Zirconium and zirconium alloy lithium content measuring method
A zirconium alloy and content technology, applied in the field of chemical analysis, can solve the problems of poor stability of measurement results, difficulty in lithium content, interference of easily ionized elements, etc., and achieve the effect of high international recognition, high accuracy and fast analysis speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
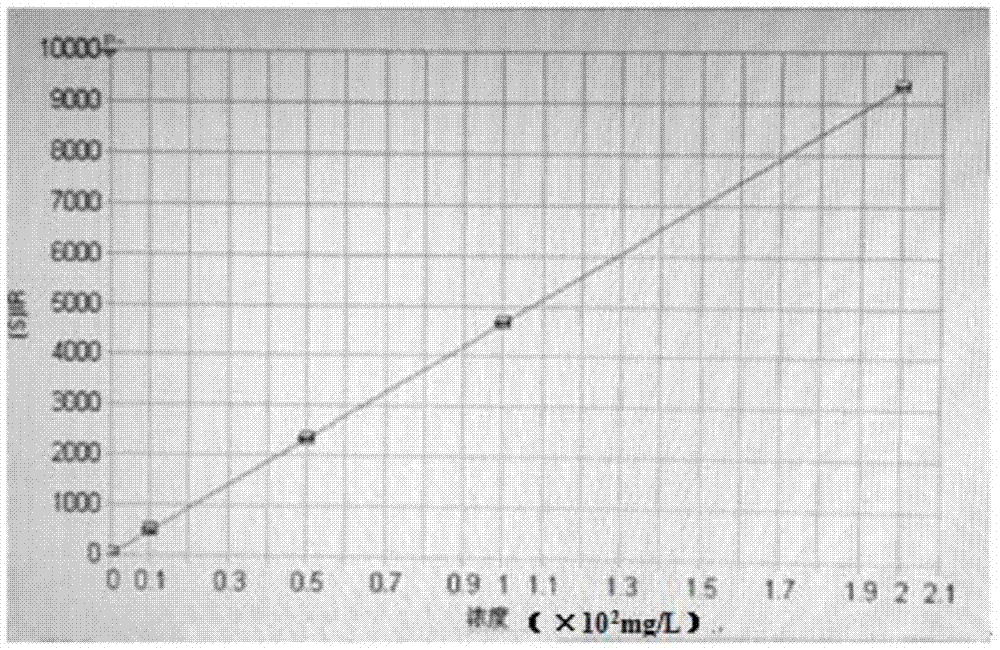
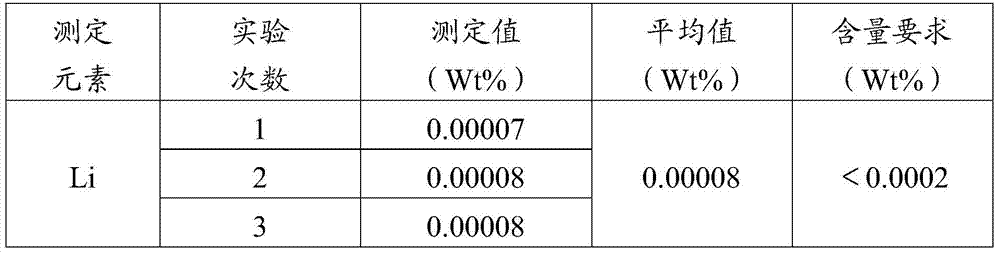
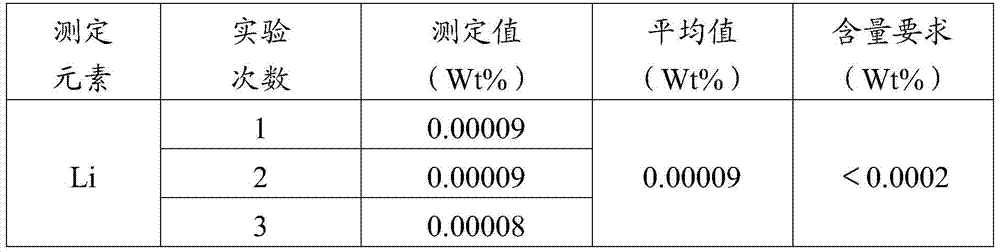
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] The method for determining lithium content in zirconium and zirconium alloys in the present embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0027] Step 1, turning pure zirconium or zirconium alloy to obtain chip-like samples, then cleaning the chip-like samples and drying them for later use;
[0028] In the specific implementation process of this embodiment, the pure zirconium or zirconium alloy chip-like sample was soaked and cleaned with absolute ethanol for more than 30 seconds, and then the sample was rinsed with pure water for more than 10 times, and then the chip-like sample was kept at a temperature not exceeding 50°C. Dry under the condition of high temperature; the absolute ethanol is above the analytical grade, and the pure water meets the requirements of GB / T 6682 laboratory grade water;
[0029] Step 2, using the heap cone quartering method to shrink and select the chip sample after drying in step 1 to obtain the sample to be tested;
[0030] In this embodiment...
Embodiment 2
[0044] The method for determining lithium content in zirconium and zirconium alloys in the present embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0045] Step 1, turning pure zirconium or zirconium alloy to obtain chip-like samples, then cleaning the chip-like samples and drying them for later use;
[0046] In the specific implementation process of this embodiment, the pure zirconium or zirconium alloy chip-like sample was soaked and cleaned with absolute ethanol for more than 30 seconds, and then the sample was rinsed with pure water for more than 10 times, and then the chip-like sample was kept at a temperature not exceeding 50°C. Dry under the condition of high temperature; the absolute ethanol is above the analytical grade, and the pure water meets the requirements of GB / T 6682 laboratory grade water;
[0047] Step 2, using the heap cone quartering method to shrink and select the chip sample after drying in step 1 to obtain the sample to be tested;
[0048] In this embodiment...
Embodiment 3
[0062] The method for determining lithium content in zirconium and zirconium alloys in the present embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0063] Step 1, turning pure zirconium or zirconium alloy to obtain chip-like samples, then cleaning the chip-like samples and drying them for later use;
[0064] In the specific implementation process of this embodiment, the pure zirconium or zirconium alloy chip-like sample was soaked and cleaned with absolute ethanol for more than 30 seconds, and then the sample was rinsed with pure water for more than 10 times, and then the chip-like sample was kept at a temperature not exceeding 50°C. Dry under the condition of high temperature; the absolute ethanol is above the analytical grade, and the pure water meets the requirements of GB / T 6682 laboratory grade water;
[0065] Step 2, using the heap cone quartering method to shrink and select the chip sample after drying in step 1 to obtain the sample to be tested;
[0066] In this embodiment...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com