A strain of Pseudomonas with high lipase production and method for fermenting and producing enzyme
A technology of Pseudomonas and lipase, which is applied in the field of microorganisms, to achieve the effects of reducing fermentation costs, increasing fermentation production capacity, and increasing application value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
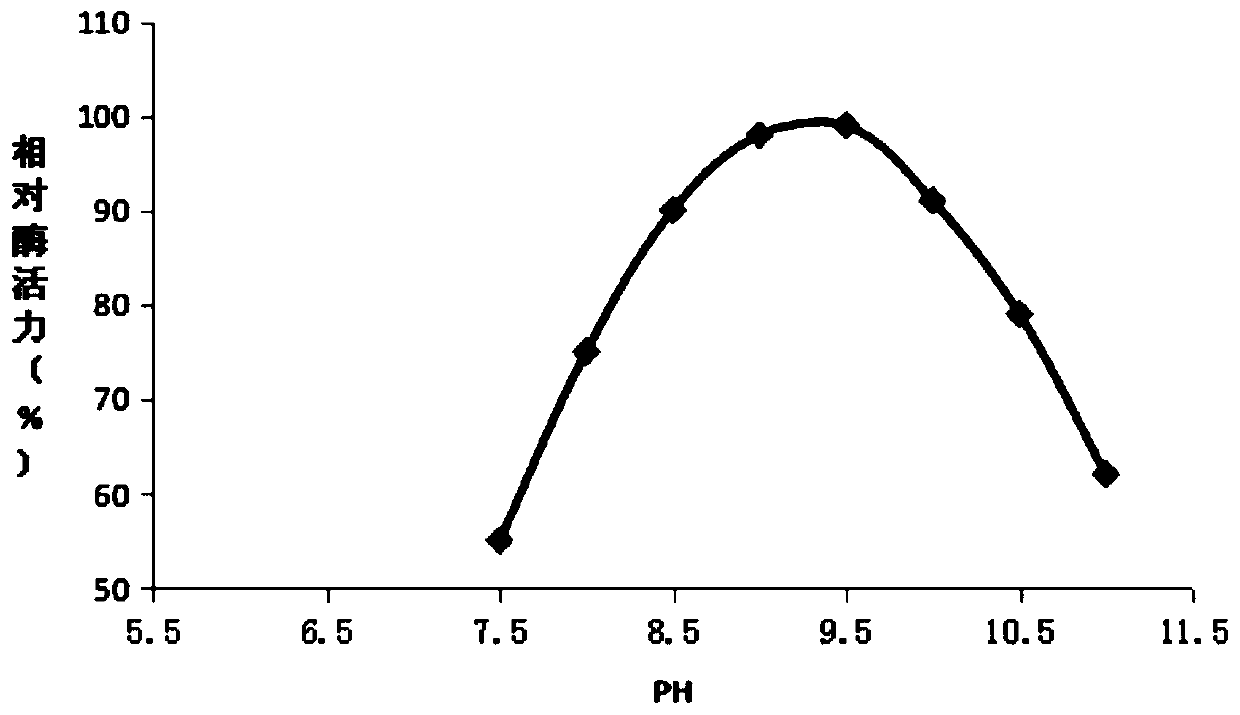
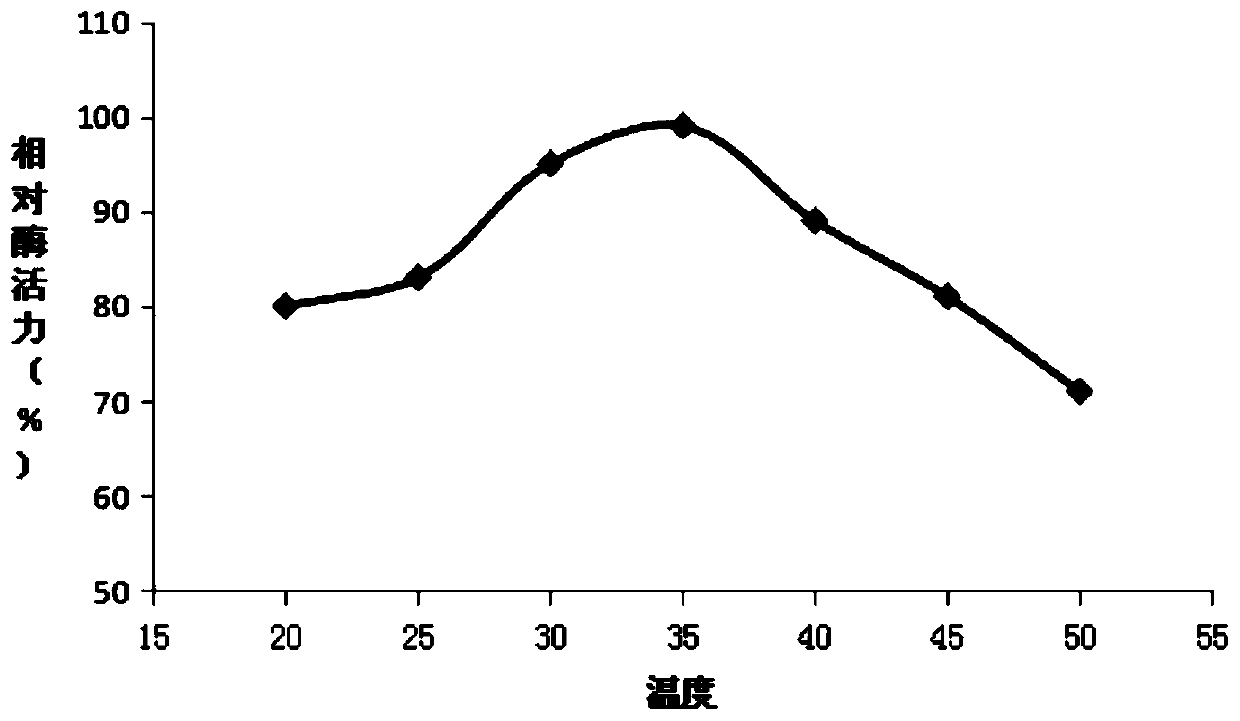
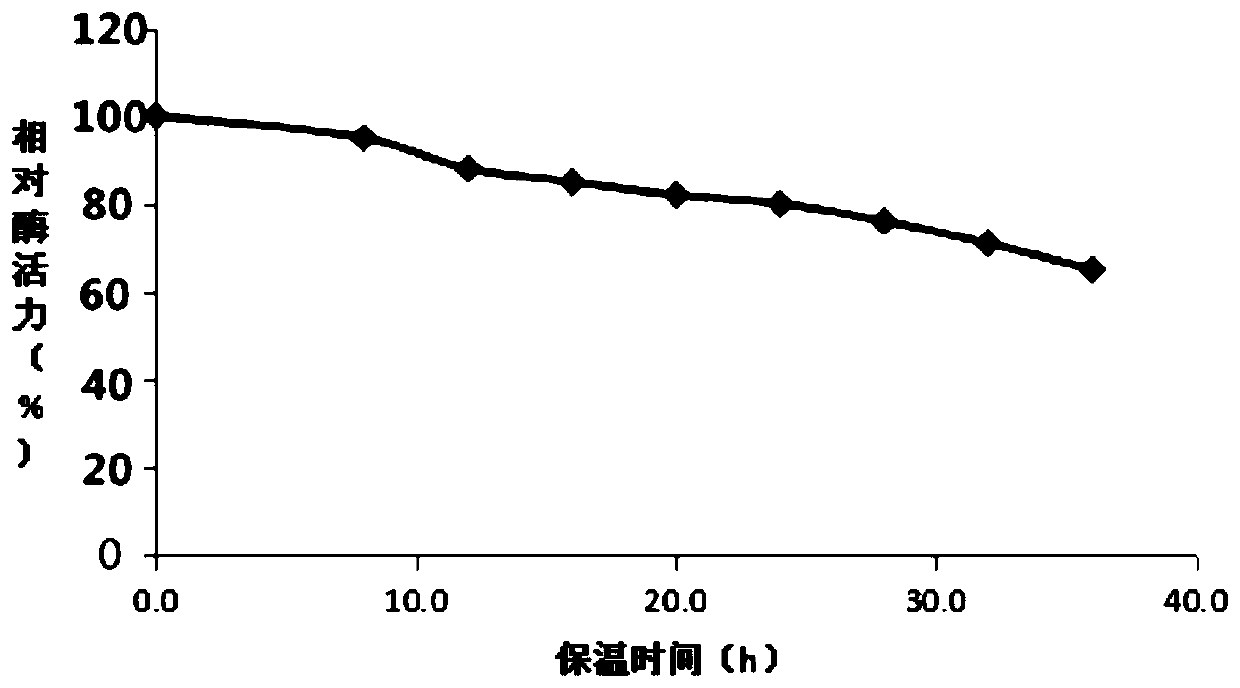
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1 Mutation Breeding of Pseudomonas LD-14
[0041] Take the fresh slant of the two starting strains LA-32, wash the bacteria with sterile water, oscillate in a test tube with glass beads to disperse the bacteria, collect the bacteria by centrifugation, resuspend the bacteria with 5% glycerol, and count them with blood cells Count the plates until the bacterial concentration is 10 7 -10 8 cells / mL, as the starting bacterial suspension.
[0042] Turn on the plasma system at normal temperature and pressure, wipe the inside and outside of the operating room with alcohol cotton, and turn on the ultraviolet lamp to sterilize for 30 minutes. After the sterilization in the operating room of the system is completed, take 10 μL of the bacterial suspension and spot it on the rough surface of the slide, and transfer the slide to the table of the operating room with tweezers under aseptic conditions. Open the helium valve, set the gas flow and mutagenesis time for mutagene...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Example 2 Fermentation of Pseudomonas LD-14 to produce enzyme
[0055] The fermentative enzyme production method of Pseudomonas LD-14 mainly comprises the following steps:
[0056] Slant culture: pick a ring of Pseudomonas LD-14 and inoculate it on a solid slant medium, and culture at a constant temperature of 35°C for 36 hours to obtain first-grade seeds;
[0057] Shake flask culture: take a ring of the first-grade seeds and insert them into the seed medium, and cultivate them for 48 hours at a constant temperature of 35°C and a shaker speed of 200r / min to obtain the second-grade seed liquid;
[0058] Seed tank culture: put the secondary seed solution into the seed tank culture medium at a ratio of 6% (v / v) of the inoculum, and cultivate for 12 hours at a constant temperature of 35°C and a rotational speed of 200r / min;
[0059] Fermentation tank culture: The seed liquid in the seed tank is inserted into the culture medium of the fermenter according to the ratio of the...
Embodiment 3
[0070] Example 3 Pseudomonas LD-14 fermentation performance verification
[0071] Carry out 50L fermenter verification experiment according to the fermentative enzyme production method of Pseudomonas LD-14 of embodiment 2, fermentation cycle 150h, its 6 batches of fermentative enzyme production situation, average enzyme production level is 25558U / mL, table 2 illustrates bacterial strain Not only high-yield lipase, but also the fermentation performance and the enzymatic activity of the lipase produced by it have remarkable stability.
[0072] Table 2 Fermentation and enzyme production of 6 batches of high lipase-producing strains
[0073] batch Fermentation period (h) Fermentation activity (U / mL) 1 150 25825 2 150 25560 3 150 25025 4 150 25590 5 150 25400 6 150 25950
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com