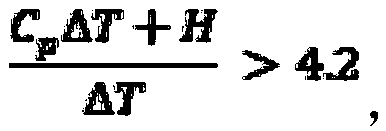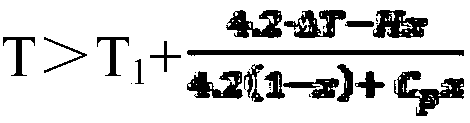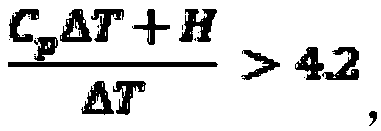Phase change micro-emulsion as cooling working substance, and applications thereof
A phase-change microemulsion and cooling medium technology, which is applied in the field of microemulsion, can solve the problems of poor universality of phase-change microemulsion, and achieve the effect of improving cooling effect, best cooling effect, and simplifying control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] When water is used to cool the heating element, the temperature of the coolant at the inlet end of the radiator is 30°C, and the temperature at the outlet end is 50°C. A phase-change microemulsion is used as a cooling liquid to replace cooling water. Based on the total mass of the phase-change microemulsion, the phase-change microemulsion includes a phase-change material and water, 0.1% gum arabic as a surfactant and 1% NaCl. The specific heat of the phase change material is C p (kJ / kg / K), the phase change enthalpy of the phase change material is H (kJ / kg), the phase change temperature of the phase change material is T (℃), and the phase change material accounts for the phase change microemulsion The mass fraction of is χ. Since the contents of gum arabic and NaCl are small and have little effect on the heat transfer performance of phase change microemulsion, the effects of surfactants and inorganic salts on heat transfer are ignored in the calculation.
[0034] The t...
Embodiment 2
[0099] When water is used to cool the heating element, the temperature of the coolant at the inlet end of the radiator is 30°C, and the temperature at the outlet end is 70°C. Paraffin 6106 (composition is a mixture of between 16 and 28 carbon atoms) supplied by Ter Hell Paraffin Hamburg, Germany can be selected. The mass fraction of the phase change material in the phase change microemulsion is 50%. Its related parameters are shown in Table 3. 0.1% gum arabic as surfactant and 1% NaCl. Since the contents of gum arabic and inorganic salts are small and have little effect on the heat transfer performance of phase change microemulsions, the effects of surfactants and inorganic salts on heat transfer are ignored in the calculation.
[0100] Table 3 Phase Change Material Parameters 1
[0101]
[0102] When the heat released by the system increases, the temperature of the phase change material rises to over 42°C, and the phase change material absorbs the heat in the heating el...
Embodiment 3
[0116] The treatment object of this embodiment is the same as that of Example 1, the difference is that the phase change microemulsion includes phase change material and water, based on the total mass of the phase change microemulsion, also includes 0.5% surfactant dodecane Sodium lauryl sulfate and 1% inorganic salt KCl, because the content of sodium lauryl sulfate and inorganic salt is small, and has little effect on the heat transfer performance of phase change microemulsion, so the surfactant and inorganic salt are ignored in the calculation. The calculation method for the influence of salt on heat transfer is the same as in Example 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| phase transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| phase transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com