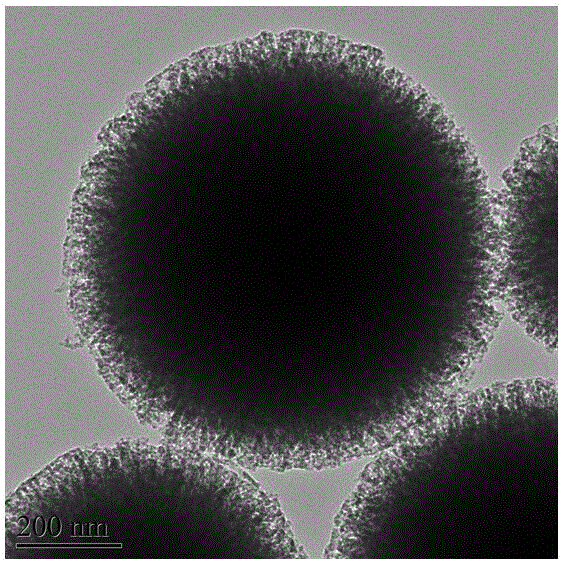
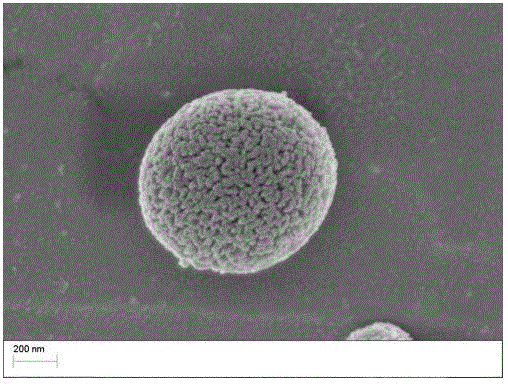
Micro-nano bioactive glass microsphere with surface nanometer pore structure and preparation method thereof
A bioactive glass and nanopore technology, applied in the field of biomedical materials, can solve the problems of low adsorption force of drugs and bioactive molecules, easy introduction of impurities, large energy consumption, etc., and achieve obvious nanopore structure on the surface and good monodispersity. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] A micro-nano bioactive glass microsphere with a surface nano-pore structure, the preparation method of which is as follows:
[0029] (1) Weigh 2.574g of calcium nitrate tetrahydrate and dissolve in a mixed solution of 180ml of deionized water and 120ml of absolute ethanol to form an aqueous phase solution; dissolve 4.05ml of ethyl orthosilicate in 50ml of cyclohexane to form an oil phase solution.
[0030] (2) Mix the aqueous phase solution and the oil phase solution obtained in step (1), then add 0.3g cetyltrimethylammonium bromide, 1ml ammonia water (25wt%) and 0.42ml triethyl phosphate in sequence, Stir evenly to obtain a bioactive glass gel solution.
[0031] (3) The bioactive glass gel solution obtained in step (2) was centrifuged, washed with deionized water to obtain a wet gel precipitate, and then placed in a 50°C oven to dry for 2 days. A bioactive glass gel powder is obtained.
[0032] (4) The obtained bioactive glass gel powder is heat-treated in a high-te...
Embodiment 2
[0035] A micro-nano bioactive glass microsphere with a surface nano-pore structure, the preparation method of which is as follows:
[0036] (1) Weigh 5.148g of calcium nitrate tetrahydrate and dissolve in a mixed solution of 150ml of deionized water and 150ml of absolute ethanol to form an aqueous phase solution; dissolve 8.1ml of ethyl orthosilicate in 50ml of cyclohexane to form an oil phase solution.
[0037] (2) Mix the aqueous phase solution and the oil phase solution obtained in step (1), then add 0.9g of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide, 2ml of ammonia water (25wt%) and 0.84 of triethyl phosphate in sequence, and stir Uniformly obtain bioactive glass gel solution.
[0038] (3) The bioactive glass gel solution obtained in step (2) was centrifuged, washed with deionized water to obtain a wet gel precipitate, and then placed in a 60°C oven to dry for 2 days. A bioactive glass gel powder is obtained.
[0039] (4) The obtained bioactive glass gel powder was heat-treated in ...
Embodiment 3
[0042] A micro-nano bioactive glass microsphere with a surface nano-pore structure, the preparation method of which is as follows:
[0043] (1) Weigh 7.722g of calcium nitrate tetrahydrate and dissolve in a mixed solution of 200ml of deionized water and 100ml of absolute ethanol to form an aqueous phase solution; dissolve 12.15ml of ethyl orthosilicate in 60ml of cyclohexane to form an oil phase solution.
[0044] (2) Mix the aqueous phase solution and the oil phase solution obtained in step (1), and then add 1.2g of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide, 1.5ml of ammonia water (25wt%) and 1.26ml of triethyl phosphate and stir evenly to obtain a bioactive glass gel solution.
[0045] (3) Centrifuge the bioactive glass gel solution obtained in step (2), wash it with deionized water to obtain a wet gel precipitate, and then place the wet gel precipitate in an oven at 80°C to dry for 1 day. A bioactive glass gel powder is obtained.
[0046](4) The obtained bioactive glass gel powder ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com