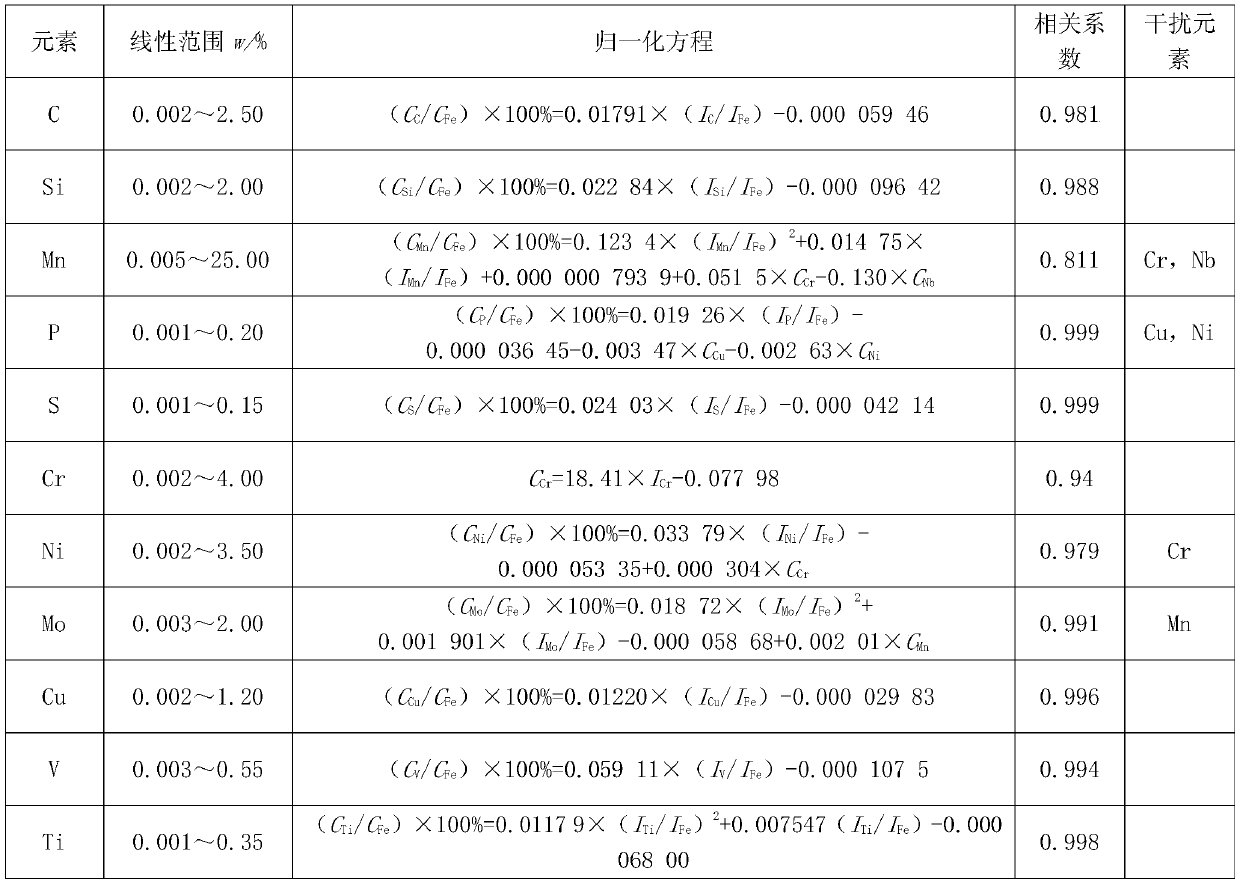
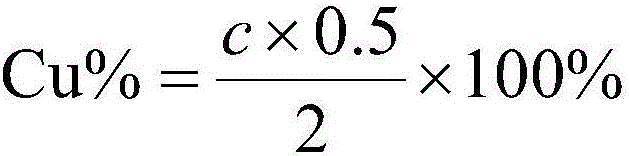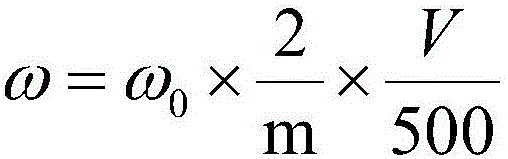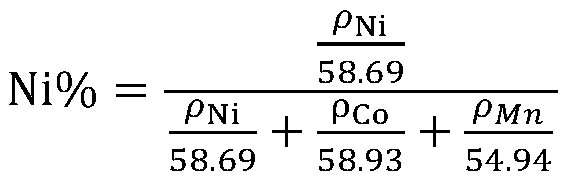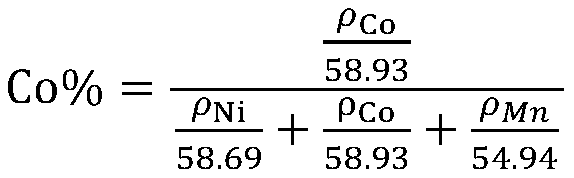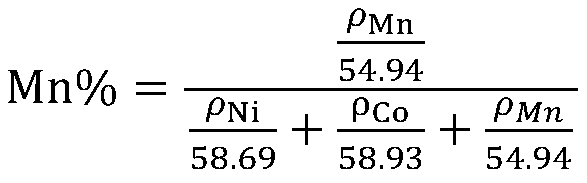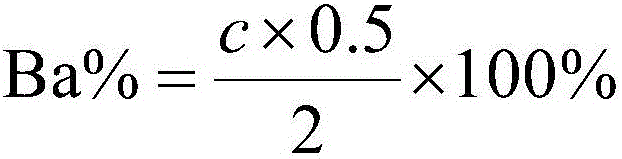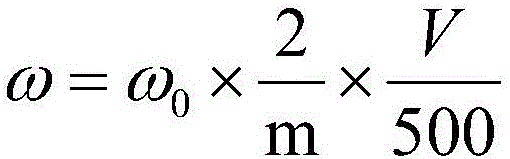Patents
Literature
55results about How to "Small matrix effect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
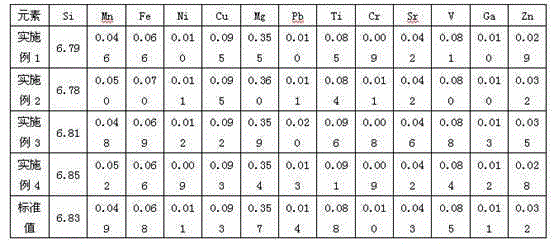
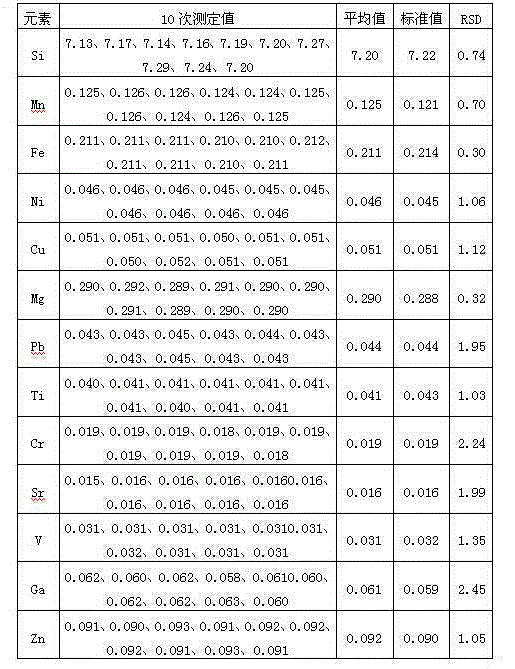
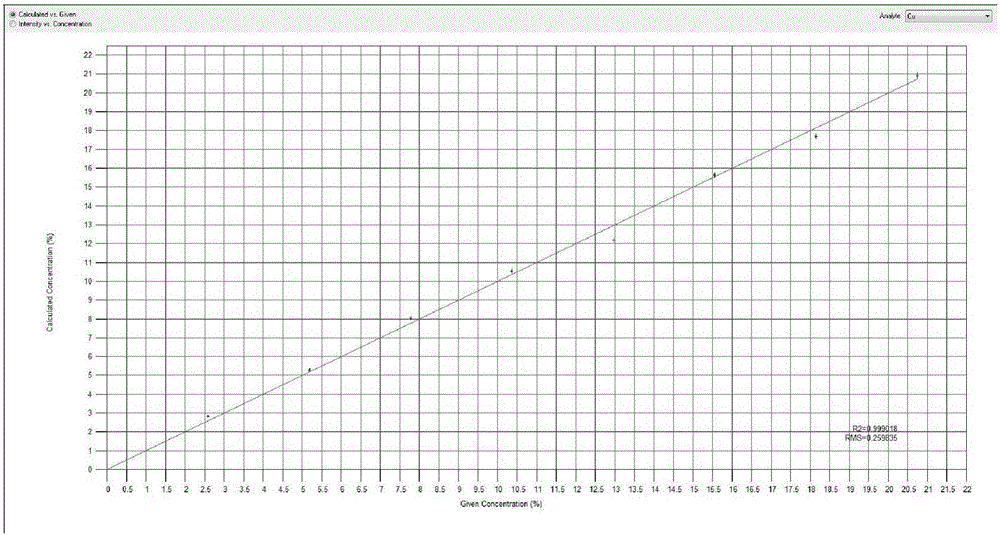
Metal alloy XRF spectrometry utilizing new sample preparation technology
InactiveCN102207475AHigh melting pointSolve the problem that cannot be detected by X-ray fluorescence spectroscopyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPreparing sample for investigationCarbonizationAcid dissolution
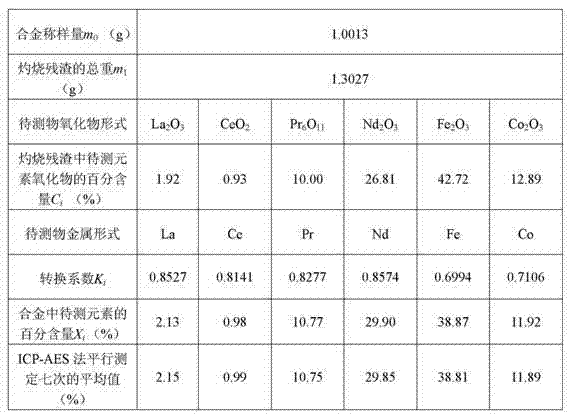
The invention provides a metal alloy XRF spectrometry utilizing a new sample preparation technology. The technology comprises the following steps: 1) acid dissolution: dissolving a metal alloy with inorganic acid; 2) precipitation: adjusting the above dissolved sample solution to be alkaline to precipitate elements to be measured, and filtering the precipitation with ashless filter paper; 3) calcination: placing the filtered filter residues together with the filter paper in a porcelain crucible calcined to a constant weight, conversing the filter residues into metal oxides through steps of drying, carbonization, ashing, calcination, etc, and calculating a weight of calcined filter residues; 4) sheet melting: preparing the above calcined filter residues into a sample sheet by a fusion sample preparation method for detection by an XRF spectrometer, and obtaining contents of elements to be measured in the metal alloy through conversion of obtained data. The invention enables the XRF spectrometry to be applied to detections of some special metal alloys which have a high melting point, a high hardness and is easily oxidized.
Owner:INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT OF XIAMEN ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Slug flow microextraction-paper spray mass spectrometry technology
InactiveCN106404945AHigh sensitivityImprove solubilityComponent separationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryHigh pressure
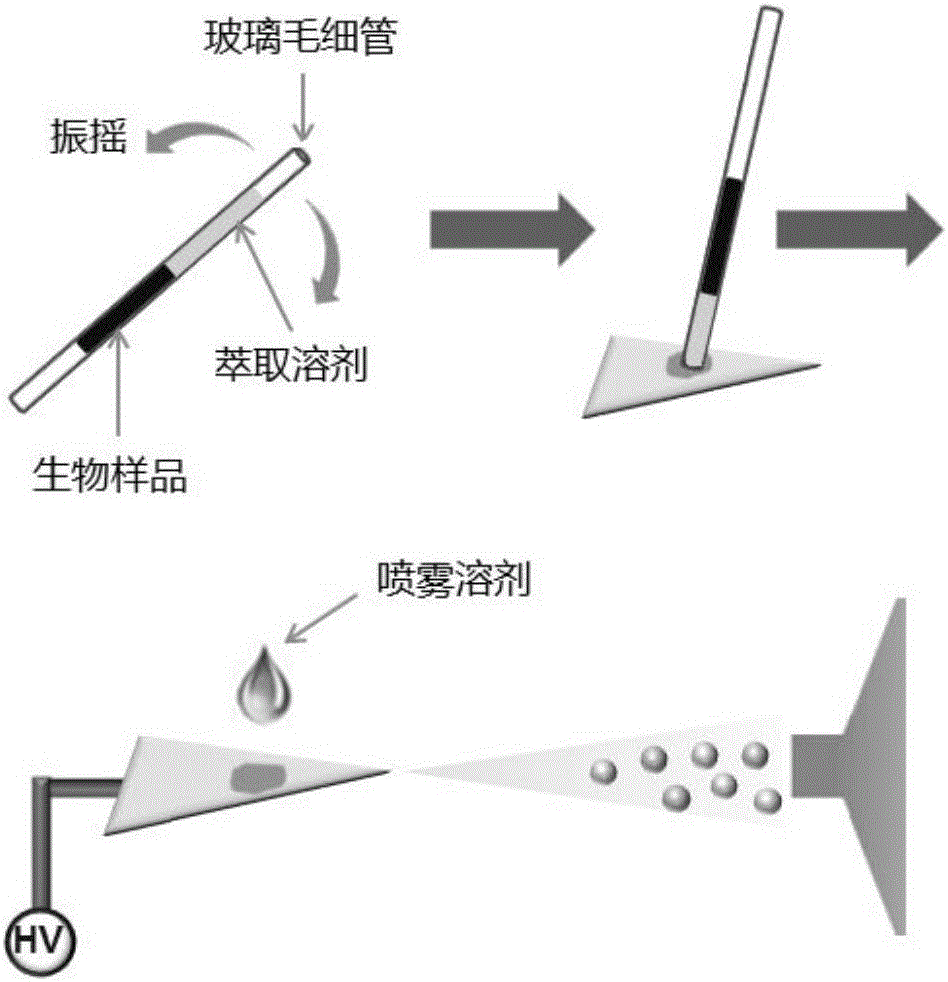
The invention belongs to the field of analytical chemistry, and relates to slug flow microextraction-paper spray mass spectrometry technology (SFME-PS-MS) and a system and application of the technology. According to the SFME-PS-MS technology, a capillary is adopted to fast extract and gather a trace compound from a complex base sample, the extracted liquid is dropwise added to paper, the obtained paper is allowed to be close to an entrance of mass spectrometry after an extraction solvent is dried through volatilization, the direct-current high-pressure electric field is applied to the paper, a spray solvent is dropwise added to the paper, and the target compound is desorbed and ionized in the action of the electric field and the spray solvent and enters the mass spectrometry for analysis. New microextraction and normal-pressure ambient mass spectrometry technology is developed, so that the trace compound in a complex biological and environmental sample can be fast, sensitively and accurately analyzed.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method for measuring indissolvable nickel-base superalloy multielement content with microwave digestion ICP method
InactiveCN105319202AAvoid hydrolysisAvoid compromising measurement accuracyAnalysis by thermal excitationPhosphoric acidHydrolysis
The invention discloses a method for measuring the indissolvable nickel-base superalloy multielement content with the microwave digestion ICP method. According to the method, a sample is digested in a microwave digestion instrument with hydrochloric acid, the acidity of a sample solution and the acidity of a standard solution are stabilized with a sulfuric acid and phosphoric acid mixture, then citric acid is added to prevent high-valent metal ion hydrolysis, the content of a matrix is adjusted for the matching purpose, a standard solution curve is made finally, and a proper analytical line is selected for measurement on an inductive coupling high-frequency plasma atomic emission spectrometer. Due to the fact that the sample is digested by means of hydrochloric acid, pollution to a hydrofluoric acid eroding instrument by a quartz feeding system of the instrument is avoided, and then measurement accuracy can not be affected. Meanwhile, the acidity of the sample solution and the acidity of the standard solution are stabilized with the sulfuric acid and phosphoric acid mixture, then citric acid is added to prevent high-valent metal ion hydrolysis, the content of the matrix is adjusted for the matching purpose, and therefore matrix effect is reduced.
Owner:GUIZHOU AEROSPACE PRECISION PRODS
Method for simultaneously determining content of phosphorus, magnesium, iron, aluminum, silicon, calcium, titanium, manganese and strontium in phosphorite by adopting ICP-AES
InactiveCN106290318ANo distractionNo apparent interferencePreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationLithium metaborateLithium bromide
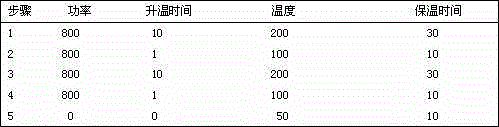
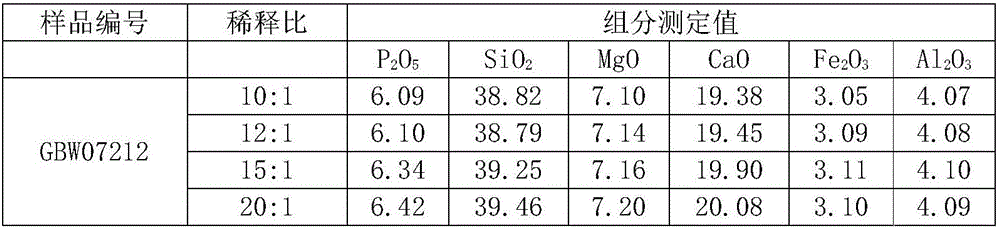
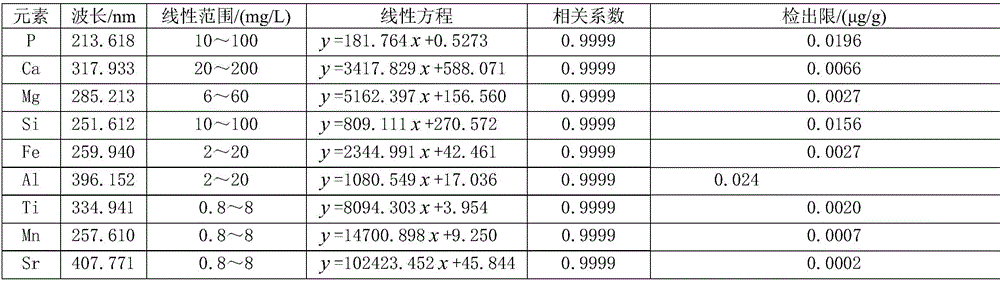
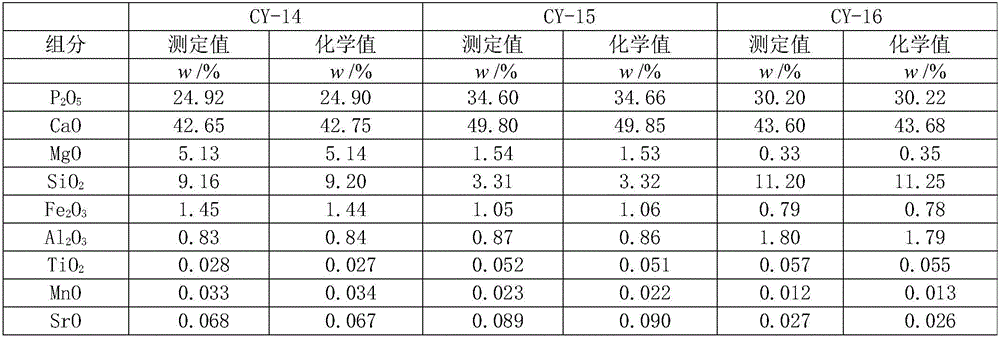
The invention relates to the technical field of analysis test, and in particular relates to a method for simultaneously determining content of phosphorus, magnesium, iron, aluminum, silicon, calcium, titanium, manganese and strontium in phosphorite by adopting inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES). Specifically, lithium metaborate is a non-oxidant solvent with a high melt point, has high decomposition capacity for a majority of test samples, and can effectively decompose rocks and minerals difficult to dissolve. The method comprises the following steps: placing a phosphorite test sample into a platinum crucible, adding the lithium metaborate solvent and a lithium bromide releasing agent, melting and decomposing the phosphorite sample by using a high-frequency sample melting machine, pouring in a polytetrafluoroethylene beaker with 10 percent nitric acid at a high temperature by virtue of a magnetic stirrer, after the primary sample melting acidification sizing, performing matrix matching by adopting a national grade-I phosphorite, establishing a standard curve by adopting a Yttrium internal standard method, and determining the content of phosphorus pentoxide, magnesium oxide, iron oxide, aluminum oxide, silicon dioxide, calcium oxide, titanium oxide, manganese oxide and strontium oxide in the phosphorite by adopting the ICP-AES. The method has the advantages of rapidness, convenience and accuracy, and is particularly suitable for batch determining the phosphorite samples.
Owner:YUNNAN PHOSPHATE CHEM GROUP CORP
Method for measuring trace element content in aluminium alloy by ICP method
InactiveCN105136777AAchieve complete dissolutionReduce dosagePreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationTrace element5005 aluminium alloy
The invention discloses a method for measuring trace element content in aluminium alloy by an ICP method. A mixture of concentrated hydrochloric acid, concentrated nitric acid and water with a proportion of 1:1:2 is employed for dissolving samples. In the method, an aluminium alloy sample containing higher element silicon content can be entirely dissolved; the contents of a plurality of elements dissolved in the same solution are measured simultaneously and separately in one determination; and the analysis efficiency is high. The matrix is matched and matrix effect is reduced. An aluminium alloy national standard sample is measured and the measurement result meets the requirements; the analysis result is accurate and reliable. The dissolution method is simple and rapid; the method needs little reagent and saves test cost. The correction curve has a wide linear range, can meet test requirements of samples with contents from low to high. In the method, the contents of a plurality of elements are determined simultaneously in one solution; the analysis efficiency is high; and the analysis result is accurate and reliable.
Owner:HEBEI IRON AND STEEL
Method for determining copper content in pyrotechnic composition for fireworks and crackers
InactiveCN106093098AAccurate determination of copper contentReduce matrix effectMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationCu elementFireworks
The invention discloses a method for determining the copper content in a pyrotechnic composition for fireworks and crackers. The method comprises the steps that copper standard solutions with series of the concentration are prepared, an energy dispersion type X-ray fluorescence spectrophotometer is adopted as a detecting instrument, a certain sample size is assumed, an analysis method is established by adopting an intensity-correcting mathmetic correction method, the mass concentration of Cu in the copper standard solutions is converted into the mass percent concentration according to the assumed sample size of a sample material and the constant volume of a test solution, the Cu fluorescence intensity generated in each sample feeding is recorded, and a calibration curve for a Cu element is drawn; a test solution of the pyrotechnic composition to be determined is prepared, the Cu element fluorescence intensity displayed on the instrument is recorded, a Cu mass percent concentration value corresponding to the fluorescence intensity is read according to the calibration curve, and the copper content in the sample is calculated. According to the method, the matrix effect among all elements in the sample can be eliminated or basically eliminated by optimizing the sample dissolving condition and all parameter conditions of the X-ray fluorescence spectrophotometer. The method is easy to operate, short in detection period, good in accuracy and high in precision.
Owner:吴俊逸
Laser-based solution ablation injection analysis method
ActiveCN109444248AReduce distractionsReduce yieldParticle separator tubesPreparing sample for investigationInductively coupled plasmaSolvent
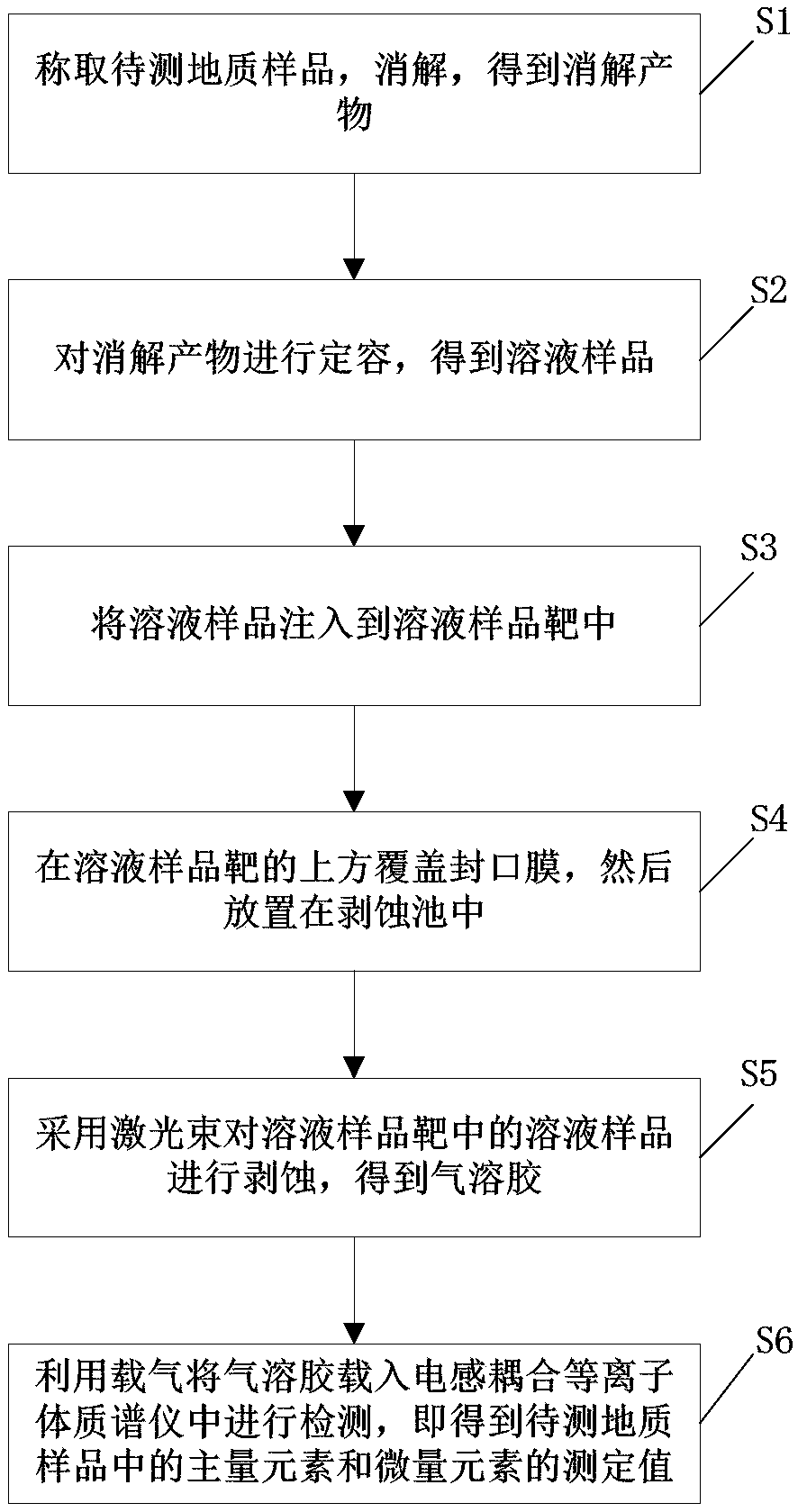
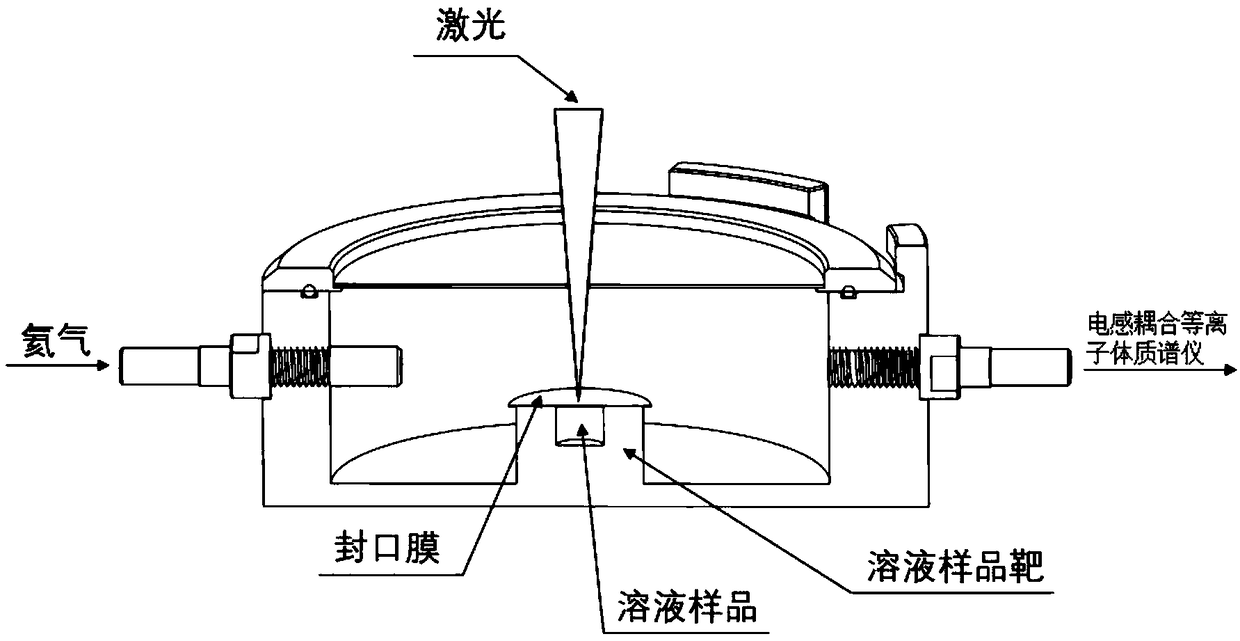
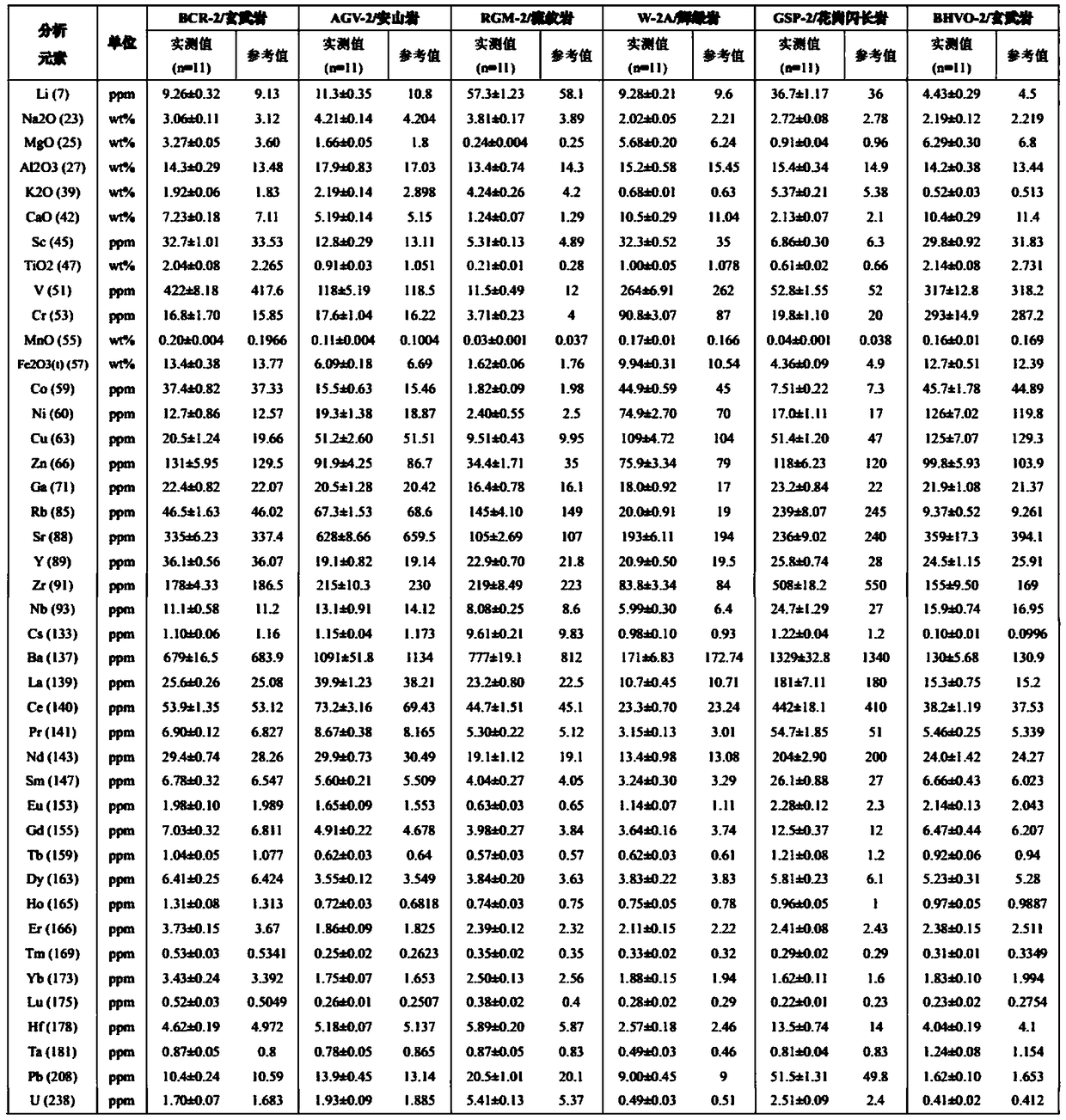
The invention provides a laser-based solution ablation injection analysis method. The method comprises the steps as follows: weighing a to-be-tested geological sample and digesting to obtain a digestion product; subjecting the digestion product to constant volume to obtain a solution sample; injecting the solution sample into a solution sample target; covering the upper part of the solution sampletarget with a sealing film, and then placing the sealed solution sample target in an ablation pool; ablating the solution sample in the solution sample target by adopting a laser beam to obtain aerosol; and loading the aerosol into an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer by utilizing a carrier gas for detection, thereby obtaining measured values of major elements and trace elements in theto-be-tested geological sample. By adopting the method provided by the invention, the problems of solvent-related polyatomic ion interference and sample matrix effect in the ICP-MS (Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometer) analysis of major elements and trace elements injected by adopting a conventional solution atomization method are overcome, and a simple, environmentally-friendly and novel injection method with a film-dissolving effect is provided for analyzing solution samples by the ICP-MS.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Method for separating and enriching trace lead in substrate
InactiveCN102141487AHigh recovery rateHigh removal ratePreparing sample for investigationHigh concentrationCentrifugation
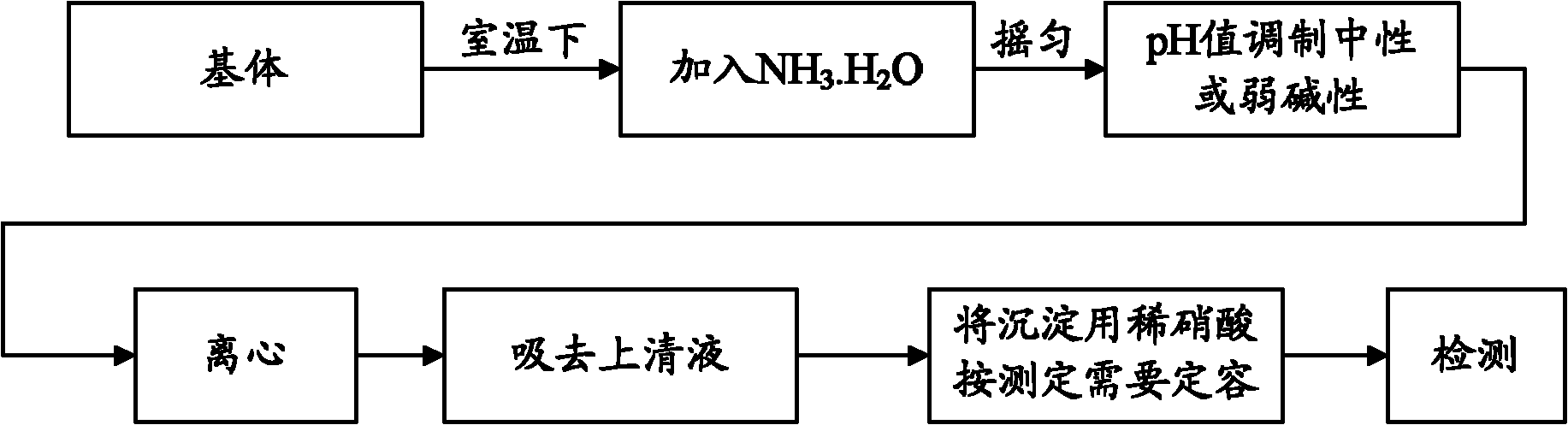
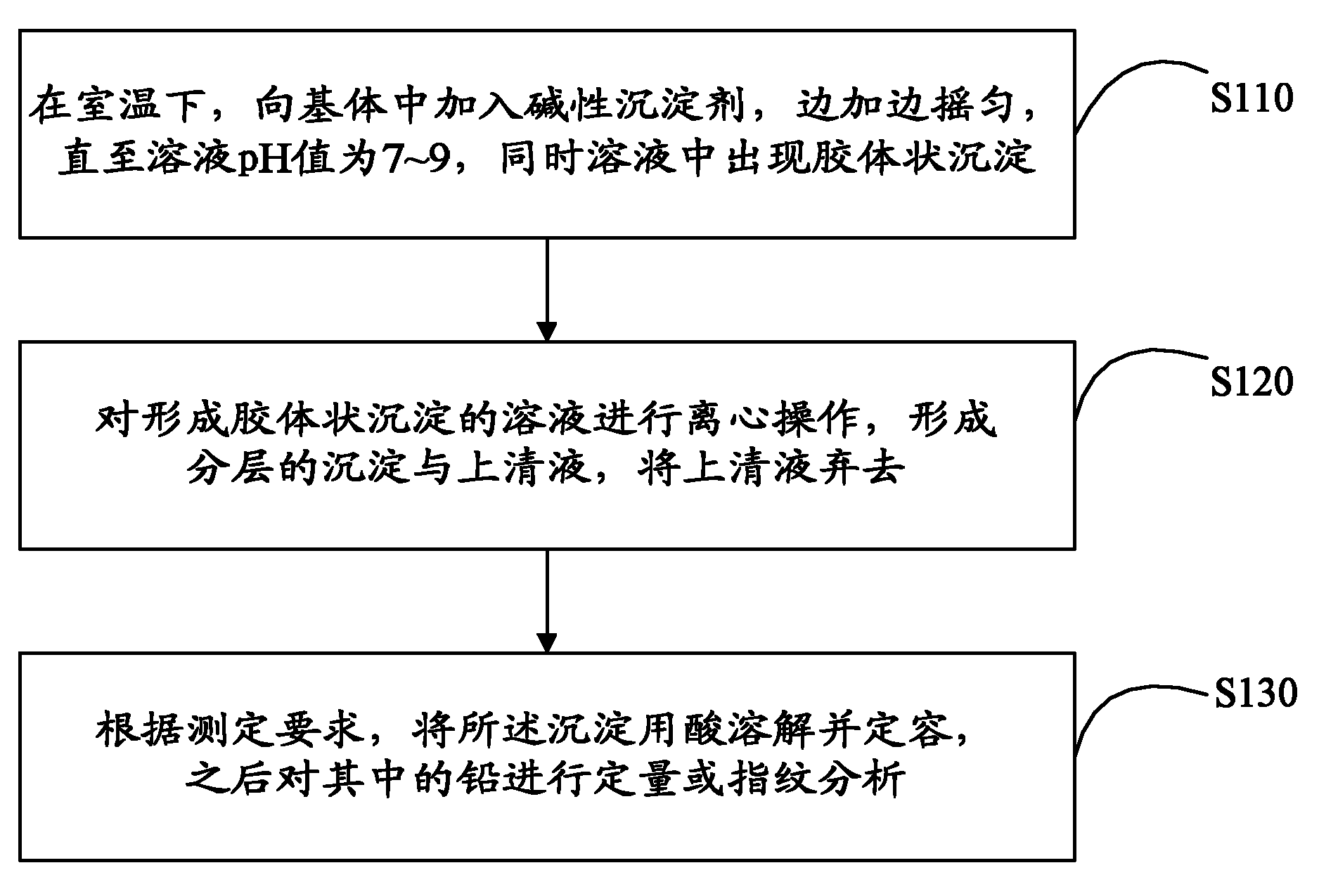
The invention discloses a method for separating and enriching trace lead in a substrate, which comprises the following steps: adding an alkaline precipitator into the substrate with shaking till the pH value of the solution is 7 to 9 and gelatinous precipitate appears in the solution; centrifuging the solution to obtain separated precipitate and supernate and removing the supernate; and according to test requirements, dissolving the precipitate in acid, fixing volume, and performing quantitative or fingerprint analysis on the lead in the solution. In the invention, a precipitation-centrifugation process is used to remove a large amount of Na, K and other ions which are not precipitated in the substrate from the supernate, the trace lead ions are separated and enriched at one step, the operation is simple and convenient, the repeatability is high, the recovery rate is high, fewer pollutants are introduced, and the method can be used for samples in which the substrate has high concentration and complex components.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
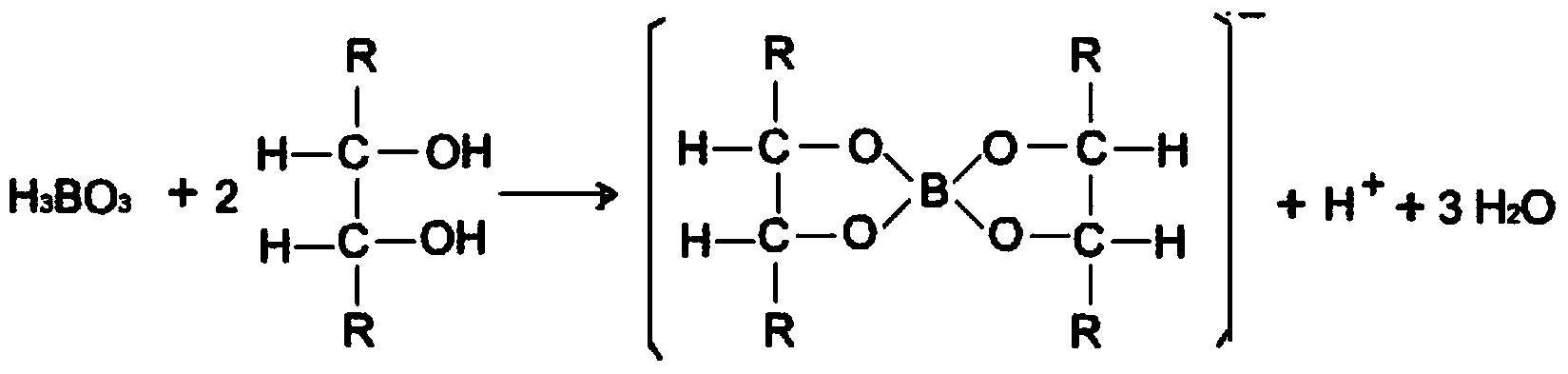
Method for rapidly measuring trace boron impurities in polysilicon
ActiveCN103760218AReduce lossesShorten the dissolution timePreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPotassium carbonateImpurity
The invention relates to a method for rapidly measuring trace boron impurities in polysilicon. The method comprises the following steps: weighting a polysilicon sample; adding a mannitol solution into the sample; adding a potassium carbonate solution into the sample; adding hydrofluoric acid, then slowly dropping nitric acid in the sample and carrying out acidified dissolving; after the sample is dissolved, heating the obtained object, and stopping heating until white smoke is emitted completely; adding hydrochloric acid into the sample and soaking, diluting with a small amount of pure water, and cooling; adding methanol into the solution, uniformly shaking and making up to volume; rinsing ICP-MS (Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry) respectively by using ammonia water and pure water; and after the ICP-MS is rinsed completely, detecting the solution sample with metered volume by using ICP-MS, so that the boron content of the sample can be accurately measured. The method disclosed by the invention is simple in process, low in cost, can measure accurately, and rapidly measure the boron content of polysilicon.
Owner:福建上杭兴恒硅品有限责任公司
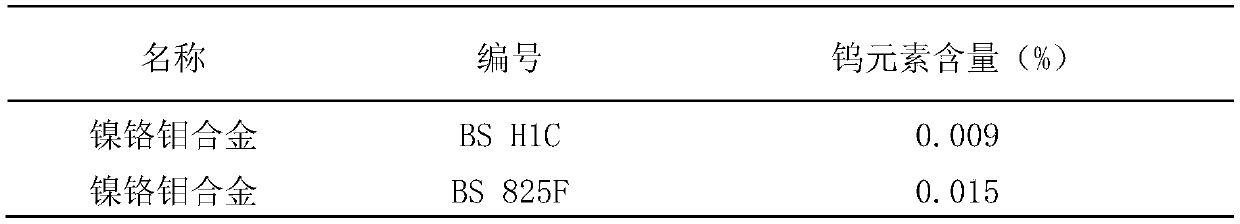
Method for determining content of tungsten element in nickel-based alloy
PendingCN111426679AGood precisionImprove detection efficiencyAnalysis by electrical excitationOptical spectrometerPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a method for determining the content of a tungsten element in a nickel-based alloy by applying a glow discharge spectrometer approach technology method. The method comprises the following specific determination steps: (1) determining analysis conditions; (2) drawing and confirming a calibration curve; (3) standardizing types; (4) analyzing a sample; and (5) processing testdata. The detection method provided by the invention is convenient to operate, rapid in measurement and accurate in detection, greatly improves the detection efficiency and accuracy of the tungsten element in the nickel-based alloy, widens the detection range of the tungsten element in the nickel-based alloy, and is suitable for measuring the content of the tungsten element in nickel-based alloysof various models.
Owner:HEBEI IRON AND STEEL
Method for determining calcium, magnesium, iron and copper in industrial boiler through microwave digestion-inductive coupling plasma emission spectrometry
InactiveCN109115590AAvoid cross contaminationHigh precisionPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationWater qualityPollution
The invention provides a method for determining calcium, magnesium, iron and copper in industrial boiler through a microwave digestion-inductive coupling plasma emission spectrometry. According to themethod provided by the invention, microwave digestion is used as a pre-treatment technology, and time and temperature for microwave digestion of a sample are optimized; a suitable analysis line is selected, so that the measurement time is reduced and the measurement accuracy is improved; a reagent blank background can be reduced and crossed pollution of the sample is avoided; meanwhile, an inductive coupling plasma emission spectrometry is combined, so that the method has various advantages of high precision, rapid analysis speed, small matrix effect, low detection limit, environment friendliness, capability of realizing simultaneous determination of a plurality of elements in water and the like, and the working efficiency is effectively improved.
Owner:河北省特种设备监督检验研究院
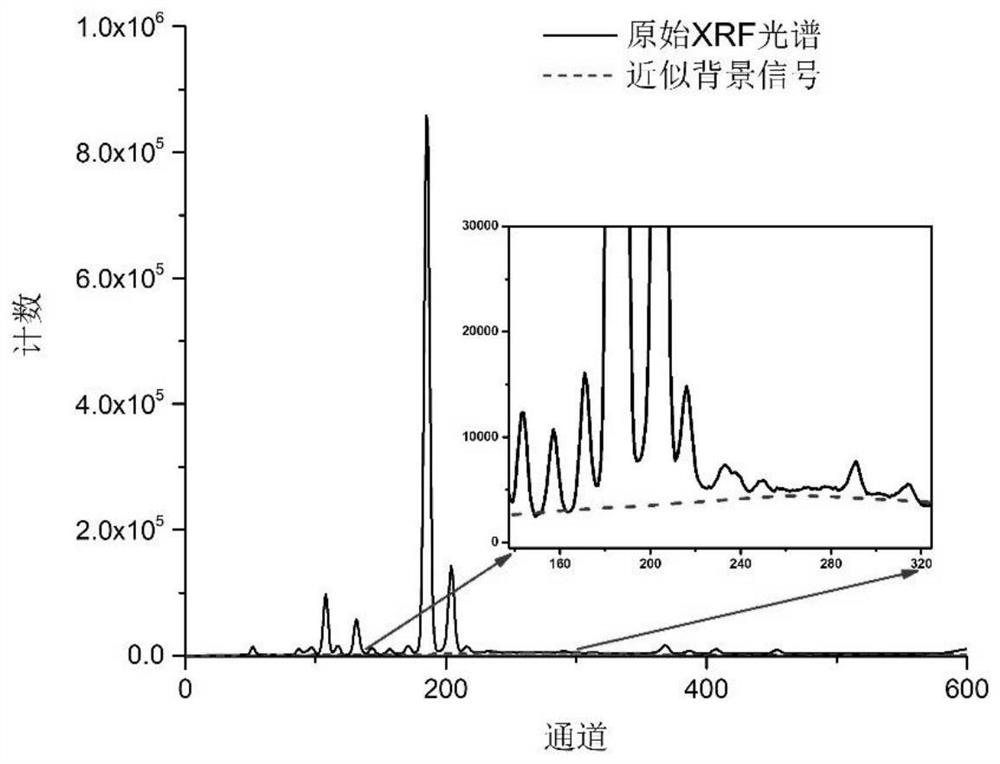
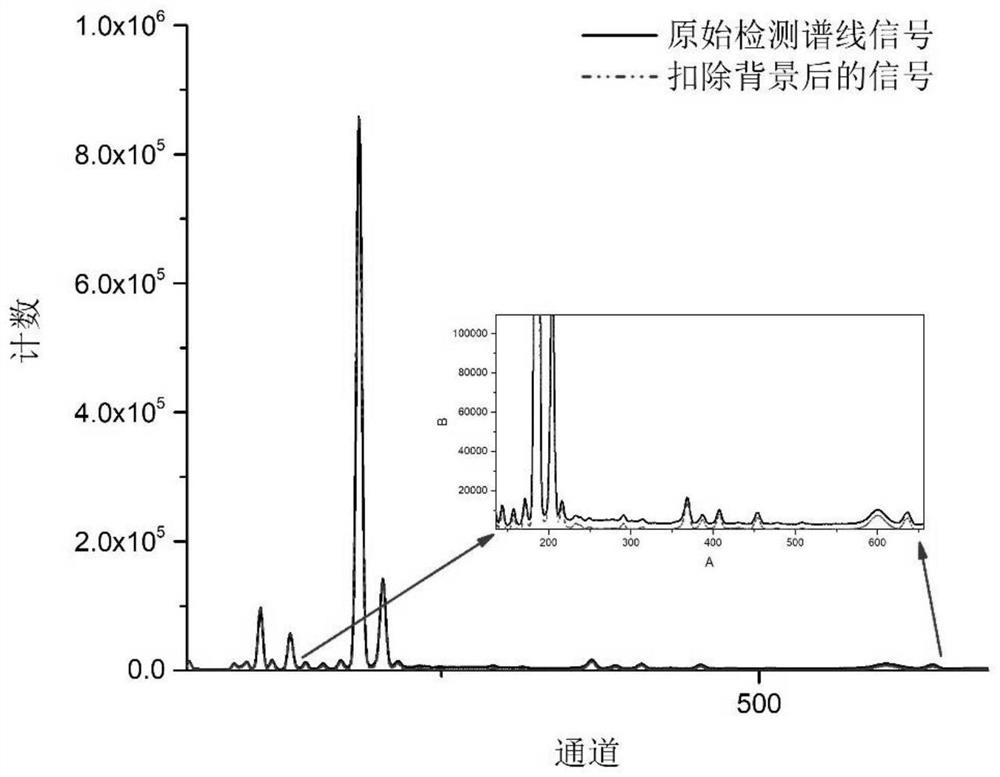
Trace element XRF determination method based on iterative discrete wavelet background deduction
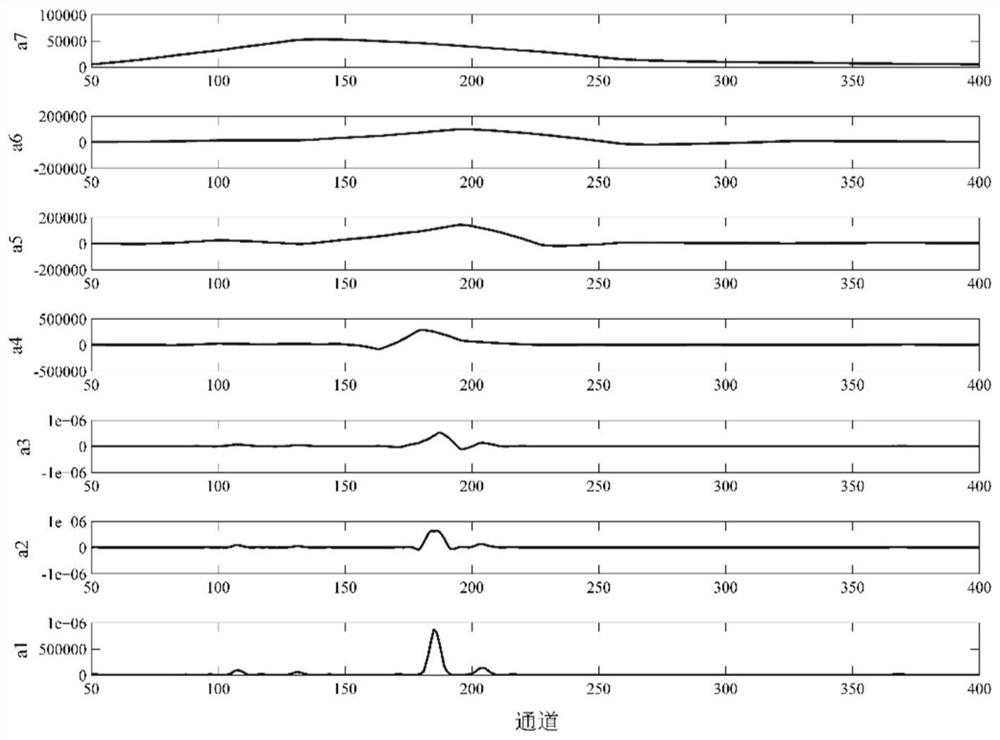
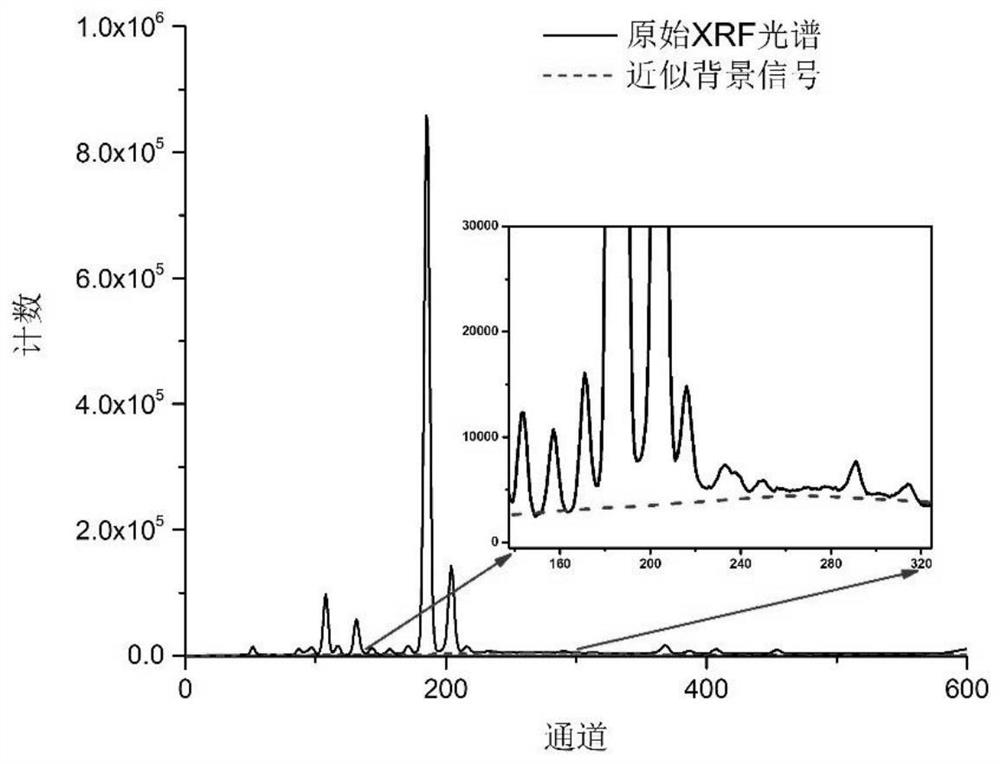
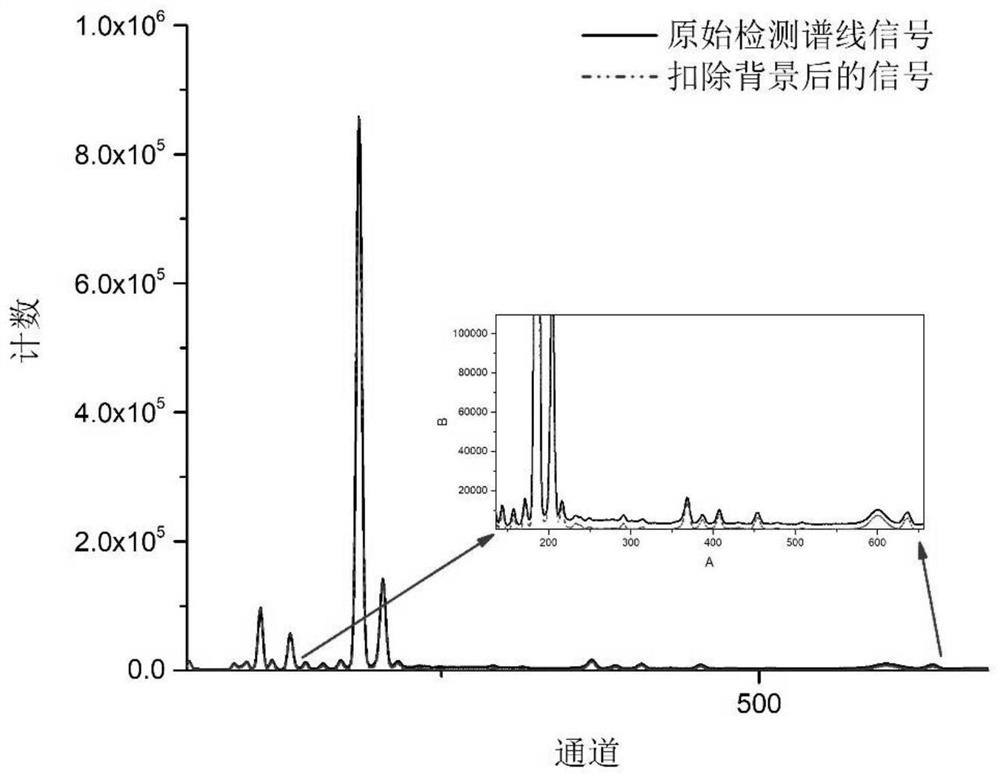
ActiveCN112748140AAvoid offsetAvoid areaMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationCharacter and pattern recognitionWavelet decompositionTrace element
The invention discloses a trace element XRF determination method based on iterative discrete wavelet background deduction, and the method comprises the following steps of: performing L-layer one-dimensional discrete wavelet decomposition on an original detection spectral line signal of a to-be-detected sample to obtain a primary low-frequency approximation coefficient of each layer, and selecting an optimal decomposition layer and a corresponding primary low-frequency approximation coefficient av; carrying out iterative discrete wavelet decomposition on the primary low-frequency approximation coefficient av, stopping iteration when the difference value of two continuous N adjacent iteration results is smaller than preset precision, and taking the last iteration result as an approximate background signal, thus obtaining a background-deducted signal; respectively calculating the Compton peak scattering intensity and the characteristic X-ray fluorescence intensity of a target element, and carrying out approximate treatment to obtain a quantitative analysis value of the target element. The method provided by the invention can effectively avoid the influence of peak offset and original spectrogram signal peak area, improve the quantitative detection precision of trace elements, improve the detection signal-to-noise ratio by three times or more, and reduce the detection limit of trace elements.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for determining content of elements in potassium-bearing ore by ICP (Inductively Coupled Plasma) internal standard method
InactiveCN105806826ASmall matrix effectHigh precisionAnalysis by thermal excitationPotassiumInductively coupled plasma
The invention relates to a method for determining the content of elements in a potassium-bearing ore by an ICP (inductively coupled plasma) emission spectroscopy internal standard method. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, with sodium carbonate-sodium tetraborate as a molten solvent, melting a potassium-bearing ore sample at a high temperature, and dissolving melt with a dilute hydrochloric acid solution; and carrying out qualitative and quantitative analysis on multiple elements in the ore by ICP. In the measurement process, the determination accuracy of the elements is affected due to introduction of the molten solvent and hydrochloric acid, the molten solvent element which is equivalent to the sample is added to a standard solution to remove the matrix effect, an yttrium element is selected as the internal standard to be added to the standard solution and the sample solution at the same concentration, and the relative intensity is measured to compensate a signal value drift caused by an instrument. By combining the internal standard method and a matrix matching method, interference caused by changes of the instrument operating condition, the atomization efficiency and the like is reduced; the matrix effect is effectively removed; the accuracy and the precision of the determination result are improved; and the method is suitable for accurate analysis of multiple elements in the potassium-bearing ore.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for simultaneous determination of multi-element content in high manganese steel
InactiveCN109752366ANo pollution in the processHigh precisionAnalysis by electrical excitationWide dynamic rangeStain
The invention provides a method for simultaneous determination of multi-element contents in high manganese steel. Through preparation and treatment of samples, a glow discharge emission spectrometer is used for excitation determination of the samples after spectral tracing and drift correction are carried out. The method for the simultaneous determination of the multi-element contents in the highmanganese steel comprises the following steps that (1) an excitation voltage of the glow discharge emission spectrometer is 1250 V, an excitation current is 45 mA, pre-burning time is 60 s, and integral time is 10 s; (2) the high manganese steel is sampled, specifically, requirements of homogeneous and representative compositions of the samples are met, and the samples do not contain inclusions, cracks, pores, oil stains, dust and oxides; (3) sample preparation of the high manganese steel is carried out, specifically, requirements that both surfaces of a sample are smooth and a sample analysissurface is polished carefully; and (4) the purity and the flow rate of argon for an analysis are ensured. The method for the simultaneous determination of the multi-element contents in the high manganese steel has the advantages of high precision, a low detection limit, a small matrix effect, a wide dynamic range of detection concentration, simultaneous detection of multiple elements, short analysis time, simple sample pretreatment, no pollution to the environment and the like.
Owner:BENGANG STEEL PLATES
Method for measuring proportions of nickel, cobalt and manganese in ternary elements NCM
PendingCN109884037AReduce concentrationSmall matrix effectPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationIonYttrium
The invention discloses a method for measuring proportions of nickel, cobalt and manganese in ternary elements NCM. According to the method, an ICP instrument is used for measuring the proportions ofnickel, cobalt and manganese in to-be-tested solution. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing standard solution and preparing three standard points, wherein the standard solution STD1at the first standard point has a metal ion total concentration of 120-200 mg / L, the standard solution STD2 at the second standard point has a metal ion total concentration of 230-320 mg / L, the standard solution STD3 at the third standard point has a metal ion total concentration of 330-390 mg / L, and the metal ions are metal ions of nickel, cobalt and manganese. According to the method, only the ICP is adopted to measure the proportions of nickel, cobalt and manganese, so that the requirement for the operations such as weighing, capacity setting and movement is not high, the operation is convenient and the material pretreatment process is accelerated. Compared with the existing industrial standard, the method is capable of saving the interior label yttrium element and saving the fussy operations without influencing the stability of the test result.
Owner:HUAYOU NEW ENERGY TECH (QUZHOU) CO LTD +1
Inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES) method for testing chemical components of blue phosphors of plasma display panel (PDP)
InactiveCN103353453ARapid Simultaneous DeterminationLow detection limitAnalysis by thermal excitationHigh concentrationOperating instruction
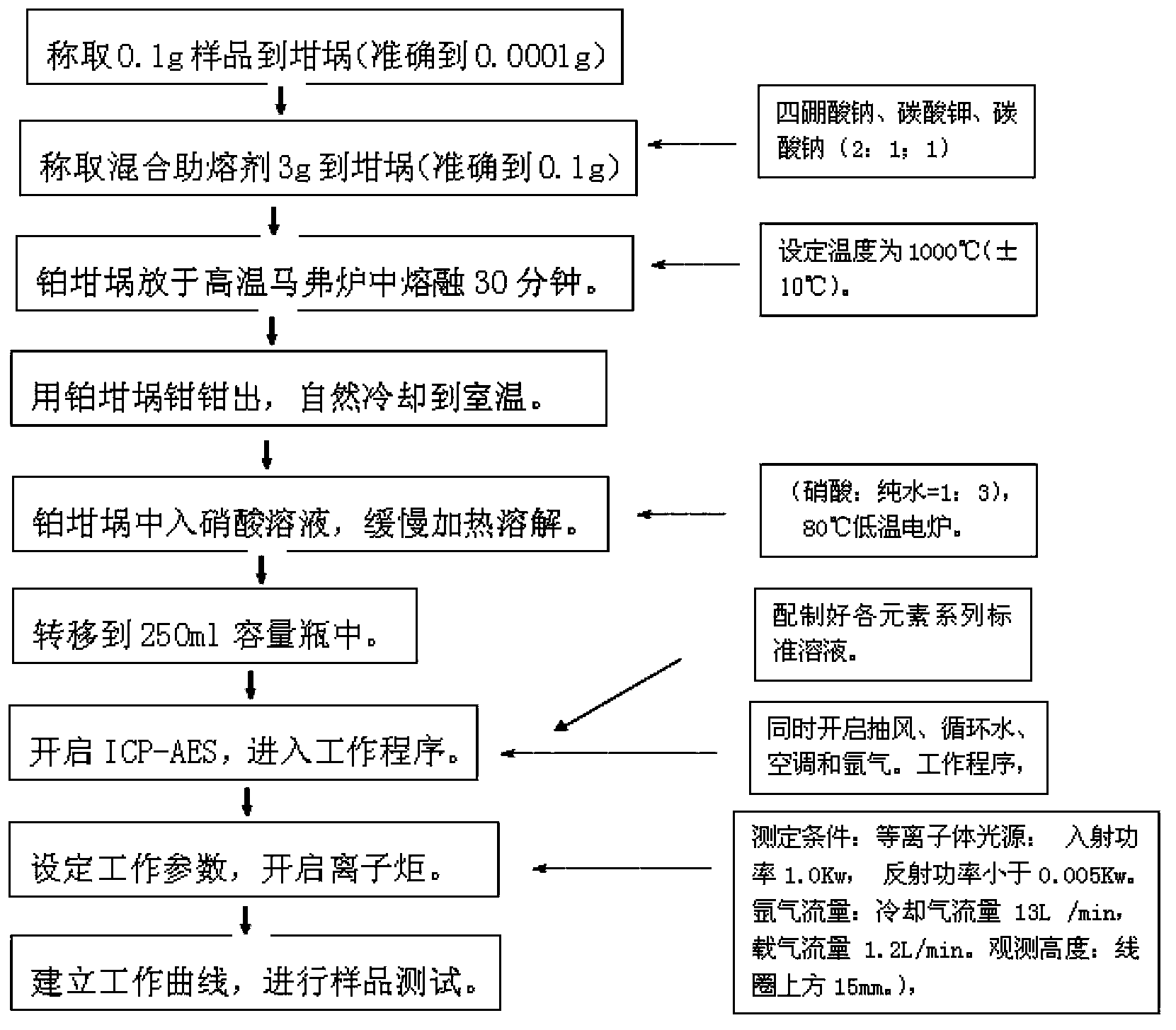
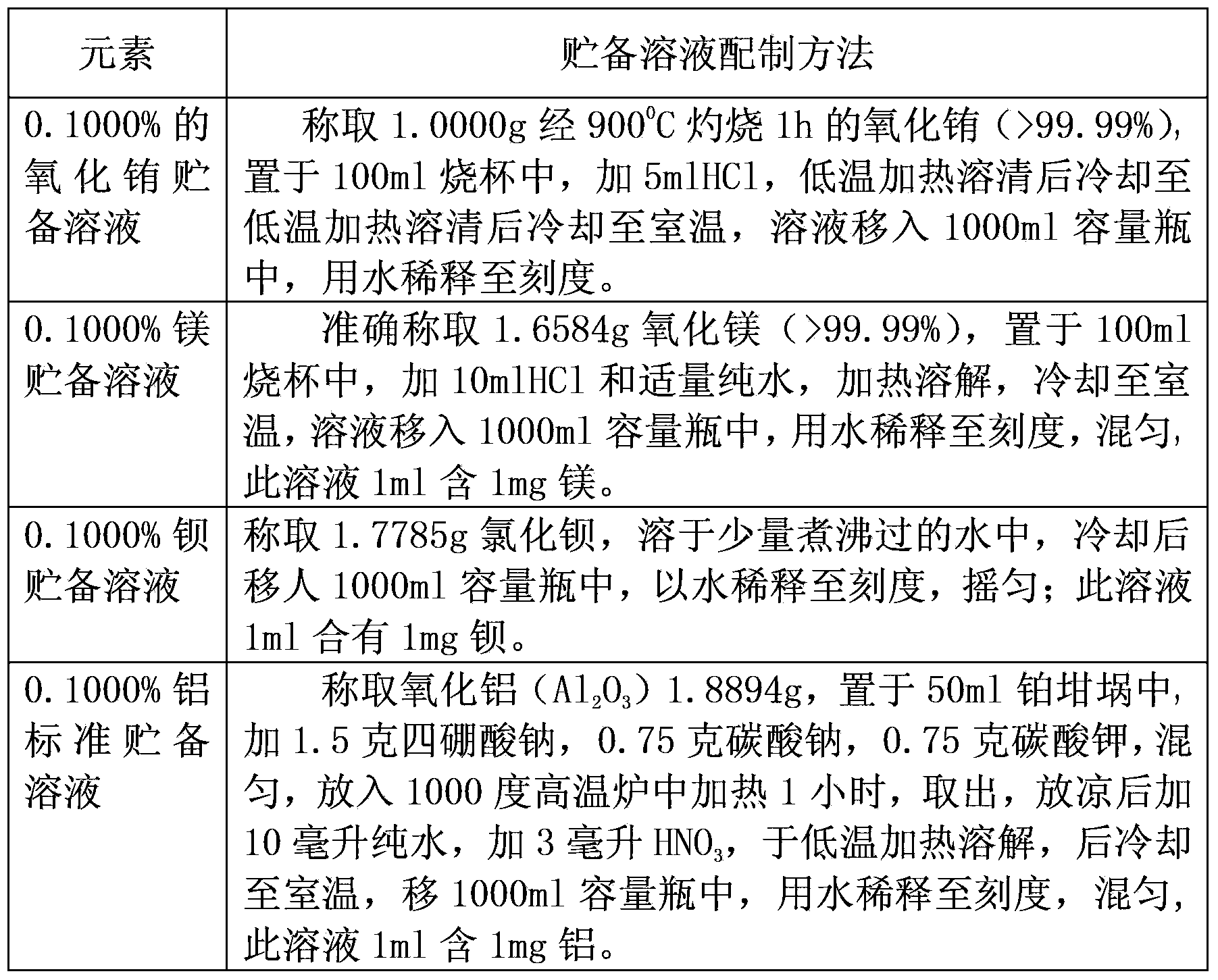
The invention discloses an inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES) method for testing chemical components of blue phosphors of a plasma display panel (PDP). The method comprises the following steps of: mixing the PDP blue phosphors and a mixed fluxing agent, melting the mixture in a high-temperature muffle furnace, cooling, adding a nitric acid solution, slowly heating, transferring the mixed solution into a 250ml volumetric flask after the mixture is dissolved, preparing a series of standard solutions of various elements, starting ICP-AES, starting ventilation, circulating water, air-conditioning and argon, setting operating parameters, turning on an ion torch, establishing an operating method of each element according to the operating instruction of the ICP-AES, sequentially injecting prepared standard solutions according to a sequence from low concentration to high concentration, drawing a working curve, detecting a sample solution, and calculating the contents of measured elements in the sample according to the working curves of the elements and the intensity value of the sample. The method has the characteristics of rapid and simultaneous measurement on multiple elements, high measurement precision, low detection limit and slight matrix effect.
Owner:CAIHONG GRP ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for analyzing content of main elements in nickel cobalt lithium manganate positive electrode material
PendingCN113311015AAvoid damageReduce the number of exposures to hazardsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationOptical spectrometerManganate
The invention provides a method for analyzing the content of main elements in a nickel cobalt lithium manganate positive electrode material. The analyzing method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out tabletting treatment on a standard sample, then testing the tableted sample by adopting an X-ray fluorescence spectrometer, selecting a model calibration curve spectrogram, preprocessing the curve spectrogram, and establishing a corresponding standard curve; and (2) carrying out tabletting treatment on a to-be-detected sample, then testing the tableted sample by adopting the X-ray fluorescence spectrometer, and obtaining the content of the main elements in the to-be-detected sample according to the corresponding standard curve in the step (1). According to the method, the X-ray fluorescence spectrophotometer is adopted to analyze multiple elements such as Ni, Co and Mn in NCM at a time, and the method is easy to operate, high in analysis speed, safe, rapid, low in cost, high in accuracy, good in stability, high in detection efficiency, high in practicability and suitable for actual production.
Owner:HUBEI JINQUAN NEW MATERIALS CO LTD
Method for separating Co, Zn and Ni isotopes in solution or solid sample and application
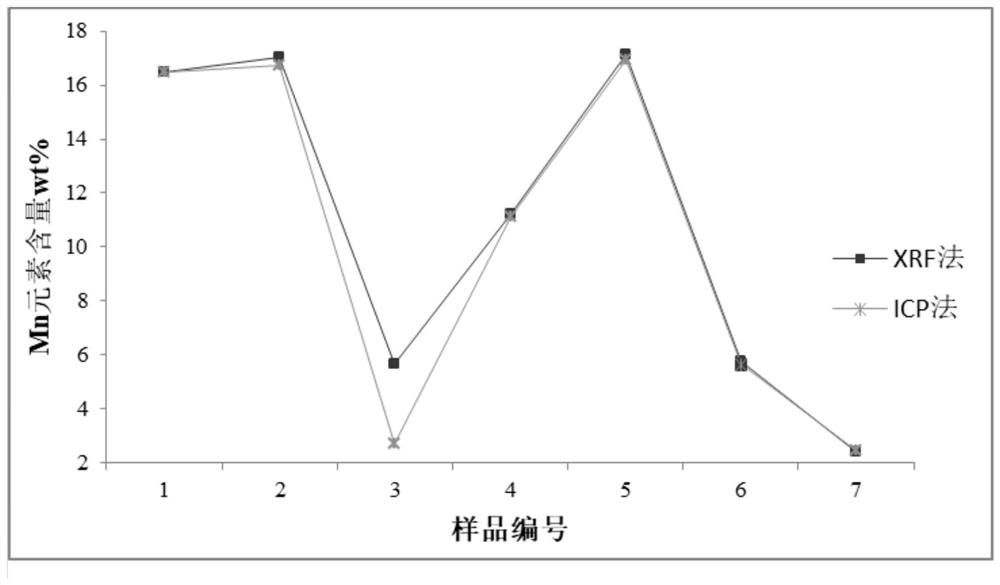
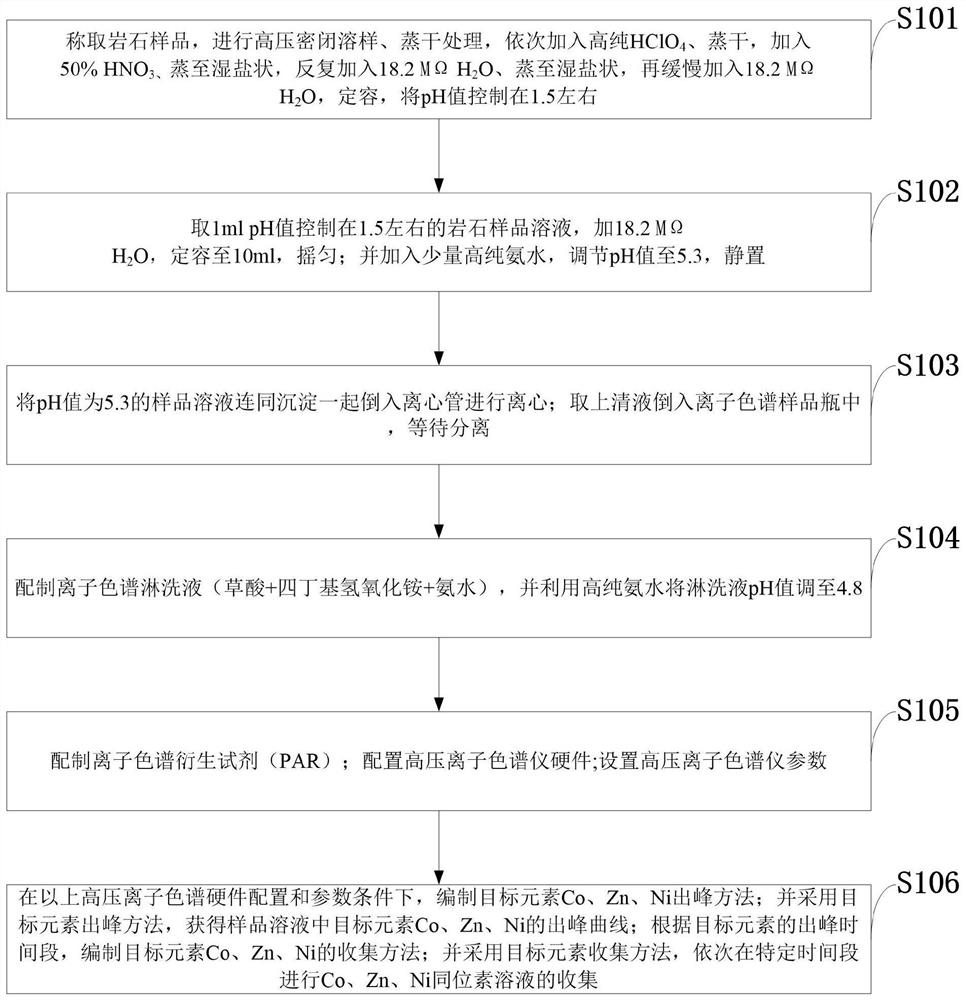
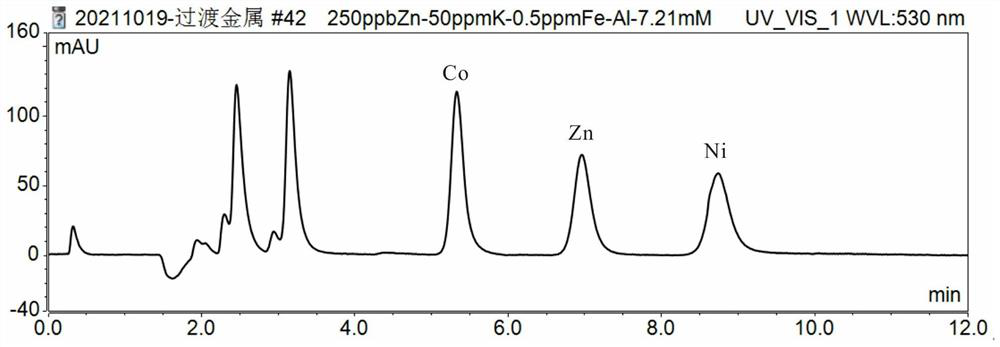
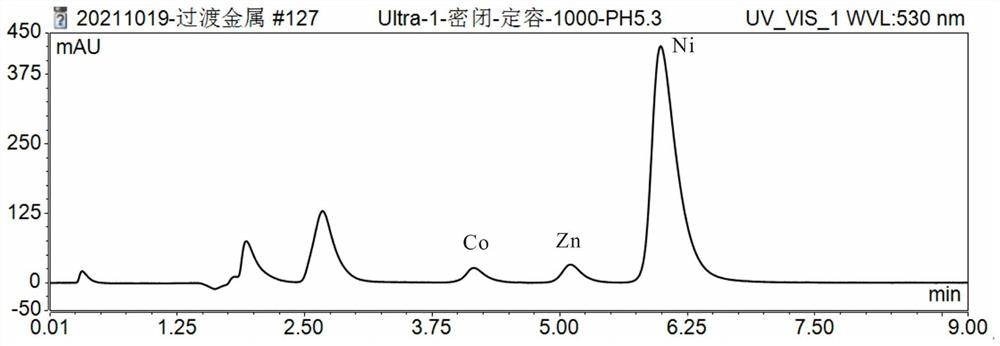
PendingCN114354782AAchieve simultaneous separationDoes not affect solubilityComponent separationIon chromatographyDissolution
The invention belongs to the technical field of isotope testing, and discloses a method for separating Co, Zn and Ni isotopes in a solution or a solid sample and application, the method comprises the following steps: adjusting the pH value of a rock sample solution twice to match the components and pH value of an ion chromatography leacheate; the pH value of the rock sample solution is adjusted for the first time: after the rock sample is subjected to high-pressure closed ore dissolution and evaporation to dryness, HClO4 is added for evaporation to dryness, HNO3 is added for evaporation to a wet salt state, H2O is repeatedly added for evaporation to a wet salt state, then the volume is fixed, and the pH value is controlled to be about 1.5; adjusting the pH value of the rock sample solution for the second time: taking the rock sample solution of which the pH value is controlled to be about 1.5, diluting, adding high-purity ammonia water, and adjusting the pH value to 5.3; the matching of the components and the pH value of the ion chromatography leacheate comprises the following steps: preparing the ion chromatography leacheate, and adjusting the pH value of the leacheate to 4.8 by using high-purity ammonia water. According to the method, the matrix effect of main transition metal elements such as Fe is reduced, and Co, Zn and Ni isotopes are rapidly and simultaneously separated.
Owner:XIAN CENT OF GEOLOGICAL SURVEY CGS
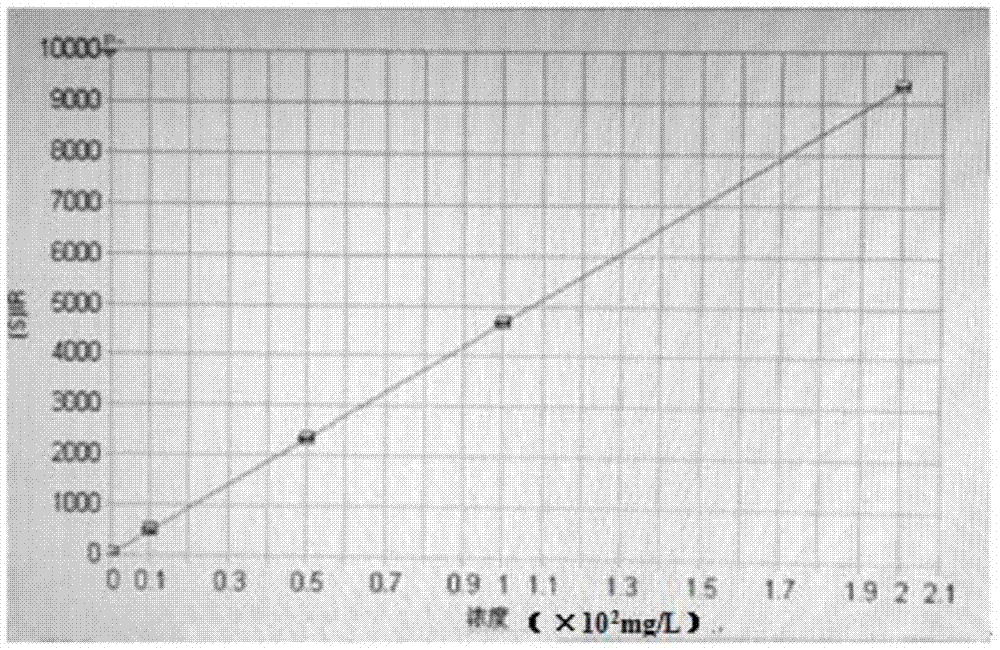
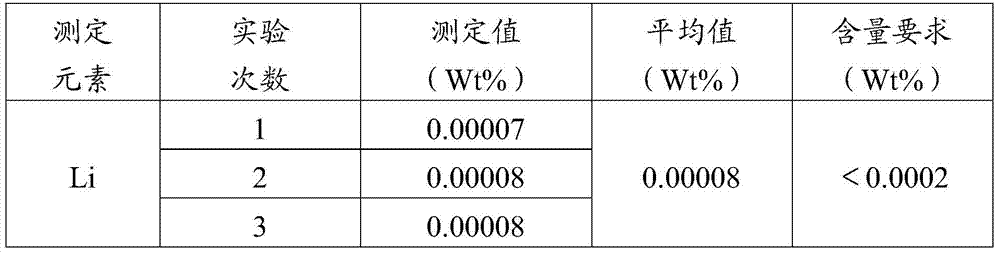
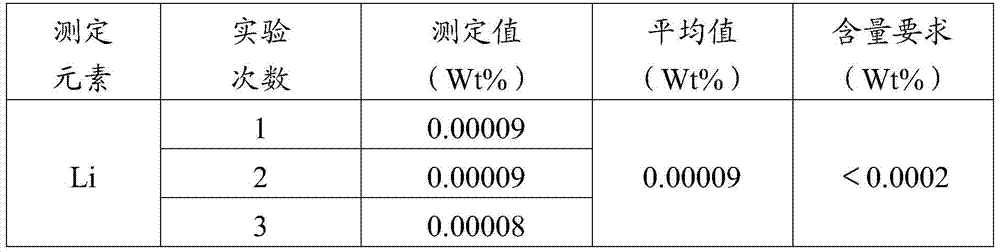
Zirconium and zirconium alloy lithium content measuring method
ActiveCN107462567AImprove accuracySmall matrix effectPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationSpectrographInductively coupled plasma
The invention provides a zirconium and zirconium alloy lithium content measuring method. The zirconium and zirconium alloy lithium content measuring method comprises the following steps of, firstly, turning pure zirconium or zirconium alloy to obtain scrap samples, cleaning and drying the scrap samples; secondly, performing a sampling process through coning and quartering; thirdly, dissolving the samples, transferring the solution into a volumetric flask for volume fixing to obtain a solution to be detected; fourthly, preparing a series of lithium calibrating solutions of different concentrations; fifthly, performing measurement one by one through an inductively coupled plasma emission spectrograph to establish a calibration curve of the correspondence between the concentration of the lithium calibrating solutions and lithium characteristic spectrum intensity; sixthly, measuring the lithium characteristic spectrum intensity of the solution to be detected through the inductively coupled plasma emission spectrograph, and according to the calibration curve, computing the mass content of lithium in the pure zirconium or zirconium alloy. The zirconium and zirconium alloy lithium content measuring method overcomes the difficulties that the vertical observation technology for detecting easily ionizable elements is vulnerable to interference as well as the inductively coupled plasma emission spectrograph cannot meet the requirements of trace analysis on detection limit during measurement of a zirconium-based hypersaline environment, thereby meeting the zirconium and zirconium alloy detecting requirements of the nuclear industry.
Owner:国核宝钛锆业股份公司 +1
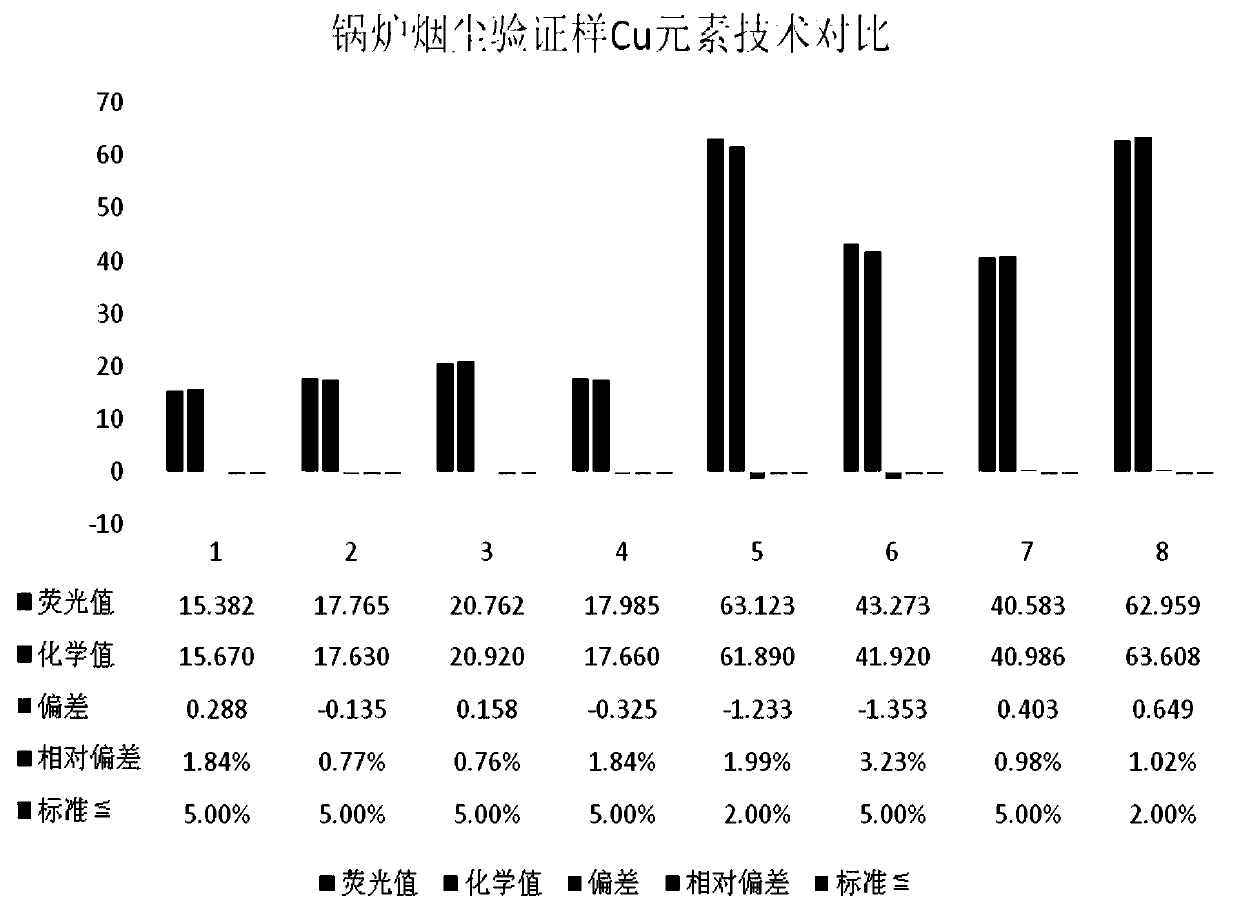
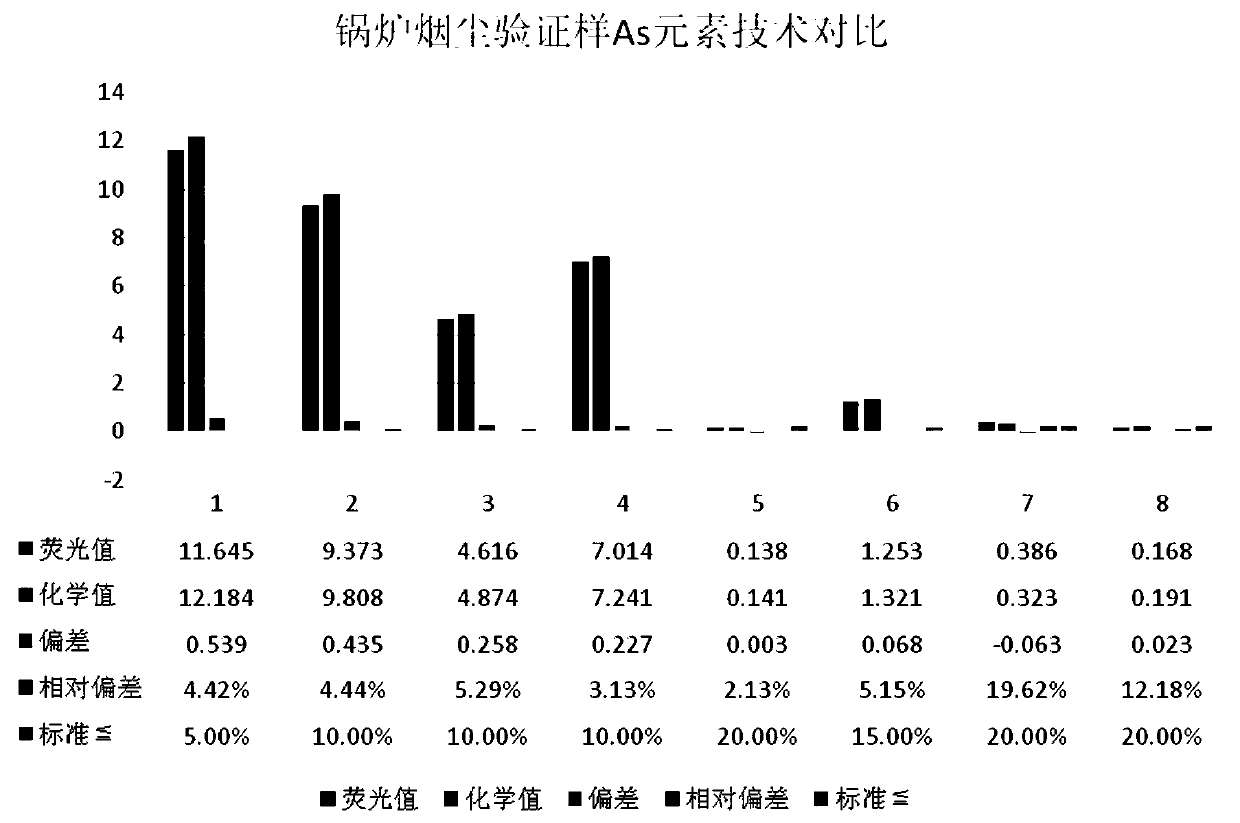
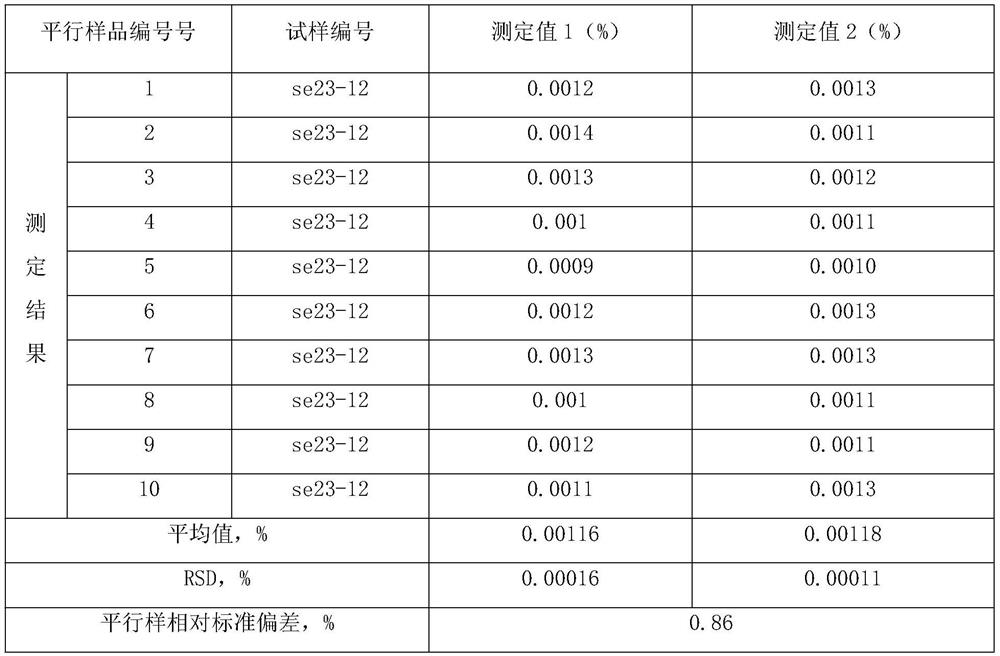
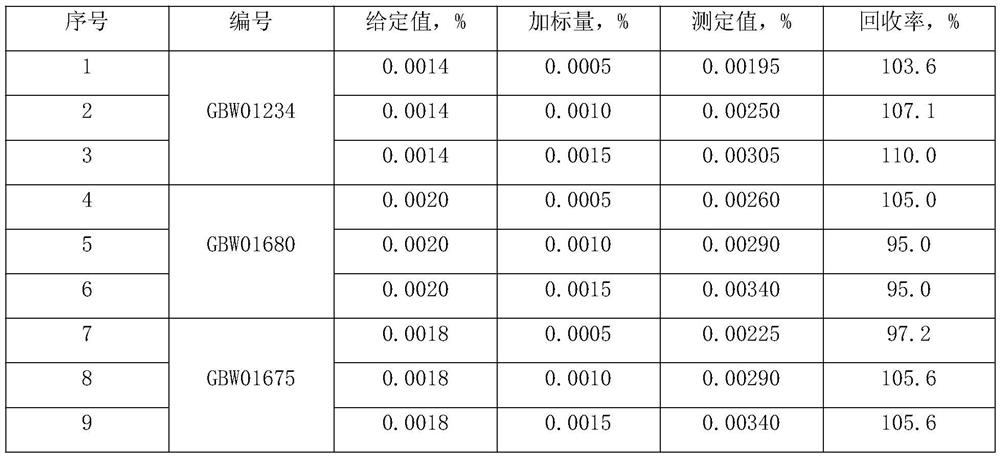
Method for analyzing Cu, As, Pb and Zn elements in boiler smoke by X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy
InactiveCN110376230AGuaranteed smoothnessGuaranteed tightnessMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAdhesiveEngineering
The invention discloses a method for analyzing Cu, As, Pb and Zn elements in boiler smoke by X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy. A direct compression method is used in a sample preparation process, a module group does not need to be specially produced, and adhesive does not need to be added in addition so that a sample for analysis and detection can be obtained. Preparation cost is greatly reduced, and safety during an operation process is improved. After the prepared sample is detected by the detection method of the invention, high accuracy, good stability and high detection efficiency are possessed, and the sample is highly practical, and is worth promoting.
Owner:LIANGSHAN MINING CO LTD
Method for measuring zinc element in electroslag steel by ICP-OES
The invention provides a method for measuring a zinc element in electroslag steel by ICP-OES. The method comprises the steps of S1, sampling; S2, waiting for detection; S3, preparing a series of standard solutions; S4, forming a series of standard solutions; S5, establishing a working curve; S6, calculating the content of related elements in the sample according to the working curve; S7, determining working parameters of the instrument; S8, drawing a working curve; and S9, determining the content of the zinc element in the sample solution. According to the method, the number of used samples in the detection process is small, damage to the surface of the steel ingot is minimized, few chemical reagents are used, the whole process from the steel ingot to detection is rapid and environmentally friendly, and the method is simple, convenient and easy to implement. The method disclosed by the invention is small in matrix effect, wide in linear range, low in detection limit, good in precision, less in chemical interference and small in spectral line self-absorption, overcomes the defects in the prior art, and can be suitable for electroslag steel production inspection.
Owner:青海西钢特殊钢科技开发有限公司 +1
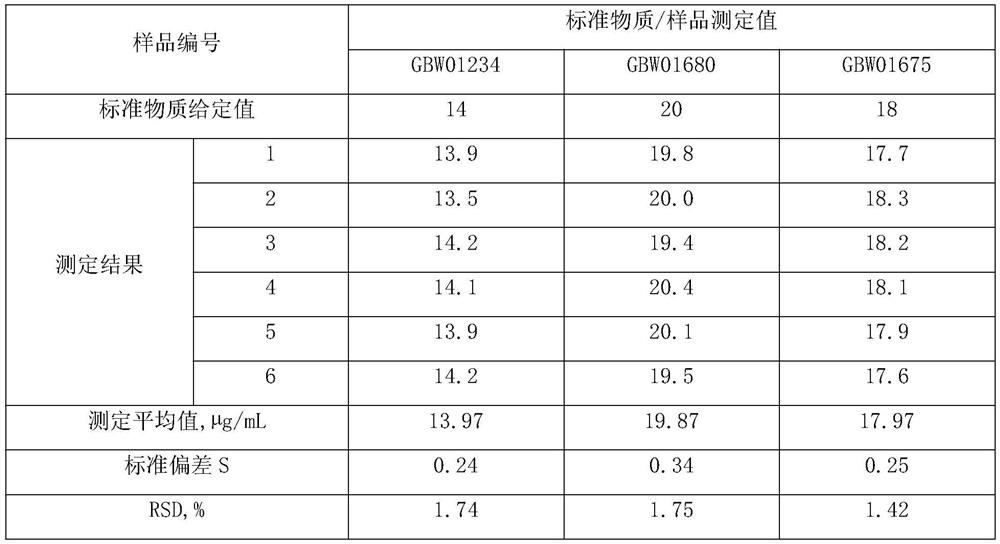
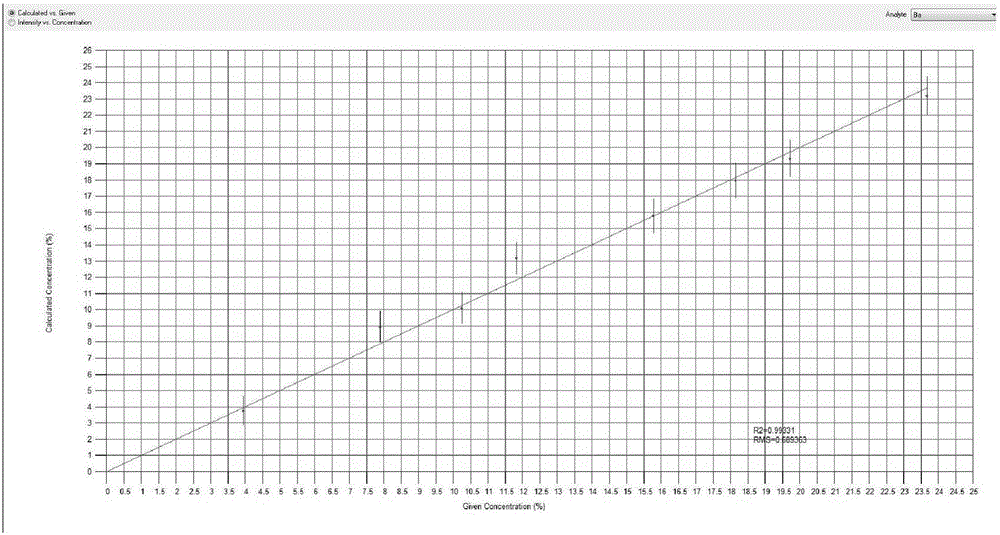
Method for measuring content of barium in barium nitrate for fireworks and crackers
InactiveCN106093096AEliminate unevennessReduce matrix effectMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationFireworksX-ray
The invention relates to a method for measuring the content of barium in barium nitrate for fireworks and crackers. The method comprises the following steps: preparing multiple barium nitrate working solutions with different concentrations, establishing an analysis method by adopting a mathematic correction method for intensity correction through taking an energy dispersion type X-ray fluorescence spectrophotometer as a detecting instrument and supposing a certain sample size, converting mass concentrations of Ba in multiple prepared barium nitrate working solutions into mass percentage concentrations of Ba, recording the fluorescence intensity of each sample feeding, and drawing a calibration curve; preparing a sample solution from a barium nitrate raw material for to-be-measured fireworks and crackers, recording the fluorescence intensity of Ba displayed on an instrument, recording a mass percentage concentration value of corresponding Ba according to the determined calibration curve according to the fluorescence intensity, and calculating the content of Ba in the sample. According to the method, by optimizing dissolving conditions of the sample and parameter conditions of the X-ray fluorescence spectrophotometer, the matrix effect among elements of the sample can be eliminated or basically eliminated; and the operation is simple, the detection period is short, the accuracy is good, and the precision is high.
Owner:吴俊逸
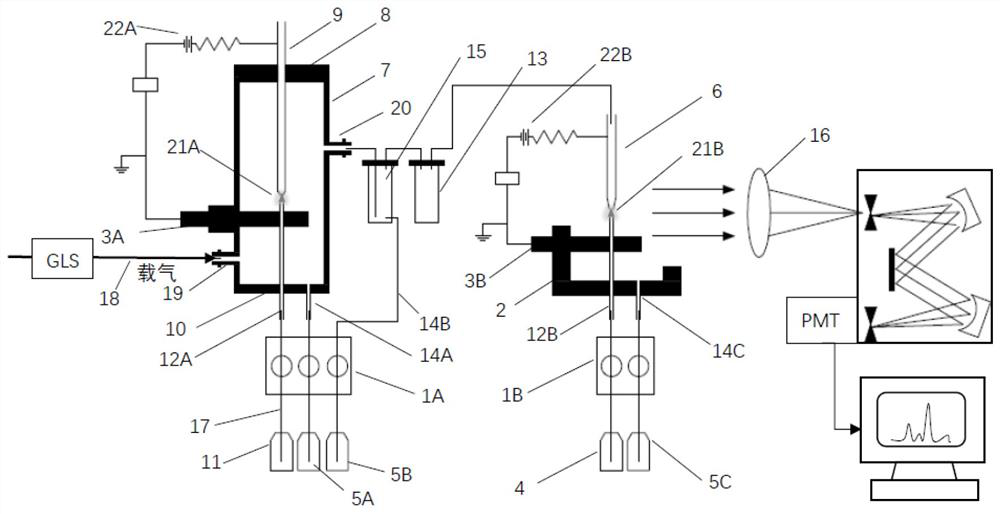
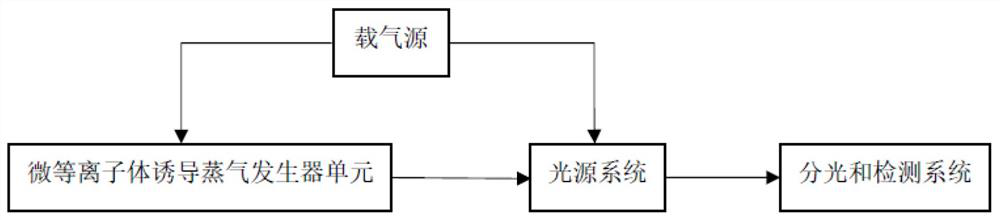
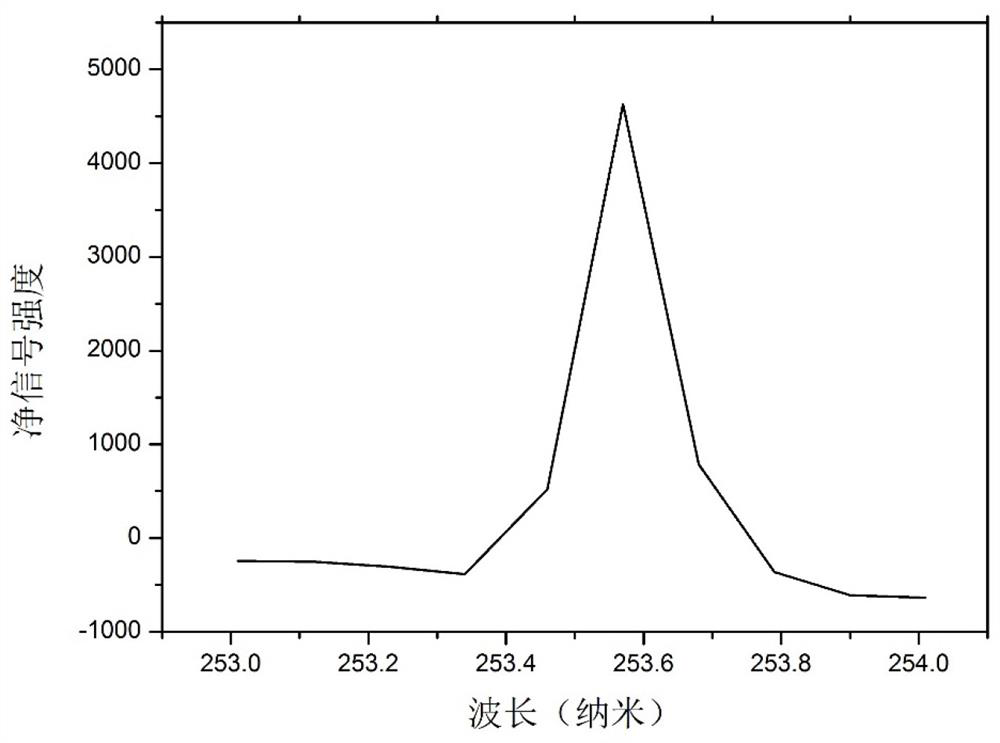
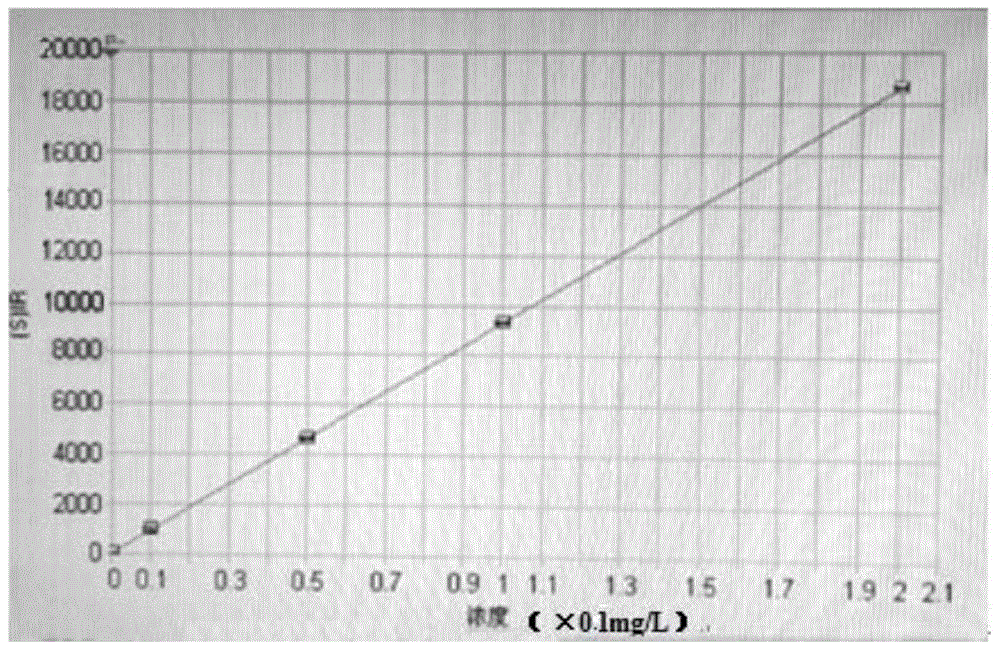
Sampling system for liquid cathode glow discharge spectrometer
InactiveCN112782150AReduce distractionsReduce Potential ContaminationAnalysis by electrical excitationLiquid cathodeOptical spectrometer
The invention relates to a sampling system for a liquid cathode glow discharge spectrometer. The sampling system comprises a micro-plasma induced steam generator unit and a connecting unit for connecting the liquid cathode glow discharge spectrometer and the micro-plasma induced steam generator unit. The micro-plasma induced steam generator unit induces a sample solution to be detected to generate steam based on liquid cathode glow discharge micro-plasma; the connecting unit is used for conveying mixed gas of to-be-detected metal ion steam generated by the micro-plasma induced steam generator unit and carrier gas to a hollow anode of the liquid cathode glow discharge spectrometer through the connecting unit, and the mixed gas enters a glow discharge area and is excited to generate a characteristic emission spectral line. The sampling system based on atmospheric pressure liquid cathode glow discharge micro plasma induced steam generation is used for realizing gas sampling of SCGD-OES.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
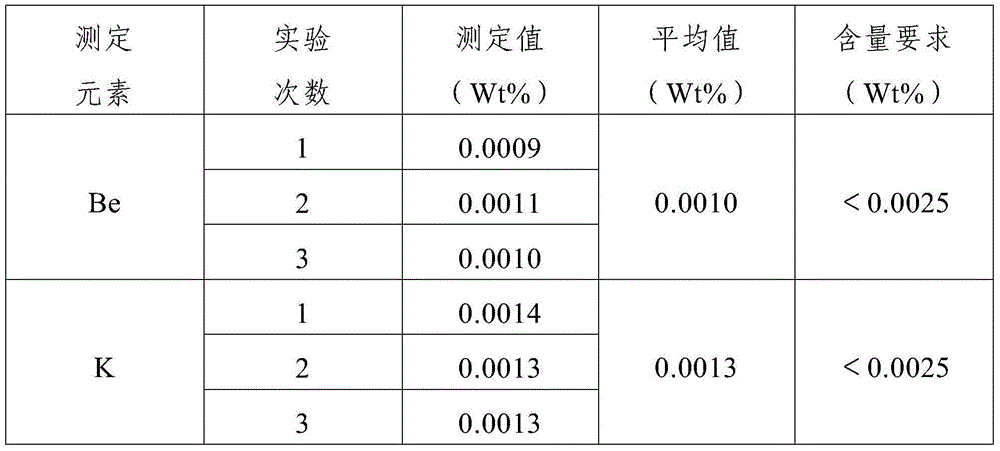
Method for measuring beryllium and potassium content in zirconium and zirconium alloy at the same time
InactiveCN104697985AImprove accuracySmall matrix effectAnalysis by thermal excitationPotassiumVolumetric flask
The invention provides a method for measuring the beryllium and potassium content in zirconium and zirconium alloy at the same time. The method includes the following steps that 1, pure zirconium or zirconium alloy is turned to obtain cuttings-shaped samples, and then the samples are cleaned and dried; 2, coning and quartering are adopted to conduct sampling; 3, the samples are dissolved, a solution is transferred to a volumetric flask to conduct constant volume, and a solution to be measured is obtained; 4, a series of beryllium-potassium correction solutions of different concentration are mixed; 5, the element feature spectral intensity of beryllium and potassium in the beryllium-potassium correction solutions of all concentration is measured one by one through an inductive coupling plasma emission spectrometer, and a correction curve is established; 6, the element feature spectral intensity of the beryllium and potassium in the solution to be measured is measured through the inductive coupling plasma emission spectrometer, and the beryllium content and the potassium content in the pure zirconium samples or the zirconium alloy samples are worked out according to the correction curve. By means of the method, the difficulty that a vertical observation technology is prone to being interfered when measuring elements which are ionized easily can be overcome, and the nuclear industry zirconium and zirconium alloy detection requirement is met.
Owner:国核宝钛锆业股份公司
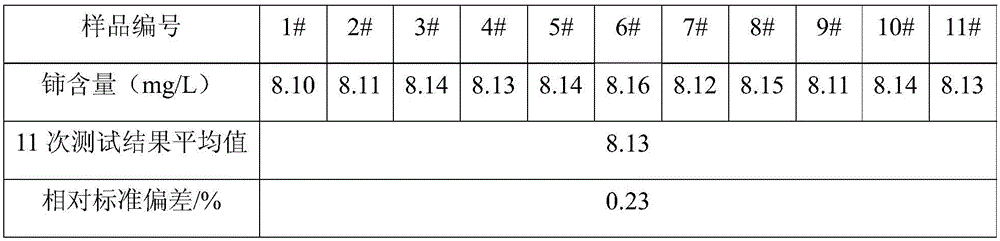
Method for measuring content of cerium in glass
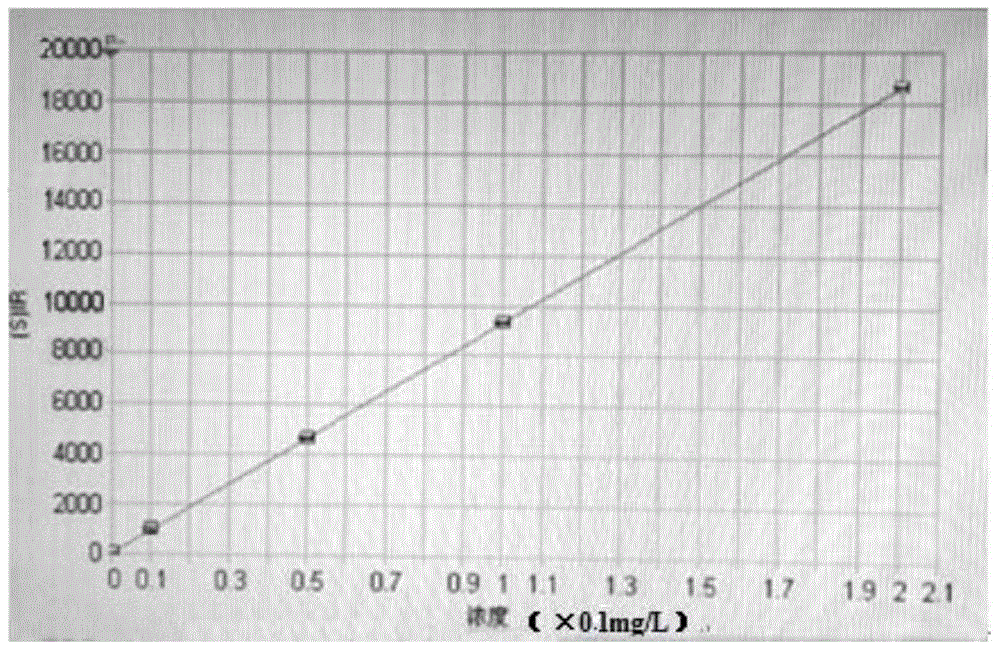
InactiveCN105699365ASolve the problem that low content components cannot be detectedHigh precisionAnalysis by thermal excitationHydrofluoric acidCerium
The invention relates to the field of glass processing, and discloses a method for measuring cerium content in glass. The method comprises: (1) grinding the glass to be tested into glass powder, adding hydrofluoric acid to the glass powder for first heat treatment, and then Add perchloric acid to the product obtained by the first heat treatment and carry out the second heat treatment to obtain a complete solution of glass; (2) dilute the complete solution of glass with water to obtain a constant volume solution, and measure the volume of the constant volume solution (3) Determine the cerium content in the glass to be tested according to the volume of the constant volume solution and the measured cerium content. The method for measuring the cerium content in glass of the present invention has the advantages of simple operation, small matrix effect, high precision, high recovery rate of standard addition, low detection limit and high reliability of the result, and can fully meet production requirements.
Owner:WUHU DONGXU OPTOELECTRONICS EQUIP TECH +2
A Rapid Method for Measuring Trace Boron Impurities in Polysilicon
ActiveCN103760218BSolve time-consuming puzzlesImprove stabilityPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPotassium carbonateImpurity
The invention relates to a method for rapidly measuring trace boron impurities in polysilicon. The method comprises the following steps: weighting a polysilicon sample; adding a mannitol solution into the sample; adding a potassium carbonate solution into the sample; adding hydrofluoric acid, then slowly dropping nitric acid in the sample and carrying out acidified dissolving; after the sample is dissolved, heating the obtained object, and stopping heating until white smoke is emitted completely; adding hydrochloric acid into the sample and soaking, diluting with a small amount of pure water, and cooling; adding methanol into the solution, uniformly shaking and making up to volume; rinsing ICP-MS (Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry) respectively by using ammonia water and pure water; and after the ICP-MS is rinsed completely, detecting the solution sample with metered volume by using ICP-MS, so that the boron content of the sample can be accurately measured. The method disclosed by the invention is simple in process, low in cost, can measure accurately, and rapidly measure the boron content of polysilicon.
Owner:福建上杭兴恒硅品有限责任公司
Label-free nuclease analysis method based on stable isotope detection
PendingCN111812185AHigh sensitivityEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansEnzyme digestionNuclease
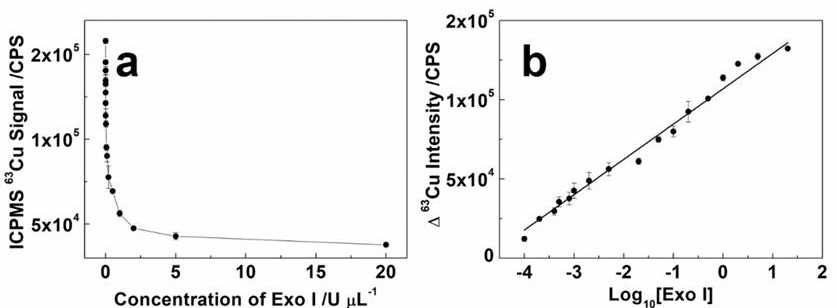
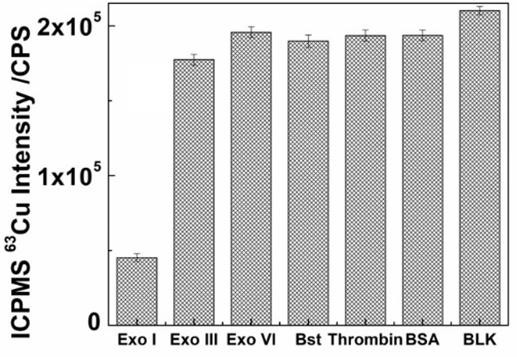
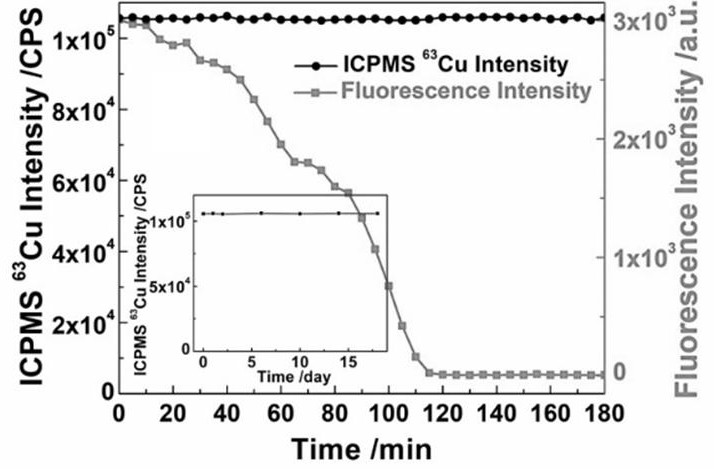
The invention provides a label-free analysis method based on stable isotope detection and application of the label-free analysis method in nuclease detection. In the presence of nuclease, a template DNA sequence for synthesizing CuNPs is subjected to enzyme digestion, DNA fragments obtained after enzyme digestion lose the template effect, and CuNPs cannot be synthesized under the action of ascorbic acid and copper ions. The synthesized CuNPs are digested by nitric acid to form copper ions, and ICPMS quantitative analysis can be carried out. The invention provides the analysis method capable ofrealizing long-time stable label-free detection on nuclease. According to the invention, an analysis signal can be kept stable for a long time without attenuation; the method has the advantages thatcost is low, tedious operation steps are omitted, and response is rapid; and meanwhile, the advantages of low detection limit and excellent stability of ICPMS for stable isotope detection are utilized, so long-time stability is greatly improved while nuclease detection sensitivity is improved, and long-time stable detection and real-time monitoring can be achieved.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
A XRF Determination Method of Trace Elements Based on Iterative Discrete Wavelet Background Subtraction
ActiveCN112748140BAvoid offsetAvoid areaMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationCharacter and pattern recognitionFluorescenceTrace element
The invention discloses an XRF determination method for trace elements based on iterative discrete wavelet background subtraction. The original detection spectral line signal of the sample to be measured is decomposed by L-layer one-dimensional discrete wavelet to obtain the primary low-frequency approximation coefficient of each layer, and select the most The optimal decomposition layer and the corresponding first-order low-frequency approximation coefficient a v ; Then for a low-frequency approximation coefficient a v Carry out iterative discrete wavelet decomposition. When the difference between the results of two consecutive iterations of N consecutive iterations is less than the preset accuracy, the iteration is stopped, and the result of the latest iteration is used as the approximate background signal, and then the signal after subtracting the background is obtained; The quantitative analysis value of the target element is obtained after approximate processing of the scattering intensity of the Puton peak and the characteristic X-ray fluorescence intensity of the target element. The method of the invention can effectively avoid the influence of the peak shift and the peak area of the original spectrum signal, improve the quantitative detection accuracy of trace elements, increase the detection signal-to-noise ratio by more than three times, and reduce the detection limit of trace elements.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
A pretreatment method for improving the sensitivity of elements in solid detection samples
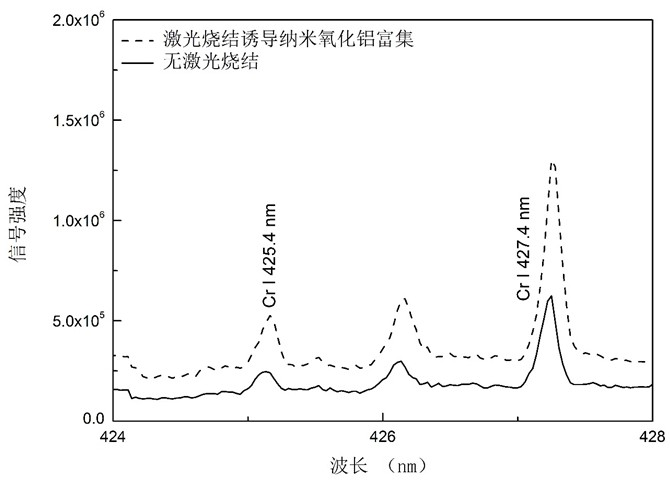
ActiveCN108287102BEffective adsorption and concentrationLaser Induced Breakdown Spectral Intensity EnhancementPreparing sample for investigationPretreatment methodPhysical chemistry
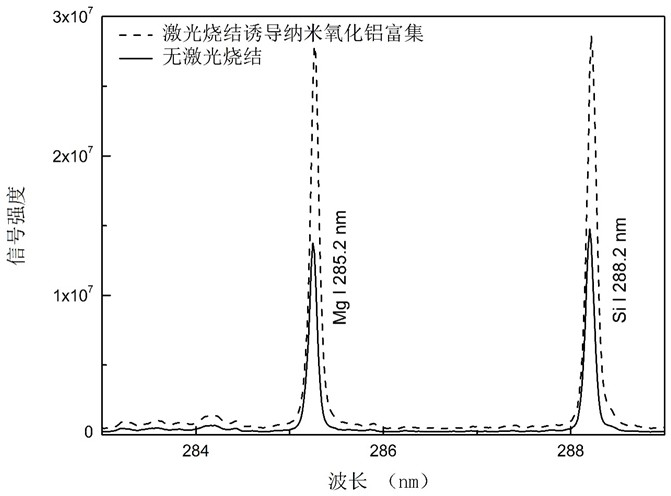
The invention discloses a pretreatment method of improving element sensitivity in a solid detection sample. The method comprises the steps of: a) grinding the sample to be detected into fine powder, adding a nano oxide for uniform mixing, and performing pressing and sheeting, b) heating and sintering the surface of a sample pressing sheet, and c) fixing the heated and sintered sample pressing sheet on an objective table, detecting the sample pressing sheet and calibrating target elements in the sample pressing sheet, wherein the surface of the sample pressing sheet is heated by a continuous laser or a quasi-continuous laser; the size of a laser spot is the same as that of the surface of the sample pressing sheet; and the surface of the sample pressing sheet is sintered by adjusting laser energy. The nano oxide is doped in the sample to be detected; since the nano oxide has strong adsorptive capacity on metal cations, metal elements in the sample are enriched and concentrated under a heating condition; matrices of the different samples are unified via the doping of the nano oxide; the spectral intensity of the target elements of a laser induced breakdown spectral test is improved ina sintering area finally; a matrix effect is weakened; and the element calibration is achieved.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
A "fluorescence-stable isotope" dual-mode detection method for p-trinitrotoluene
ActiveCN109765203BHigh sensitivityImprove stabilityFluorescence/phosphorescenceAptamerTNT - Trinitrotoluene
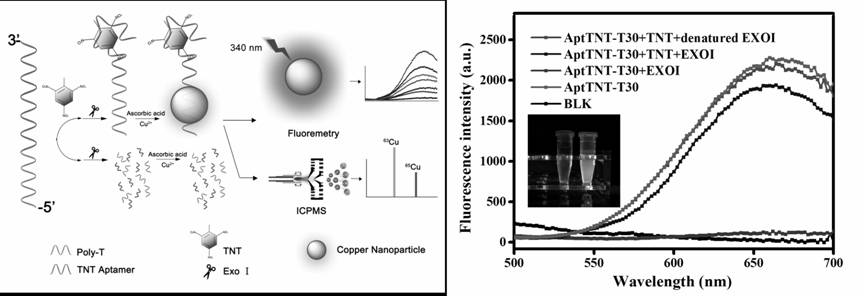
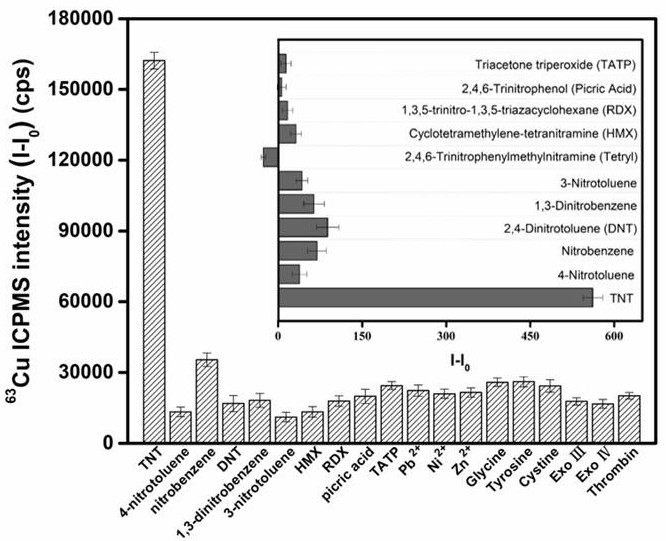
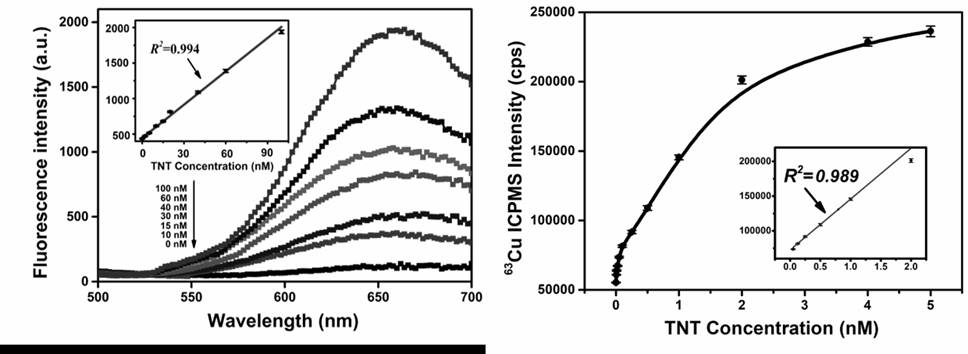
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a "fluorescence-stable isotope" dual-mode detection method for p-trinitrotoluene (TNT). The assay consists of a polythymidine‑nucleic acid aptamer probe (AptTNT‑T30) and dual-modality detection with fluorescence detection and stable isotope detection. The principle of the present invention is: the TNT nucleic acid aptamer (AptTNT) sequence can be specifically combined with the target TNT molecule for terminal protection, avoiding exonuclease cutting, and the polythymine sequence (T30) at the 5' end can be used as a template Synthesis of copper nanoparticles. The synthesized copper nanoparticles can be detected in dual modes: in the fluorescence detection mode, rapid fluorescence detection can be performed; after the copper nanoparticles are digested in nitric acid, in the stable isotope detection mode, the inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer can be used for highly sensitive and stable quantitative analysis , which can respectively satisfy the on-site rapid detection and highly sensitive and accurate detection of TNT.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com