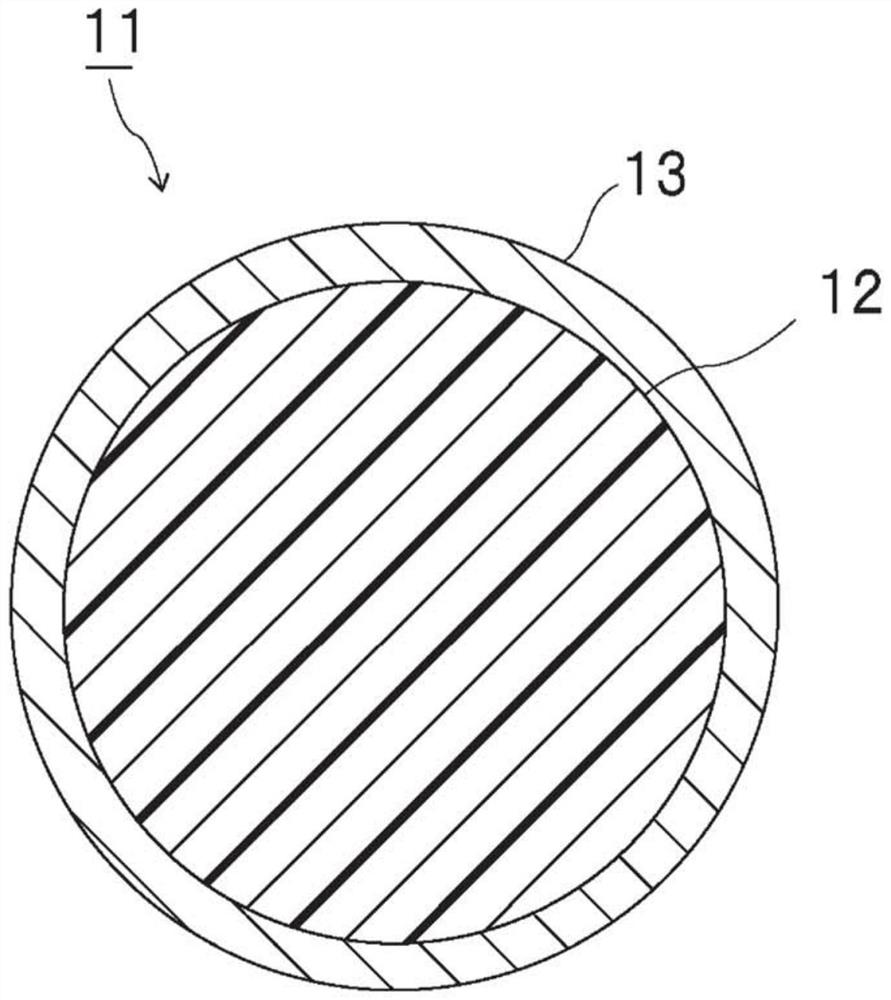
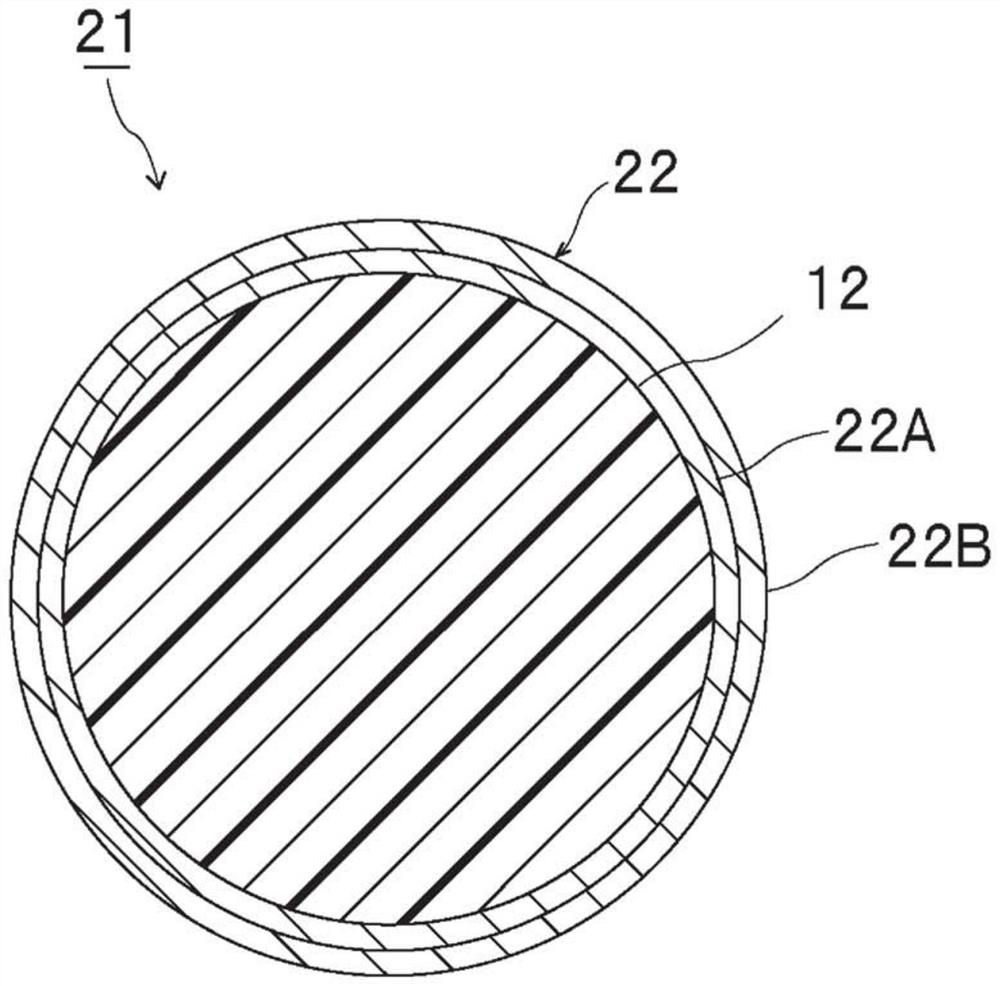
Connecting materials and connecting structures
A technology for connecting materials and connecting parts, applied in the direction of connecting, welding/cutting media/materials, conductive materials, etc., can solve the problems of lowering melting point or sintering temperature and accumulation state, increasing surface area, etc., to suppress the generation of cracks, improve The effect of connection strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0171] (1) Production of polysiloxane oligomers
[0172] 1 part by weight of 1,3-divinyltetramethyldisiloxane (amount to be the weight % in the table) and 0.5% by weight of p-toluenesulfonic acid were placed in a 100 ml separable flask set in a warm bath 20 parts by weight of aqueous solution. After stirring at 40° C. for 1 hour, 0.05 parts by weight of sodium bicarbonate was added. Thereafter, 40 parts by weight of methylvinyldimethoxysilane (in the amount of weight % in the table), 10 parts by weight of methylphenyldimethoxysilane (in the amount of weight % in the table), methyl 10 weight part of trimethoxysilane (the quantity used as the weight% of a table|surface) was stirred for 1 hour. Thereafter, 1.9 parts by weight of a 10% by weight potassium hydroxide aqueous solution was added, and the mixture was stirred for 10 hours while the temperature was raised to 85° C. and the pressure was reduced by an aspirator, thereby performing a reaction. After the reaction, return ...
Embodiment 2~7、13~18 and comparative example 2~3
[0182] As shown in Tables 1 and 2, the polysiloxane monomer used for the production of polysiloxane oligomers was changed, the SPG pore diameter was changed as shown in Tables 1 and 2 below, and as shown in Tables 1 and 2 Except for changing the configurations of the particles and the linking material in this way, the particles X, the linking material, and the linking structure were produced in the same manner as in Example 1.
[0183] In addition, in Examples 17 and 18, the particle which has the electroconductive part shown in Table 2 was produced.
Embodiment 19
[0185] Dispersion C of Example 1 was prepared.
[0186]With respect to 100 parts by weight of the particles in the dispersion liquid C, 1 part by weight of methyltrimethoxysilane (manufactured by Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd. "KBM-13") was added, and ammonia in such an amount that the concentration of ammonia after the addition became 1% by weight The aqueous solution was stirred at room temperature for 24 hours, and then washed with water to obtain substrate particles. Particles X were obtained by subjecting the obtained substrate particles to a classification operation.
[0187] Except having used the obtained particle X, it carried out similarly to Example 1, and produced the connection material and connection structure.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com