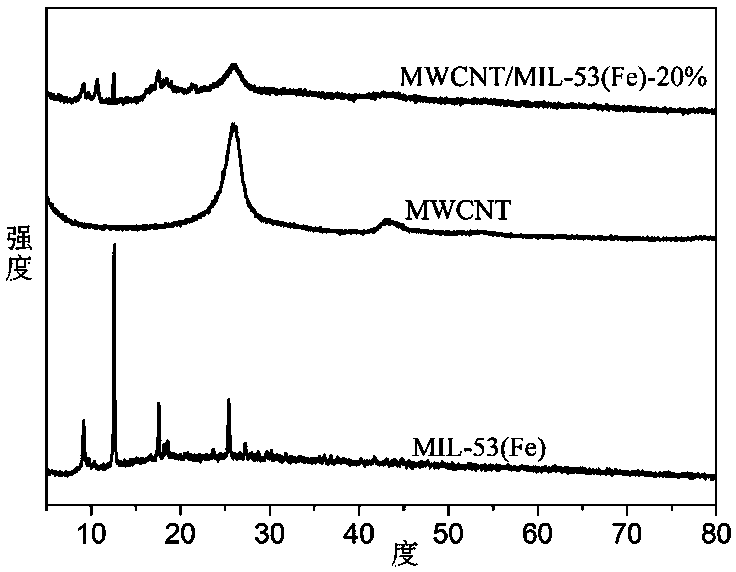
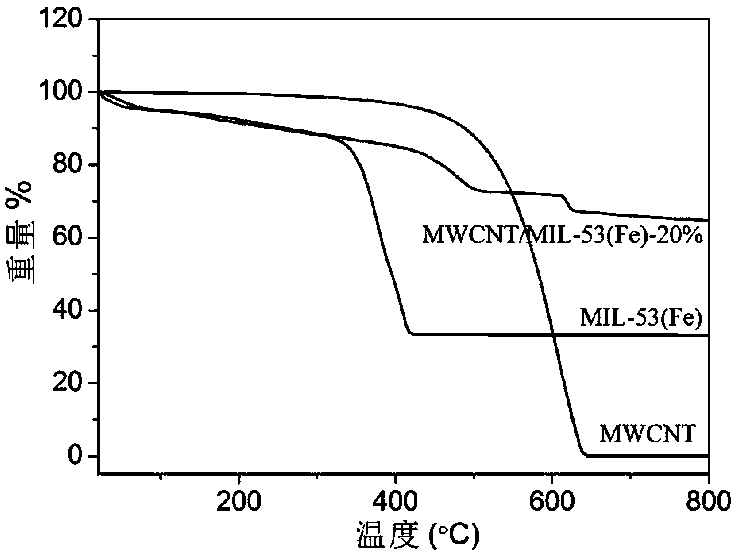
Method for adsorbing antibiotics in water through multi-walled carbon nanotube/metal organic framework composite material
A technology of multi-walled carbon nanotubes and metal organic frameworks, applied in the directions of alkali metal compounds, adsorbed water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the disadvantages of low cost, mass production of metal organic framework materials, inability to obtain better Adsorption performance, increased use of MOFs, etc., achieve the effect of simple treatment process and adsorption equipment, high application value and commercial value, and fast adsorption speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] A method for utilizing multi-walled carbon nanotubes / metal organic framework composites to adsorb antibiotics in water bodies, comprising the following steps:
[0038] Weigh 100 mg multi-walled carbon nanotubes / metal organic framework composites (MWCNT / MIL-53(Fe)-1%), multi-walled carbon nanotubes / metal organic frameworks composites (MWCNT / MIL-53(Fe)- 5%), multi-walled carbon nanotubes / metal-organic framework composites (MWCNT / MIL-53(Fe)-10%), multi-walled carbon nanotubes / metal-organic frameworks composites (MWCNT / MIL-53(Fe)- 20%), multi-walled carbon nanotubes / metal-organic framework composites (MWCNT / MIL-53(Fe)-30%), respectively added to 100mL tetracycline hydrochloride solution with a concentration of 20mg / L, mixed and dispersed evenly, at a speed of The vibration adsorption was carried out at 400r / min for 12 hours. During the vibration adsorption process, the pH value of the system was controlled to be 7.0, and the treatment of the tetracycline hydrochloride solut...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Investigate the water stability of the multi-walled carbon nanotube / metal organic framework composite material of the present invention, comprise the following steps:
[0052] Weigh 1 part of multi-walled carbon nanotube / metal organic framework composite material (MWCNT / MIL-53(Fe)-20%) prepared in Example 1 and 1 part of metal organic framework material (MIL-53(Fe)), each 20mg, were added to 50mL deionized water, and allowed to stand for 30 days. Continuously take samples to check the concentration of iron ions in the water.
[0053] Figure 6 It is the effect diagram of water stability of the multi-walled carbon nanotube / metal organic framework composite material (MWCNT / MIL-53(Fe)-20%) in Example 2. Figure 6 In this paper, the water stability of the material is evaluated by the concentration of iron ions dissolved in the aqueous solution, and the lower the concentration of iron ions in the aqueous solution, the better the water stability of the material. Depend on ...
Embodiment 3
[0057] A method for utilizing multi-walled carbon nanotubes / metal organic framework composites to adsorb antibiotics in water bodies, comprising the following steps:
[0058] Weigh 3 parts of the multi-walled carbon nanotube / metal-organic framework composite (MWCNT / MIL-53(Fe)-20%) prepared in Example 1, 20 mg each, and add to 50 mL of tetracycline hydrochloride with a concentration of 20 mg / L solution, chlortetracycline hydrochloride solution and oxytetracycline hydrochloride solution, mixed and dispersed evenly, and oscillated and adsorbed at a speed of 400r / min for 24 hours. During the oscillating adsorption process, the pH of the system was controlled to be 7.0, and the treatment of the antibiotic solution was completed.
[0059] During the oscillation adsorption process, 1mL samples were taken at regular intervals, and the samples were centrifuged, and the supernatant obtained after centrifugation was taken to measure the absorbance by a UV-visible spectrophotometer to dete...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com