Trace element XRF determination method based on iterative discrete wavelet background deduction
A discrete wavelet and trace element technology, applied in the field of spectral data analysis and processing technology improvement, can solve problems such as peak shift, low detection accuracy, and sample spectrum distortion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] This embodiment provides an XRF determination method for trace elements based on iterative discrete wavelet background subtraction, using GBW07380 (GSD-29) soil sample as the sample to be tested, and calculating the quantitative analysis value of Cu element, including the following steps:
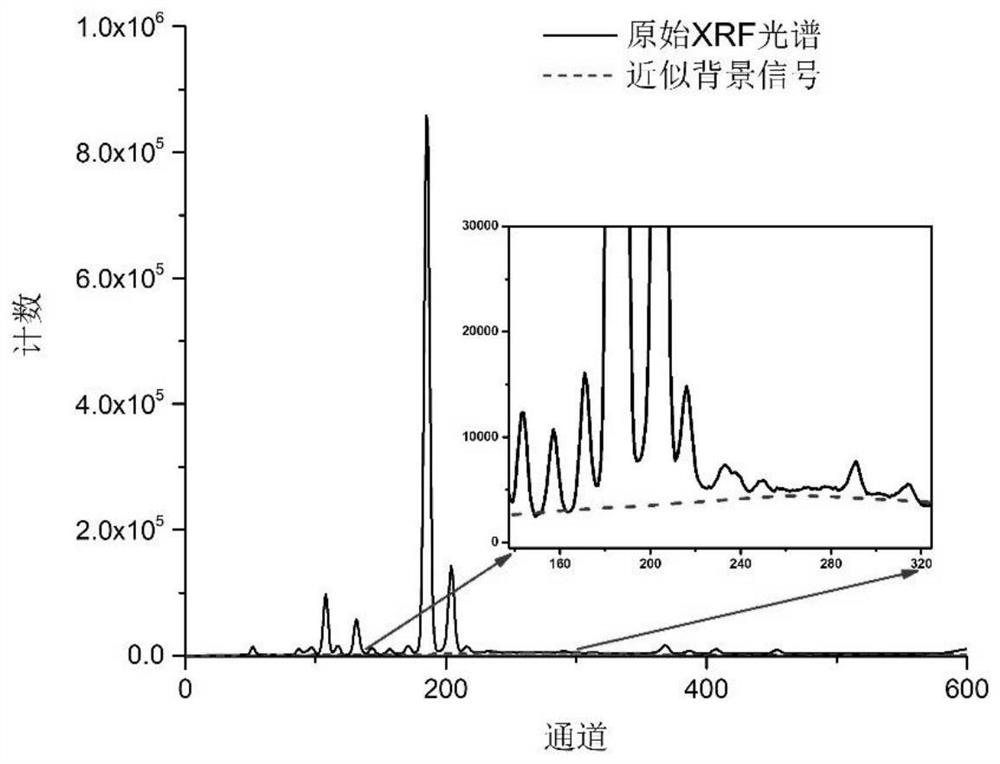
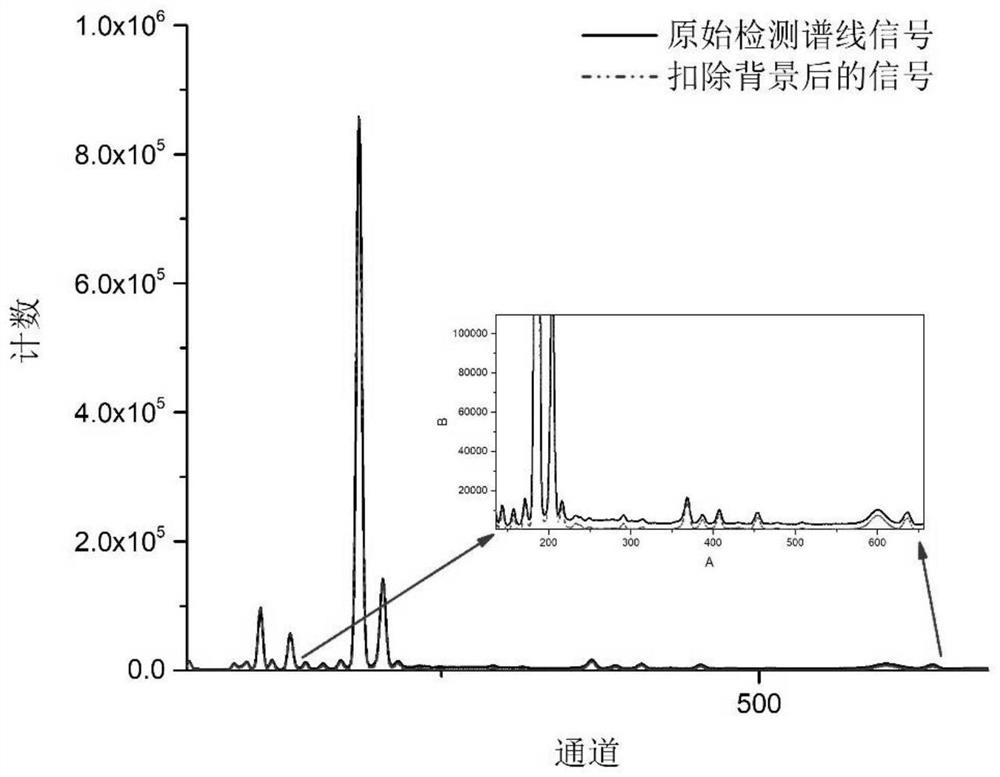
[0043]Step 1: Use the TS-XH4000-P hand-held X-ray fluorescence analyzer equipped with an Ag anode X-ray tube to detect GBW07380 (GSD-29) soil samples. When the noise ratio reaches the optimum, the original detection line signal f of the GBW07380 (GSD-29) soil sample is obtained at this time 0 ;
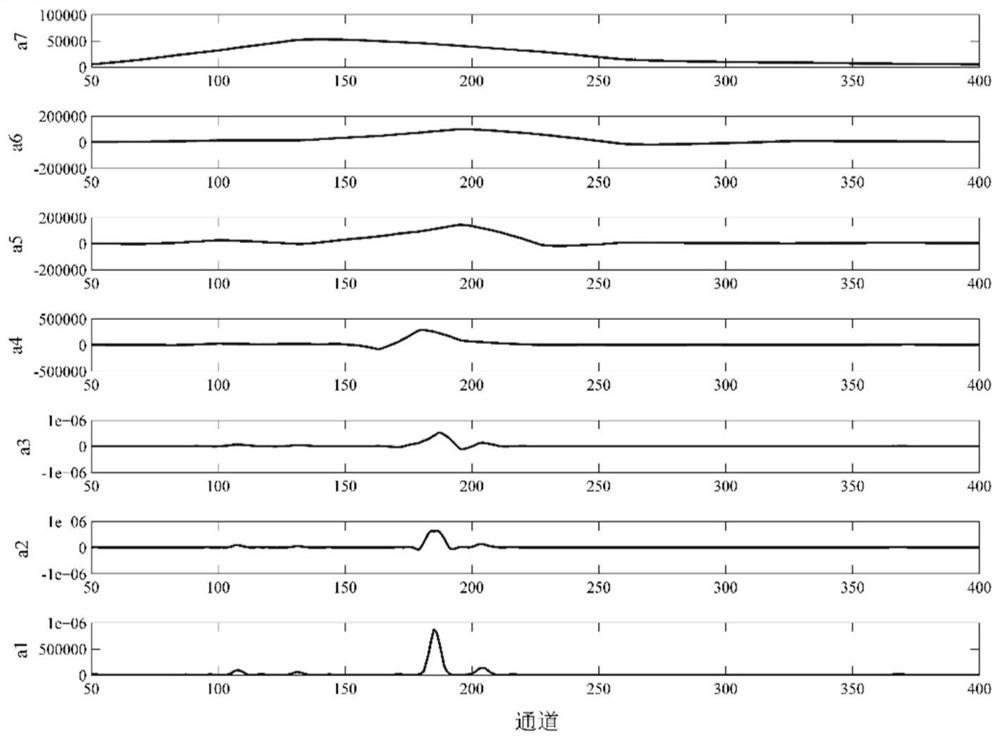
[0044] Step 2: Use the wavelet basis to compare the original detection spectral line signal f obtained in step 1 0 Perform 7 layers of one-dimensional discrete wavelet decomposition to obtain 7 layers of discrete wavelet decomposition, such as figure 1 As shown, the corresponding first-order low-frequency approximation coefficient a is reconstructed according to the discrete wavelet decomp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com