saturation.
[0021] 2. Sample preparation
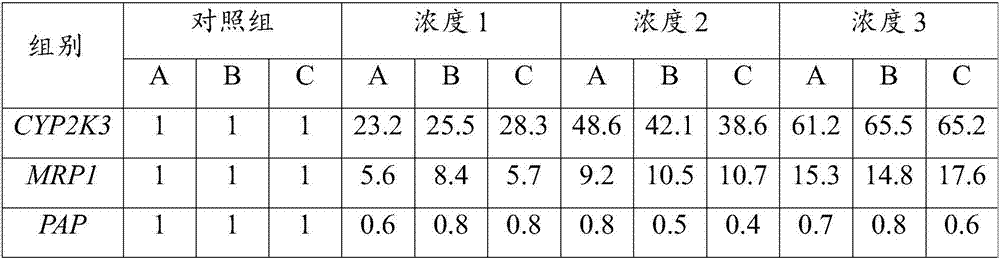
[0022] The test water is uncontaminated natural seawater, and the salinity is diluted to 20 with aerated tap water. According to Table 1, benzo(a)pyrene with a purity of 99.9% was used to prepare a control group and 3 concentration groups, and each group had 3 repetitions.
[0023] 3. Toxicity test
[0024] The test container is a 2L glass ...
Embodiment 2
[0051] 1. Experimental organisms
[0052]A 90-day-old adult mullet goby was used as the experimental organism. The experimental fish were cultured in a recirculating aquaculture system with a water temperature of 26°C and a salinity of 30°C. Artemia nauplii and compound feed were fed once a day, and 1 / 2 of the water was changed every week. 24 hours before the start of the experiment, the experimental fish were selected and raised in still water temporarily. During the temporary raising period, the temperature was controlled at 26±0.5°C, the salinity was 30±1, and the dissolved oxygen was above 60% saturation.
[0053] 2. Sample preparation
[0054] The test sample was seawater known to be polluted by PAHs in the South China Sea, and the control group was natural seawater without pollution. Prepare 1 control group and 1 concentration group, and set 3 repetitions for each group.
[0055] 3. Toxicity test
[0056] The test container is a 2L glass beaker, the test solution is ...
Embodiment 3
[0081] 1. Experimental organisms
[0082] A 90-day-old adult mullet goby was used as the experimental organism. The experimental fish were cultured in a recirculating aquaculture system with a water temperature of 26°C and a salinity of 30°C. Artemia nauplii and compound feed were fed once a day, and 1 / 2 of the water was changed every week. 24 hours before the start of the experiment, the experimental fish were selected and raised in still water temporarily. During the temporary raising period, the temperature was controlled at 26±0.5°C, the salinity was 30±1, and the dissolved oxygen was above 60% saturation.
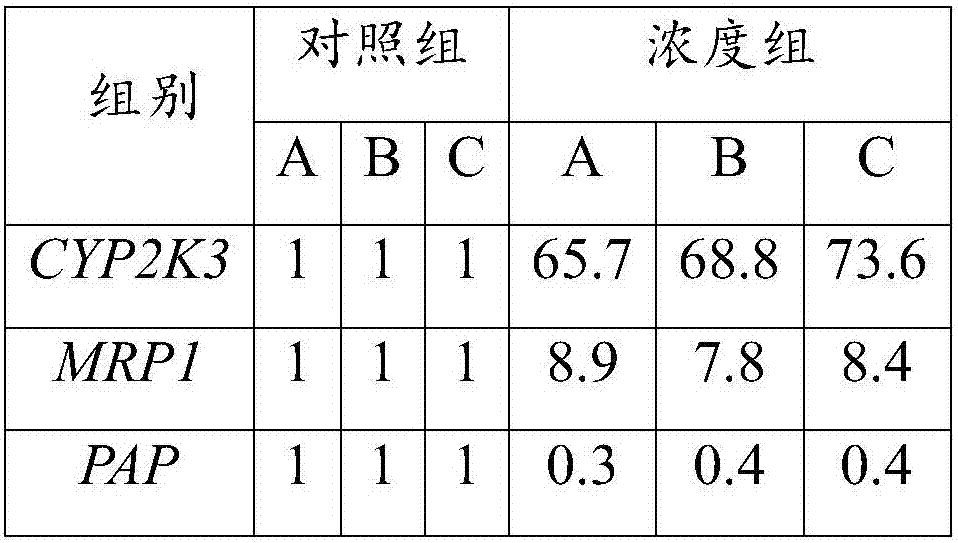
[0083] 2. Sample preparation
[0084] The samples were sediments known to be polluted by PAHs in a port in the South China Sea, and the dilution water was unpolluted natural seawater with a salinity of 30. Take the sediment and dilution water, mix them in a volume ratio of 1:4, stir at 2000r / min for 30 minutes, let stand for 1 hour, and take the supernatant for toxic...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com