Compositions and methods for treatment of cytomegalovirus
A composition and retrovirus technology, applied in the field of composition for treating cytomegalovirus, can solve problems such as toxicity and limited curative effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
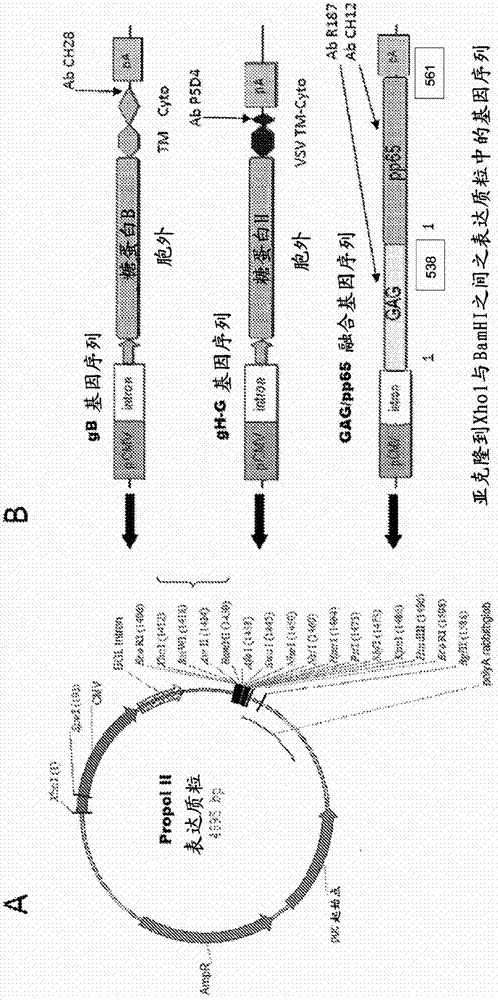
[0208] Embodiment 1: Construction of DNA expression plasmid
[0209] This example describes the development of expression plasmids and constructs for expression of recombinant HCMV gene sequences such as gB, gB-G, gH-G and Gag / pp65 fusion gene sequences. A standard expression plasmid usually consists of the following: mammalian-derived promoter sequence, intron sequence, polyadenylation signal sequence (PolyA), pUC origin of replication sequence (pUC-pBR322 is the colE1 origin of replication origin / site and antibiotic resistance genes for replication of plasmids in bacteria such as E. coli (DH5α) and as selectable markers for plasmid plaque selection. Following the introns in the plasmid are multiple restriction enzyme sites that can be used for splicing into a gene or partial gene sequence of interest.
[0210] Propol II expression plasmid contains pHCMV (for early promoter of HCMV), β-globin intron (BGL intron), rabbit globulin polyadenylation signal sequence (PolyA), pUC o...
Embodiment 2
[0213] Embodiment 2: the production of virus-like particle (VLP)
[0214] This example describes methods for producing virus-like particles (VLPs) containing various recombinant HCMV antigens described in Example 1.
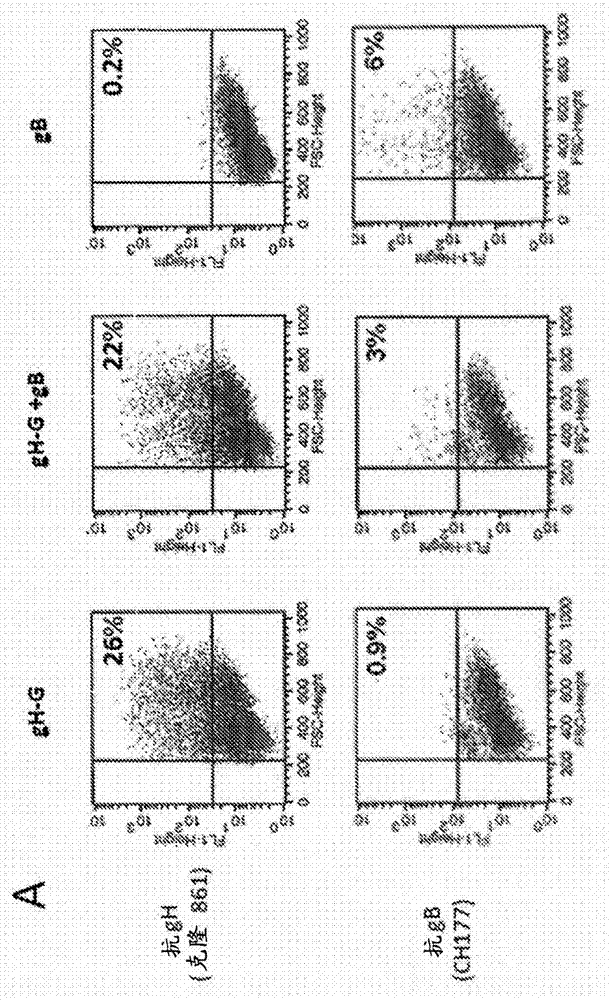
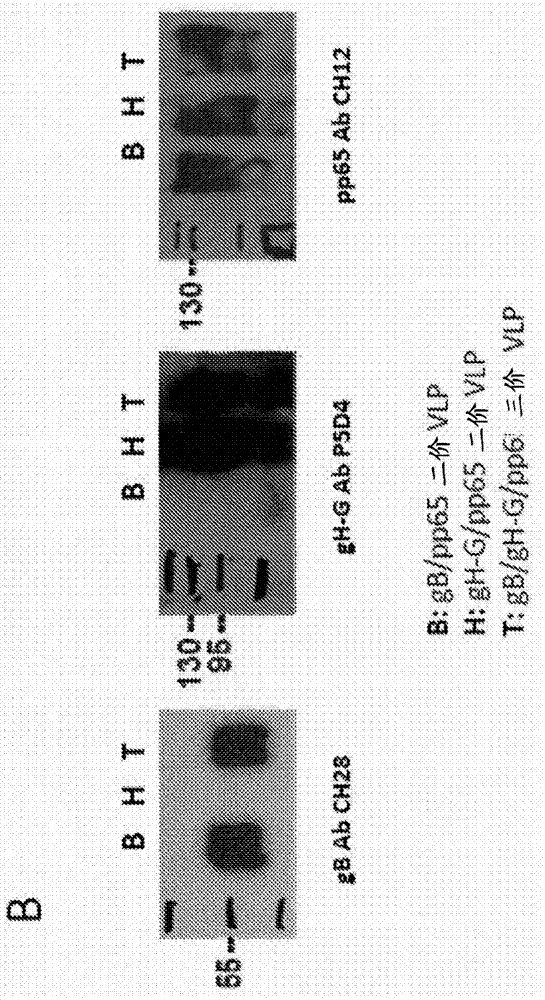
[0215] HEK 293T cells (ATCC, CRL-11268) were transiently transfected with MMLV-Gag DNA expression plasmids using the calcium phosphate method and co-transfected with gB or gB-G (data not shown) or gH-G DNA expression plasmids. Alternatively, cells were transfected with Gag / pp65 DNA expression plasmids and co-transfected with gB or gB-G (data not shown) or gH-G DNA expression plasmids. It will be appreciated that cells can be transfected with MMLV-Gag DNA expression plasmids and co-transfected with gB and gH-G or both gB-G and gH-G DNA expression plasmids. Multiple HCMV antigens expressed by HEK293 cells were confirmed by flow cytometry ( figure 2 A). 48 to 72 hours after transfection, the VLP-containing supernatant was harvested and filtered through a 0.45 μm...
Embodiment 3
[0216] Example 3: Physicochemical Characterization of Virus-Like Particles (VLPs)
[0217] Physicochemical analysis of VLPs included particle size determination and evaluation of polydispersity index using a Malvern Instrument Zeta-Sizer Nanoseries (ZEN3600). Exemplary results obtained from nanonization analysis are in Figure 3A and 3B shown in . An exemplary VLP composition (gH-G / pp65 bivalent VLP composition) was produced in two different laboratories using the same recombinant expression vector and both VLP preparations gave average particle sizes ranging from 150 nm to 180 nm in diameter . This is consistent with the size of CMV virions, which are reported to be in the range of 150 nm to 200 nm (1997 J Pathol 182:273-281 ). A low polydispersity index (PdI) of 0.214 to 0.240 indicates product homogeneity and narrow size distribution.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| polydispersity index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com