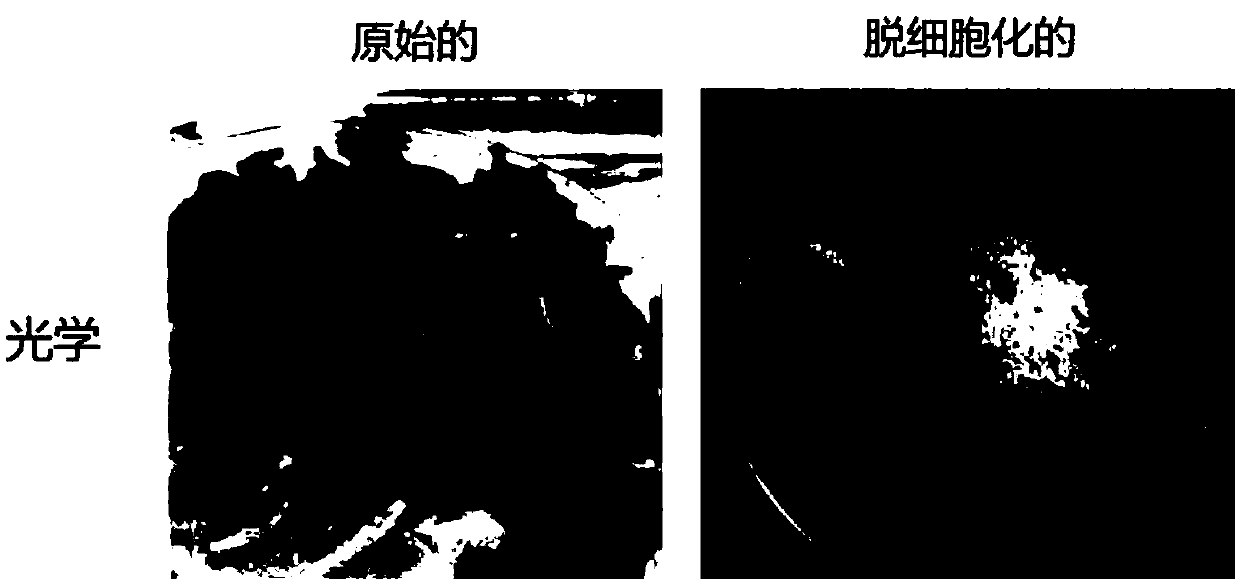
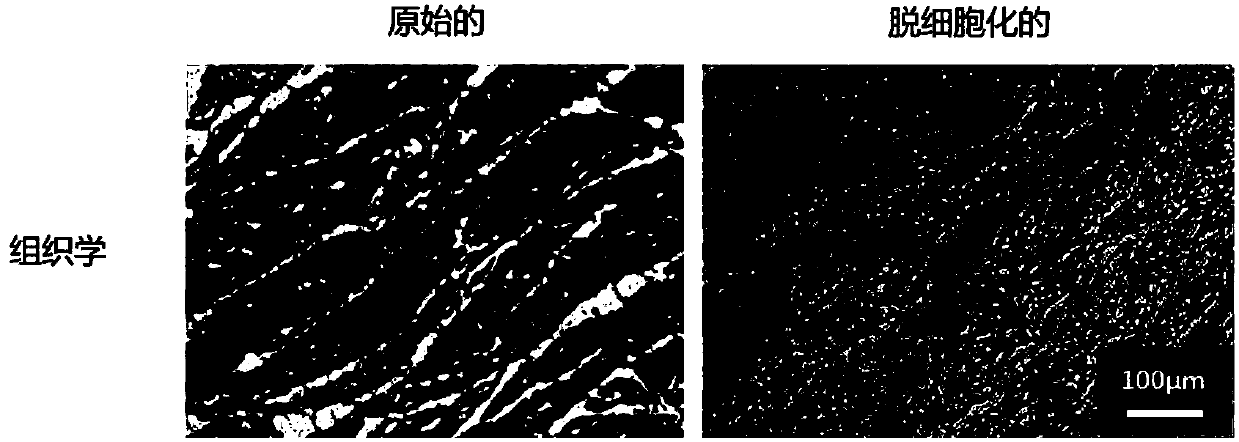
Composition for three-dimensional printing, method for preparing same, and method for manufacturing three-dimensional structure using same
A technology of three-dimensional printing and composition, applied in the direction of prosthesis, tissue regeneration, medical science, etc., can solve the problems of difficult preparation of organs, safety problems, low mechanical strength of three-dimensional structures, etc., and achieve high mechanical strength and uniform mechanical strength. and the effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Embodiment 1: Preparation of composition for three-dimensional printing
[0039] Liquid nitrogen was added to the freeze-dried hdECM and crushed with a mortar and pestle. After adding hdECM powder (330 mg) to 0.5 M acetic acid aqueous solution (10 ml), pepsin (33 mg) (P7125, Sigma-Aldrich) was added, and it stirred at normal temperature for 48 hours. While maintaining the temperature of the obtained solution below 10°C, riboflavin (2 mg) was added, and a 10M NaOH solution cooled to below 10°C was added dropwise to adjust the pH to about 7. The obtained solution in the form of a pre-gel (pre-gel) was refrigerated and stored at about 4°C.
Embodiment 2
[0040] Embodiment 2: Preparation of three-dimensional structure
[0041]A three-dimensional structure was fabricated using the composition for three-dimensional printing obtained in Example 1 according to the method disclosed in Falguni Pati, et al., Nat Commun. 5, 3935 (2014). Specifically, the polycaprolactone (PCL) framework was loaded into the syringe of the multi-head tissue and organ printing system (Jin-Hyung Shim et al., J. Micromech. Microeng. 22 085014 (2012)) ), and heated to about 80°C, causing the polymer to melt. The three-dimensional printing composition in pregel form obtained in Example 1 was charged into another syringe (second syringe), and the temperature was maintained at about 10° C. or lower. Apply an air pressure of about 600 kPa to the first syringe, thereby fabricating a thin PCL frame with a line width of about 100 μm or less, a gap of about 300 μm, and a thickness of 120 μm, and spray the contents of the second syringe on the PCL frame, and then in...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Embodiment 3: Preparation of three-dimensional structure
[0044] A three-dimensional structure was prepared by the same method as in Example 2 except that the PCL framework was not used. That is, the composition for three-dimensional printing in the pregel form obtained in Example 1 was loaded into a syringe of a multi-head tissue and organ printing system (Jin-HyungShim et al., J. Mieromech. Microeng. 22 085014 (2012)), and The temperature was maintained below about 10°C. The contents were ejected by applying an air pressure of about 600 kPa to the syringe, and then irradiated with UVA at about 360 nm for 3 minutes to perform cross-linking. Thereafter, the content of the syringe is ejected and a layer-by-layer process through the cross-linking is performed to form a three-dimensional structure shape. The obtained shape of the three-dimensional structure was placed in an incubator (humid incubator) at about 37° C. for 30 minutes to perform thermal gelation, whereby a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com