Burst-pulse-mode ultra-fast laser and working method thereof
A burst pulse and laser technology, used in lasers, laser parts, phonon exciters, etc., can solve problems such as changes in laser reliability and stability, loss of laser output power, and changes in laser output characteristics, and achieve high gain. , large bandwidth, and the effect of solving heat accumulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
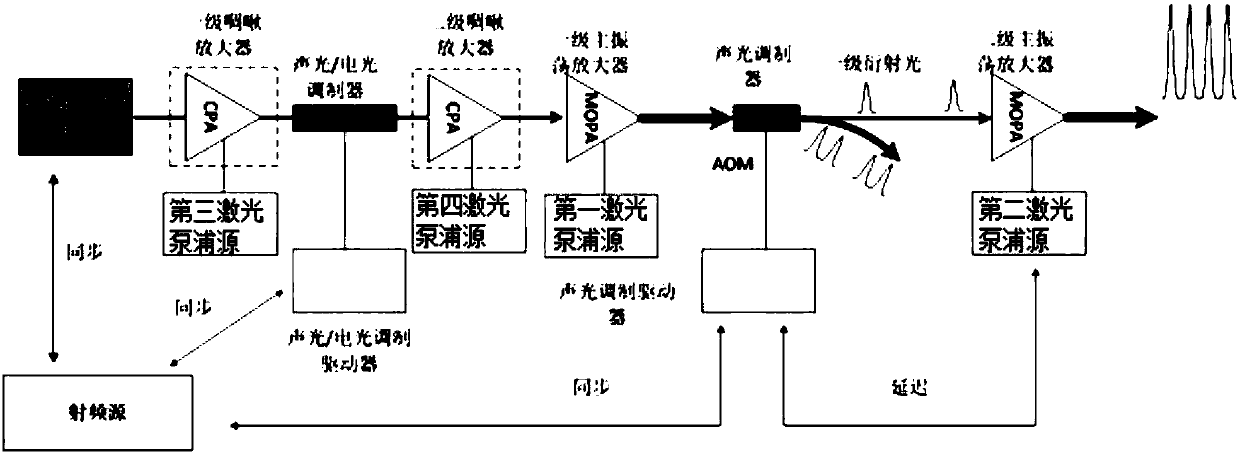
[0076] A burst-mode ultrafast laser, such as figure 1As shown, including radio frequency source, laser oscillator, fiber-coupled acousto-optic / electro-optic modulator, acousto-optic / electro-optic modulation driver, first-stage main oscillator amplifier, acousto-optic modulator, acousto-optic modulation driver, laser oscillator, fiber-coupled acoustic The optical / electro-optic modulator, the first-stage main oscillator amplifier, and the acousto-optic modulator are placed along the optical path in sequence; the acousto-optic / electro-optic modulation driver is connected to the fiber-coupled acousto-optic / electro-optic modulator, and the acousto-optic modulation driver is connected to the acousto-optic modulator;
[0077] The first-stage main oscillator amplifier includes a half-wave plate, a first Faraday isolator, a first laser diode, and a first laser gain crystal placed behind the fiber-coupled acousto-optic / electro-optic modulator and placed sequentially along the optical pat...
Embodiment 2
[0094] According to a kind of burst pulse mode ultrafast laser described in embodiment 1, its difference is that,
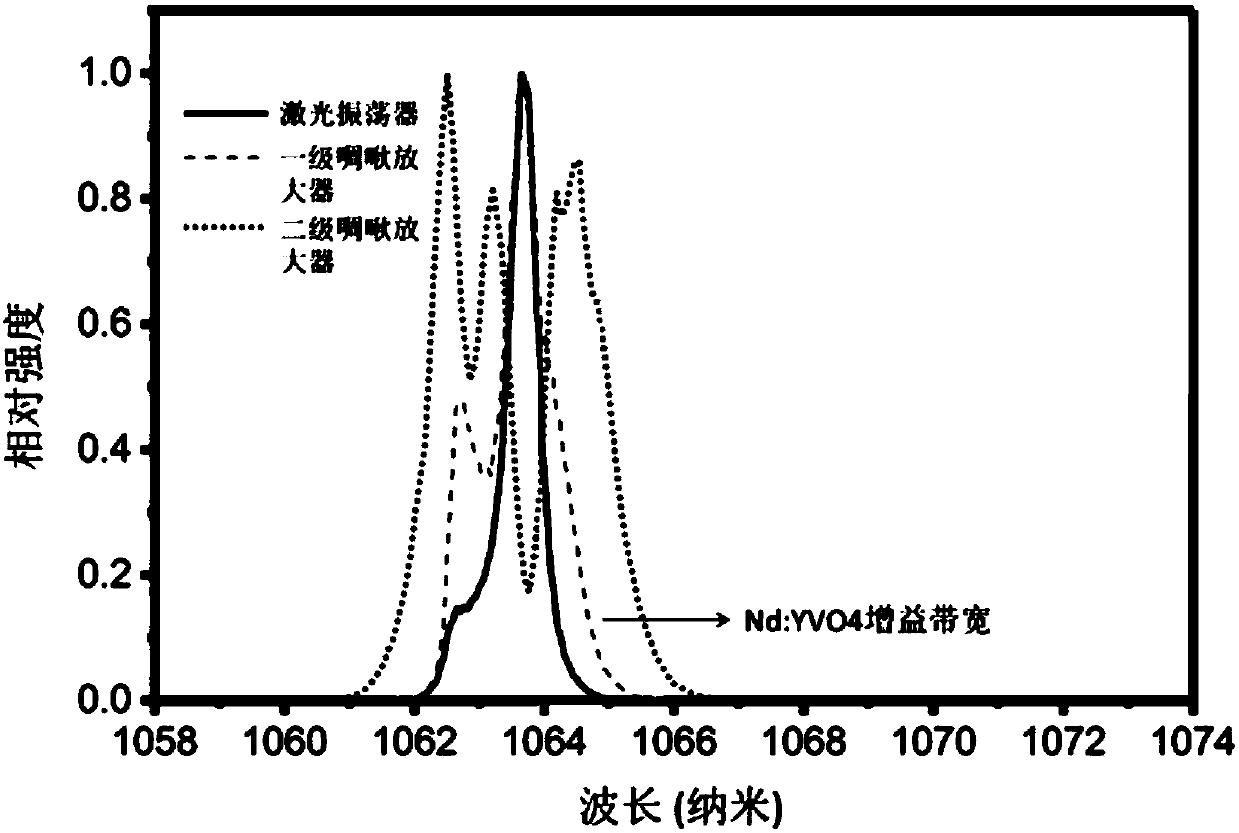
[0095] The burst pulse mode ultrafast laser also includes a secondary main oscillator amplifier, which includes a second Faraday isolator, a second laser diode, and a second laser gain amplifier placed behind the acousto-optic modulator and placed sequentially along the optical path. crystal; the second laser gain crystal is Nd:YVO4 crystal.
[0096] In view of the low optical power of the burst pulse mode, generally only 1% of the output power of the first-stage main oscillator amplifier, in order to further increase the output power and output energy, a second-stage main oscillator amplifier can be established for further amplification, and the output power of the second-stage main oscillator amplifier The structure is consistent with that of the first-stage main oscillator amplifier.
[0097] After the burst pulse mode is generated by the acousto-optic / electr...
Embodiment 3
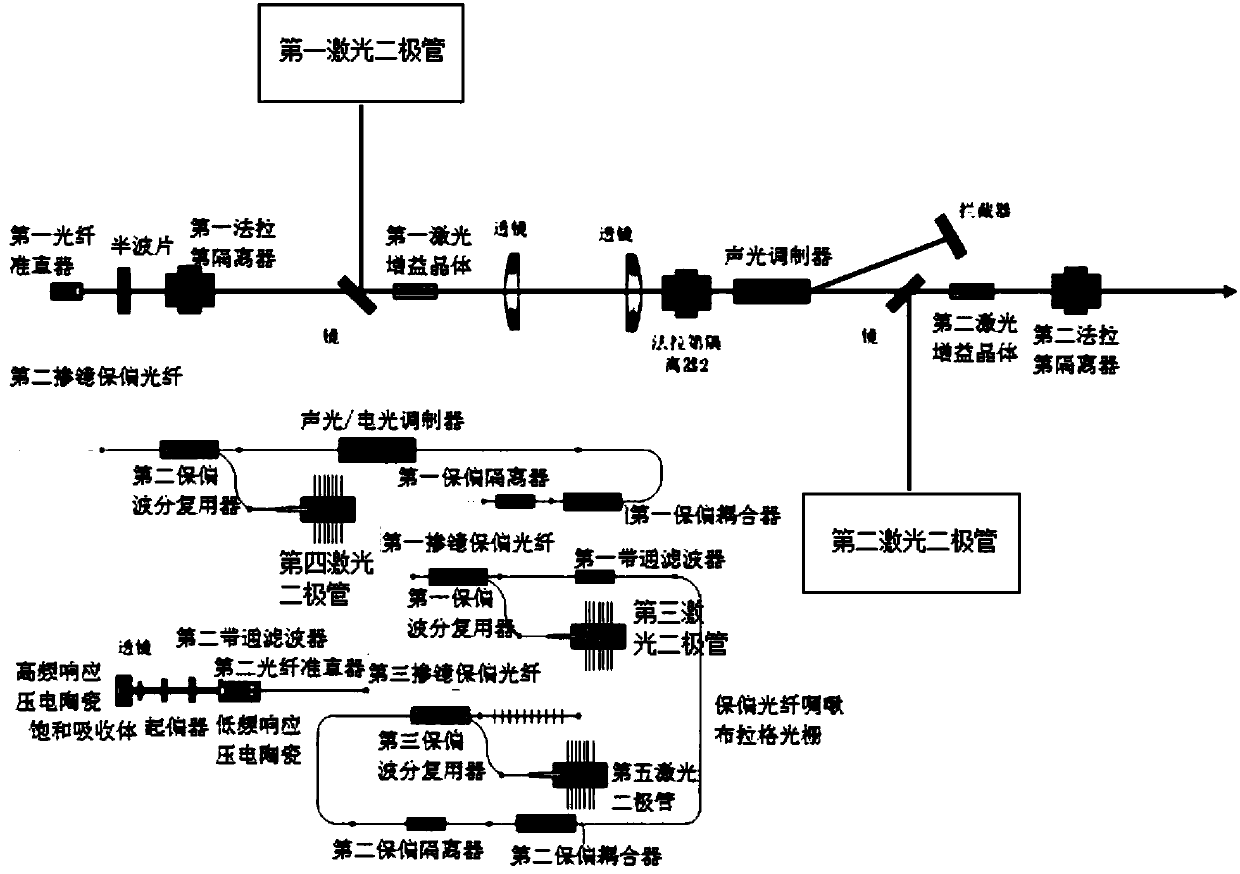
[0099] A kind of burst mode ultrafast laser according to embodiment 1 or 2, such as figure 2 As shown, the difference is that
[0100] The burst mode ultrafast laser also includes a first-stage chirped amplifier and a second-stage chirped amplifier. The first-stage chirped amplifier is set between the laser oscillator and the fiber-coupled acousto-optic / electro-optic modulator; the second-stage chirped amplifier is set at Between the fiber-coupled acousto-optic / electro-optic modulator and the first-stage main oscillator amplifier.
[0101] When the output power of the burst pulse mode ultrafast laser is far less than 10mW, it is amplified by a first-stage chirped amplifier to improve the output power and signal-to-noise ratio of the fiber-coupled acousto-optic / electro-optic modulator; when n>10, it is amplified by a second-stage The chirped amplifier amplifies the output power of the ultrafast laser in burst mode.
[0102] Considering the spontaneous emission amplification ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com